
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
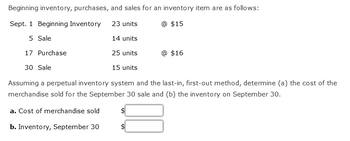
Transcribed Image Text:Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for an inventory item are as follows:
Sept. 1 Beginning Inventory
23 units
@ $15
5 Sale
14 units
17 Purchase
25 units
30 Sale
15 units
Assuming a perpetual inventory system and the last-in, first-out method, determine (a) the cost of the
merchandise sold for the September 30 sale and (b) the inventory on September 30.
a. Cost of merchandise sold
b. Inventory, September 30
@ $16
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for an inventory item are as follows: Sep. 1 Beginning Inventory 25 units @ $11 5 Sale 11 units 17 Purchase 24 units @ $14 30 Sale 17 units Assuming a perpetual inventory system and the last-in, first-out method: a. Determine the cost of the goods sold for the September 30 sale. b. Determine the inventory on September 30. %24 %24arrow_forwardPerpetual Inventory Using FIFO Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Item Zeta9 are as follows: Oct. 1 Inventory 57 units @ $25 7 Sale 46 units 15 Purchase 41 units @ $27 24 Sale 18 units Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method, determine (a) the cost of the goods sold on October 24 and (b) the inventory value on October 31. a. Cost of the goods sold on October 24 $ 464 b. Inventory value on October 31 A 324 Xarrow_forwardPerpetual inventory using FIFO Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Item Zeta9 are as follows: Oct. 1 Inventory Oct. 7 Sale 72 units @ $19 51 units Oct. 15 Purchase 61 units @ $22 29 units Oct. 24 Sale Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method, determine (a) the cost of goods sold on October 24 and (b) the inventory on October 31. a. Cost of goods sold on October 24 b. Inventory on October 31arrow_forward
- FIFO and LIFO costs under perpetual inventory system The following units of an item were available for sale during the year: DATA Beginning inventory Sale First purchase Sale Second purchase Sale Ending inventory Quantity 8,100 5,000 15,400 12,600 15,900 13,100 8,700 REQUIRED: a. What is the total cost of the ending inventory according to FIFO? b. What is the total cost of the ending inventory according to LIFO? a. FIFO method b. LIFO method Price Inventory Cost Using formulas and cell references from the problem data, perform the required analysis. Formulas entered in the green cells orange cells. Transfer amounts to CNOWv2 for grading. $160 $300 $167 Formulas $300 $172 $300arrow_forwardBeginning inventory, purchases, and sales for an inventory item are as follows: Sep. 1 Beginning Inventory 23 units @ $11 5 Sale 11 units 17 Purchase 24 units @ $12 30 Sale 18 units Assuming a perpetual inventory system and the last-in, first-out method: a. Determine the cost of the goods sold for the September 30 sale. b. Determine the inventory on September 30.arrow_forwardBeginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Item XJ-56 are as follows: May 1 Beginning inventory 90 units @ $36 each May 6 Sold 75 units @ $50 each May 15 Purchased 125 units @ $38 each May 24 Sold 80 units @ $51 each What is the cost of goods sold for May using a LIFO inventory costing method in a perpetual inventory system? Please show all calculations in order to receive credit.arrow_forward
- Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for an inventory item are as follows: Sep. 1 Beginning Inventory 24 units @ $10 5 Sale 17 units 17 Purchase 10 units @ $15 30 Sale 8 units Assuming a perpetual inventory system and the last-in, first-out method: a. Determine the cost of the goods sold for the September 30 sale.$fill in the blank 1arrow_forwardPeriodic Inventory by Three Methods; Cost of Merchandise Sold The units of an item available for sale during the year were as follows: Jan. 1 Inventory 50 units @ $102 Mar. 10 Purchase 50 units @ $112 Aug. 30 Purchase 30 units @ $120 Dec. 12 Purchase 70 units @ $126 There are 80 units of the item in the physical inventory at December 31. The periodic inventory system is used. Determine the inventory cost and the cost of merchandise sold by three methods. Round interim calculations to one decimal and final answers to the nearest whole dollar. Cost of Merchandise Inventory and Cost of Merchandise Sold Inventory Method Merchandise Inventory Merchandise Sold a. First-in, first-out (FIFO) $fill in the blank 1 $fill in the blank 2 b. Last-in, first-out (LIFO) fill in the blank 3 fill in the blank 4 c. Weighted average cost fill in the blank 5 fill in the blank 6arrow_forwardBeginning inventory, purchases, and sales for an inventory item are as follows: Sep. 1 Beginning Inventory 5 Sale 17 Purchase 30 Sale 32 units 0 19 units 35 units @ $26 35 units Assuming a perpetual inventory system and the first-in, first-out method: a. Determine the cost of the goods sold for the September 30 sale. b. Determine the inventory on September 30.arrow_forward
- Perpetual Inventory Using FIFO Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Item B901 are as follows: August 1 Inventory 41 units @ $15 9 Sale 28 units 13 Purchase 47 units @ $17 28 Sale 17 units Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method, determine (a) the cost of merchandise sold on August 28 and (b) the inventory on August 31. a. Cost of merchandise sold on August 28 $ b. Inventory on August 31 $arrow_forwardPerpetual Inventory Using FIFO Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Item Zeta9 are as follows: Oct. 1 Inventory 47 units @ $23 7 Sale 39 units 15 Purchase 35 units @ $26 24 Sale 17 units Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method, determine (a) the cost of goods sold on October 24 and (b) the inventory on October 31. a. Cost of goods sold on October 24 b. Inventory on October 31arrow_forwarderpetual Inventory Using LIFO Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Item 88-HX are as follows: Mar. 1 Inventory 110 units @ $20 8 Sale 88 units 15 Purchase 122 units @ $23 27 Sale 102 units Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method, determine (a) the cost of goods sold on Mar. 27 and (b) the inventory on Mar. 31. a. Cost of goods sold on Mar. 27 $fill in the blank 1 b. Inventory on Mar. 31 $fill in the blank 2 I asked this before 42 is not being accepted as the answer.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education