
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
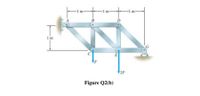
Transcribed Image Text:B
D
1 m
E
F
2F
Figure Q2(b)

Transcribed Image Text:(b) Figure Q2(b) shows that the truss supports loads at point C and E. If the value of F = 3
kN, calculate the axial forces in members BC and BE.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The trussed beam supports the uniform distributed loading. If all the truss members have a crosssectional area of 1.25 in2, determine the force in member BC. Neglect both the depth and axial compression in the beam. Take E = 29(103) ksi for all members. Also, for the beam IAD = 750 in4. Assume A is a pin and D is a rocker.arrow_forwardHelp me answerarrow_forwardThe rigid bar AB of negligible weight is supported by a pin at O. When the two steel rods are attached to the ends of the bar, there is a gap A = 4 mm between the lower end of the left rod and its pin support at C. %3D Compute the stress in the left rod after its lower end is attached to the support. The cross-sectional areas are 300 mm2 for rod AC and 250 mm? for rod BD. Use E = 200 GPa for steel. A В 0.75 m 1.5 m > 2 m Darrow_forward
- Determine the force in each member of the loaded truss. The forces are positive if in tension, negative if in compression. Assume F = 2210 N, a = 2.5 m, b = 5.0 m, 0 = 43° B A Ө a Ө C b Ө F Darrow_forwardGiven the truss below, take F₁ = 8kN, F₂= 4kN, L= 1.5m, h=2m. Use the Method of Sections. 0 21 (T) 20 (T) 5 (C) 20 (C) 5 (T) F₂ 21 (C) F₁- E A F Using a single equation of equilibrium, the force in KN in member BC. is mostly near_ LL D C TRID B harrow_forwardThe truss is composed of equilateral triangles of side a = 2.6 m. The load is L = 160 N. Determine the forces in members BC and CG. The forces are positive if in tension, negative if in compression. A 30° G a B E 30° Darrow_forward
- Problem 3 Classify each of the trusses below as statically determinate, statically indeterminate, or unstable. If indeterminate, specify the degree of indeterminacy. Hint: consider using the method of sections with a vertical section next to the vertical force P to explore if the trusses are unstable. nhinhnh (b) P (a) P P (c)arrow_forwardFor the truss shown below, applied loads are PB = 73 kN, PC = 36 kN and PD = 15 kN. Using the sign convention 'tension positive', select the correct answer for the axial force in member GH in kN: A F G B PB O 1. The axial force in member GH is -60 kN. O 2. The axial force in member GH is -78 kN. O 3. The axial force in member GH is -67.1 kN. 4@3m= 12m H Pc J D PD K E 4marrow_forward1. A pin-connected truss composed of members AB and BC is subjected to a vertical force P = 40 kN at joint B (see figure). Each member is of constant cross- sectional area: AAB = 0.004 m² and ABC =0.002 m². The diameter d of all pins is 20 mm, clevis thickness t is 10 mm, and the thickness 1 of the bracket is 15 mm. Determine the normal stress acting in each member and the shearing and bearing stresses at joint C. Fc Clevised ends 2 m A 1.5 m P=40 kNarrow_forward
- I have the answers below. I only need the solution.arrow_forwardShow all work. 1. 4 ft The truss system is loaded as shown. Assume that supprts A and K are both anchored frictionless pins. a. Is the truss stable and statically determinate? Show work. b. K c. d. Find the support reactions at A and K. Hint: what do we know about ideal truss members that lets us find all of the support reactions. Identify any obvious zero force members and state why each is. If none, state none. Using the method of joints only, find the forces in all other truss members, and indicate whether each is in compression or tension. H B C T-311-13 f₁0f ft- 1500 lb E -3 ft--3 ft--3 ft--3 ft- D 1500 lb F Iarrow_forwardUsing the method of joints, determine the force in each member of the roof truss shown. Take the load P = 1.4 kN. (Round the final answers to a single decimal place.) 6 m- 2.4 kN B 9 m 6 m 2.4 kN O 6 m 9 m The force in member DF (FDF) is 0. The force in member EF (FEF) is The force in member AB (FAB) is The force in member AC (FAC) is The force in member BC (FBC) is The force in member BD (FBD) is The force in member CD (FCD) is The force in member CE (FCE) is The force in member DE (FDE) is P 7.5 m kN. (Compression) kN. (Compression) KN. (Tension) kN. (Compression) kN. (Compression) kN. (Tension) kN. (Tension) kN. (Compression)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning