
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
I need to know how to do it
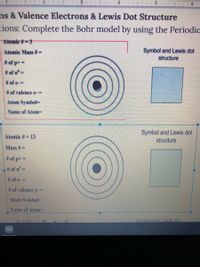
Transcribed Image Text:2 |.. 3..
4 .. L... 5.
..| . . 6
ns & Valence Electrons & Lewis Dot Structure
tions: Complete the Bohr model by using the Periodic
Atomic #-3
Atomic Mass #=
Symbol and Lewis dot
structure
# of p+ =
# of n'=
# of e-%3D
# of valence e-%3D
Atom Symbol
Name of Atom=
Symbol and Lewis dot
structure
Atomic #= 13
Mass #=
# of p+ =
L# of n=
# of e-=
# of valence e-%3D
Atom Symbol-
Name of Atom%3D
2 Edit
Symbol and Lewis dot
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Estimate the probability of finding an electron which is excited into the 2s orbital of the H atom, looking in a cubical box of volume 0.751036m3 centered at the nucleus. Then estimate the probability of finding the electron if you move the volume searched to a distance of 105.8 pm from the nucleus in the positive z direction. (Note that since these volumes are small, it does not matter whether the volume searched is cubical or spherical.)arrow_forwardHow does probability fit into the description of the atom?arrow_forwardThe wave function of an electron in the lowest (that is, ground) state of the hydrogen atom is (r)=( 1 a 0 3 )1/2exp(r a 0 )ao=0.5291010m (a) What is the probability of finding the electron inside a sphere of volume 1.0pm2 , centered at the nucleus (1pm=1012m) ? (b) What is the probability of finding the electron in a volume of 1.0pm2 at a distance of 52.9 pm from the nucleus, in a fixed but arbitrary direction? (c) What is the probability of finding the electron in a spherical shell of 1.0 pm in thickness, at a distance of 52.9 pm from the nucleus?arrow_forward
- ow does probability ?t into the description of the atom?arrow_forwardDiscuss briefly the difference between an orbit (as described by Bohr for hydrogen) and an orbital (as described by the more modern, wave mechanical picture of the atom).arrow_forward6.106 When Bohr devised his model for the atom, was he using deductive or inductive reasoning? Explain your answer.arrow_forward
- The energies of macroscopic objects, as well as those of microscopic objects, are quantized, but the effects of the quantization are not seen because the difference in energy between adjacent states is so small. Apply Bohr’s quantization of angular momentum to the revolution of Earth (mass6.01024kg) , which moves with a speed of 3.0104ms1 in a circular orbit (radius1.51011m) about the sun. The sun can be treated as fixed. Calculate the value of the quantum number n for the present state of the Earthsun system. What would be the effect of an increase in n by 1?arrow_forwardThe energy needed to remove one electron from a gaseous potassium atom is only about two-thirds as much as that needed to remove one electron from a gaseous calcium atom, yet nearly three times as much energy as that needed to remove one electron from K+ as from Ca+ . What explanation can you give for this contrast? What do you expect to be the relation between the ionization energy of Ca+ and that of neutral K?arrow_forwardUsing the periodic table and without looking at Table 7.3, write electron configurations for the following elements: (a) P (b) Zn (c) Zr (d) In (e) Pb (f) U Use the spdf and noble gas notations. When you have finished, check your answers with Table 7.3.arrow_forward
- List the charges on hydrogen-like atoms whose nuclei are of the following elements. a lithium, b carbon, c iron, d samarium, e xenon, f francium, g uranium, h seaborgiumarrow_forwardSpectroscopic studies of Li also show that Zeff(2p)=1.02 . Estimate the energy of the 2p orbital of Li. Calculate the average distance of the electron from the nucleus in the 2p orbital of Li. Comparing your results with those in Problem 13 shows that the energy values differ by about 50%, whereas the average distances are nearly equal. Explain this observation.arrow_forwardThe helium ion He+ is a one-electron system whose wave functions and energy levels are obtained from those for H by changing the atomic number to Z=2 . Calculate the average distance of the electron from the nucleus in the 2s orbital and in the 2p orbital. Compare your results with those in Problem 11 and explain the difference.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Cengage Learning