
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305251052
Author: Michael Cummings
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:b. The coding sequence begins with AUG. What does AUG signify in terms of translation?
The Standard Genetic Code
When RNA polymerase initially transcribes the insulin gene into messenger RNA, two introns - totaling
966 additional nucleotides - are included in the precursor form of the insulin mRNA. These intron
sequences are removed from the mRNA in a splicing reaction as the mRNA is being transported out of
the nucleus of the cell. You might want to discuss why almost all eukaryotic genes contain introns.
3'
3'-
Val
35
(V)
Ala
(A)
G
Arg (R) A
Ser (S)
Lys (K)
Asp
(D)
Glu
0
이
Phe
(F)
Leu
(L) Ser
(S)
CODOCCAGUCAGUCAGUCAGUC
C
G
A
C
G
A
S%vcS\¢
Asn
(N)
G
Thr
E
A
GU
C
GU
AC
CUG
ACUGACUGAC
Met (M) Q
A
A
G
Tyr
35
UTO.
U
G
(Y)
Cys (C)
U
C
A
G
Trp (W)
3'
U
C
A
G
30
Leu
(L)
C
U
Pro
ခြာ
UG
Gln
lle
Arg
(Q)
(R)
09
His
(H)
Start
Stop
Figure 9: The codon sun shows the coding amino acid for each codon. Working from the inside outward,
the first, second and third nucleotides indicate the cognate amino acid of the sequence or stop.
Translating mRNA into Protein
11
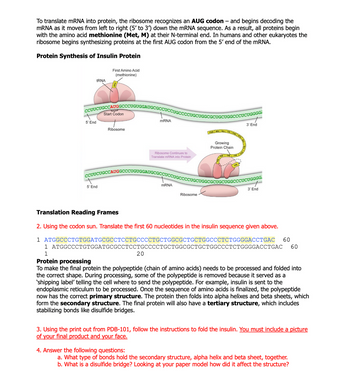
Transcribed Image Text:To translate mRNA into protein, the ribosome recognizes an AUG codon - and begins decoding the
mRNA as it moves from left to right (5' to 3') down the mRNA sequence. As a result, all proteins begin
with the amino acid methionine (Met, M) at their N-terminal end. In humans and other eukaryotes the
ribosome begins synthesizing proteins at the first AUG codon from the 5′ end of the mRNA.
Protein Synthesis of Insulin Protein
tRNA
First Amino Acid
(methionine)
CCUUCUGCCAGGCCCUGUGG
Start Codon
5' End
CCUUCUGCC
5' End
mRNA
Ribosome
Ribosome Continues to
Translate mRNA into Protein
Growing
Protein Chain
eno na
GGCCCU
mRNA
Ribosome
UGGGG
3' End
CCUCUGGGG
+
3' End
Translation Reading Frames
2. Using the codon sun. Translate the first 60 nucleotides in the insulin sequence given above.
1 ATGGCCCTGTGGATGCGCCTCCTGCCCCTGCTGGCGCTGCTGGCCCTCTGGGGACCTGAC
1 ATGGCCCTGTGGATGCGCCTCCTGCCCCTGCTGGCGCTGCTGGCCCTCTGGGGACCTGAC
1
20
60
60
Protein processing
To make the final protein the polypeptide (chain of amino acids) needs to be processed and folded into
the correct shape. During processing, some of the polypeptide is removed because it served as a
'shipping label' telling the cell where to send the polypeptide. For example, insulin is sent to the
endoplasmic reticulum to be processed. Once the sequence of amino acids is finalized, the polypeptide
now has the correct primary structure. The protein then folds into alpha helixes and beta sheets, which
form the secondary structure. The final protein will also have a tertiary structure, which includes
stabilizing bonds like disulfide bridges.
3. Using the print out from PDB-101, follow the instructions to fold the insulin. You must include a picture
of your final product and your face.
4. Answer the following questions:
a. What type of bonds hold the secondary structure, alpha helix and beta sheet, together.
b. What is a disulfide bridge? Looking at your paper model how did it affect the structure?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Given the following mRNA, write the double-stranded DNA segment that served as the template. Indicate both the 5 and the 3 ends of both DNA strands. Also write out the tRNA anticodons and the amino acid sequence of the protein encoded by the mRNA message. DNA: mRNA: 5-CCGCAUGUUCAGUGGGCGUAAACACUGA-3 protein: tRNA:arrow_forwardA normal mRNA that reads 5’ - UGCCAUGGUAAUAACACAUGAGGCCUGAAC- 3’ has an insertion mutation that changes the sequence to 5' -UGCCAUGGUUAAUAACACAUGAGGCCUGAAC- 3’. Translate the original mRNA and the mutated mRNA, and explain how insertion mutations can have dramatic effects on proteins. (Hint: Be sure to find the initiation site.)arrow_forwardSuppose that in the formation of phenylalanine hydroxylase mRNA, the exons of the pre-mRNA fail to splice together properly and the resulting enzyme is nonfunctional. This produces an accumulation of high levels of phenylalanine and other compounds, which causes neurological damage. What phenotype would be produced in the affected individual?arrow_forward
- Briefly describe the function of the following in protein synthesis. a. rRNA b. tRNA c. mRNAarrow_forwardGiven the following tRNA anticodon sequence, derive the mRNA and the DNA template strand. Also, write out the amino acid sequence of the protein encoded by this message. tRNA: UAC UCU CGA GGC mRNA: protein: How many hydrogen bonds would be present in the DNA segment?arrow_forwardThe pre-mRNA transcript and protein made by several mutant genes were examined. The results are given below. Determine where in the gene a likely mutation lies: the promoter region, exon, intron, cap on mRNA, or ribosome binding site. a. normal-length transcript, normal-length nonfunctional protein b. normal-length transcript, no protein made c. normal-length transcript, normal-length mRNA, short nonfunctional protein d. normal-length transcript, longer mRNA, shorter nonfunctional protein e. transcript never madearrow_forward
- Is an entire chromosome made into an mRNA during transcription?arrow_forwardAlternative Splicing Possibilities Suppose exon 17 were deleted from the fast skeletal muscle troponin T gene (Figure 29.46). How many different mRNAs could now be generated by alternative splicing? Suppose that exon 7 in a wild-type troponin T gene were duplicated. How many different mRNAs might be generated from a transcript of this new gene by alternative splicing?arrow_forwardIf the coding region of a gene (the exons) contains 2,100 base pairs of DNA, would a missense mutation cause a protein to be shorter, longer, or the same length as the normal 700 amino acid proteins? What would be the effect of a nonsense mutation? A sense mutation?arrow_forward
- The Events in Transcription Initiation Describe the sequence of events involved in the initiation of transcription by E. coil RNA polymerase. Include in your description those features a gene must have for proper recognition and transcription by RNA poIymerase.arrow_forwardCompare bacterial and eukaryotic mRNAs, and explain the functional significance of their structural differences.arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is false? a. GTP is an energy source during various stages of translation. b. In the ribosome, peptidyl transferase catalyzes peptide bondformation between amino acids. c. When the mRNA code UAA reaches the ribosome, there isno tRNA to bind to it. d. A long polypeptide is cut off the tRNA in the A site so its Metamino acid links to the amino acid in the P site. e. Forty-two amino acids of a protein are encoded by 126nucleotides of the mRNA.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning