
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
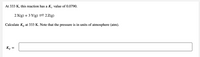
Transcribed Image Text:At 333 K, this reaction has a K. value of 0.0790.
2 X(g) + 3 Y(g)=2Z(g)
Calculate Kp at 333 K. Note that the pressure is in units of atmosphere (atm).
Kp =
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The equilibrium constant, K., is calculated using molar concentrations. For gaseous reactions another form of the equilibrium constant, Kp, is calculated from partial pressures instead of concentrations. These two equilibrium constants are related by the equation K₂ = K. (RT)An where R = 0.08206 L-atm/(K-mol), T is the absolute temperature, and An is the change in the number of moles of gas (sum moles products - sum moles reactants). For example, consider the reaction N₂(g) + 3H₂(g) = 2NH3(g) for which An=2-(1+3) = -2.arrow_forwardBe sure to answer all parts. The equilibrium constant K, for the reaction I(g) 5 21(g) is 3.75 x 10 at 726°C. Calculate K, and Kp for the equilibrium 21(g) S1(g) at the same temperature. K.= X 10 %3D (Enter your answer in scientific notation.) Kp = %3Darrow_forwardThe equilibrium constant, Kc, for the following reaction is 77.5 at 600 K. CO(g) + Cl₂(g) 80 F3 [CO] [Cl₂] Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of reactant and products when 0.245 moles of Co and 0.245 moles of Cl₂ are introduced into a 1.00 L vessel at 600 K. = [COCI₂] = = $ 4 Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. Submit Answer NOV 30 Q ? An error has been detected in your answer. Check for typos, miscalculations etc. before submitting your answer. F4 CoCl₂(g). % 5 M M M Retry Entire Group 16 F5 tv ♫ 9 A 6 9 more group attempts remaining MacBook Air C F6 & 7 F7 * 8 DII F8 9 Previous Email Instructor F9 ) - O Next Save and Exit 4 F10 Iarrow_forward
- Use the References to Consider the following reaction where K, = 2.01 at 500 K: PCI, (g) + Cl,(g)PCI,(g) If the three gases are mixed in a rigid container at 500 K so that the partial pressure of each gas is initially one atm, what will happen? Indicate True (T) or False (F) for each of the following: 1. A reaction will occur in which PCI,(g) is consumed 2. K, will decrease. v 3. A reaction will occur in which PCI, is consumed. | 4. Qis greater than K 5. The reaction is at equilibrium. No further reaction will occur.arrow_forwardThe elementary reaction 2 H, O(g) = 2 H, (g) + O,(g) proceeds at a certain temperature until the partial pressures of H, O, H,, and O, reach 0.0350 atm, 0.00550 atm, and 0.00700 atm, respectively. What is the value of the equilibrium constant at this temperature? K, =arrow_forwardChoose the letter of the correct answer. N204 (g) = (reversible to) 2NO2 (g), K = 4.63 x 10-3 I. the given is equation is an example of homogenous equilibrium II. Equilibrium will lie to the right Which statement(s) is/are correct?arrow_forward
- At 429 K, this reaction has a K. value of 0.0407. X(g) + 2 Y(g) = Z(g) Calculate Kp at 429 K. Note that the pressure is in units of atmosphere (atm). Kp =arrow_forwardFor the equilibrium reaction. 2IBr (g) I2 (g) + Br2 (g) Kc=.0085. If .025 M of IBr is introduced to an empty flask and allowed to reach equilibrium, calculate the final concentrations of all components. Consider the decomposition reaction at 555 K 4POCl3 (g) P4 (g) + 2O2 (g) + 6Cl2 (g) If .450 atm of POCl3 is introduced to an otherwise empty flask and the reaction is allowed to reach equilibrium, the final total pressure is .850 atm. Find Kp and Kc.arrow_forwardAt 487 K, this reaction has a Ke value of 0.0463. 2 X(g) + 3 Y(g) = 2Z(g) Calculate Kp at 487 K. Note that the pressure is in units of atmosphere (atm). Kp =arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY