
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
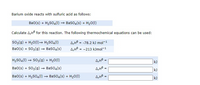
Transcribed Image Text:Barium oxide reacts with sulfuric acid as follows:
Bao(s) + H2SO4(I) → Baso4(s) + H,0(1)
Calculate A,H° for this reaction. The following thermochemical equations can be used:
so;(g) + H20(1)→ H2SO4(1)
A,Hô = -78.2 k) mol-1
A,Hô = -213 kJmol-1
Ba0(s) + SO3(g) → BasO4(s)
H2S04(1) → So;(g) + H20(1)
kJ
Ba0(s) + SO3(g) → Baso4(s)
4,48 .
kJ
Ba0(s) + H2SO4(1) → Baso4(s) + H20(1)
%3D
kJ
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- When N₂(g) reacts with H₂(g) to form NH3(g), 92.2 kJ of energy are evolved for each mole of N₂(g) that reacts. Write a balanced thermochemical equation for the reaction with an energy term in kJ as part of the equation. Note that the answer box for the energy term is case sensitive. Use the SMALLEST INTEGER coefficients possible and put the energy term (including the units) in the last box on the appropriate side of the equation. If a box is not needed, leave it blank. + + +arrow_forwardThe oxidation of glucose, C6H12O6(s), is described by the following thermochemical equation:C6H12O6(s) + 6 O2(g) → 6 CO2(g) + 6 H2O(l) ΔH = -2772 kJHow much heat, in kilojoules, can be produced by the oxidation of 3.56 g of fuel C6H12O6?Molar mass of C6H12O6 = 180.156 g/molarrow_forwardiv to vi pleasearrow_forward
- When HCl(g) reacts with NH3(g) to form NH4CI(s) , 176 kJ of energy are evolved for each mole of HCl(g) that reacts. Write a balanced thermochemical equation for the reaction with an energy term in kJ as part of the equation. Note that the answer box for the energy term is case sensitive. Use the SMALLEST INTEGER coefficients possible and put the energy term (including the units) in the last box on the appropriate side of the equation. If a box is not needed, leave it blank. + + +arrow_forwardIn a coffee cup calorimeter, 10.0mL of 1.00M AgNo3 and 10.0mLof 1.00M NaCl are mixed and the following reaction occurs (assume reaction goes to completion) Ag+ (aq) + Cl-(aq) ----> AgCl(s) The 2 solutions are intitially at 25.0C and the final temperature is 36.2C. Assuming density of the solution is 1.00g/mL and the heat capactity of the solution is 4.18J/K/g. Calculate q for the reaction in KJarrow_forward4. What mass of propane must be burned to supply 700. kJ as heat? The thermochemical equation for the combustion of propane is: C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g) → 3 CO2(g) + 4H₂O(1) AH°-2220. kJarrow_forward
- Liquid hydrogen peroxide, an oxidizing agent in many rocket fuel mixtures, releases oxygen gas on decomposition: 2 H2O2 (l) --> 2H2O (l) + O2 (g) Delta H = -196.1 kJ Calculate the heat for the decomposition of 780. kg of H2O2.arrow_forwardUse the following information to answer the question: What is the ΔH (in kJ/mol) for the following reaction? (Show work) CS2(l) + 3 O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2 SO2(g) Given: C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g); ΔHf = -393.5 kJ/mol S(s) + O2(g) → SO2(g); ΔHf = -296.8 kJ/mol C(s) + 2 S(s) → CS2(l); ΔHf = 87.9 kJ/molarrow_forwardThe reaction between hydrogen and oxygen to yield water vapor has AH" = -1843 2H₂(g) + O₂(g) 2H₂O(g)AH <=-484kJ Part A What is the enthalpy change in kilojoules when 0.70 mol of H₂ reacts with 0.35 mol of O, to produce 0.70 mol of H₂ at constant pressure of 1.00 atm? Express your answer as a whole number. AH = Submit Part B W= Submit 1957 ΑΣΦ How much PV work is done in kilojoules for this reaction at constant pressure of 1.00 atm if the volume change is-9-2 L? Express your answer using two significant figures. 100 ΑΣΦΑ Part C Request Answer Request Answer kJ What is the value of AE for this reaction in kilojoules?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY