
Steel Design (Activate Learning with these NEW titles from Engineering!)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337094740
Author: Segui, William T.
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Please solve it manually! And show your work. Thank you
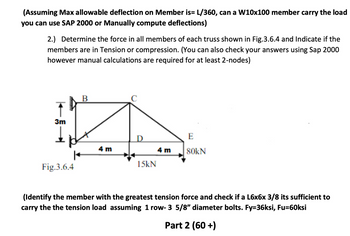
Transcribed Image Text:(Assuming Max allowable deflection on Member is= L/360, can a W10x100 member carry the load
you can use SAP 2000 or Manually compute deflections)
2.) Determine the force in all members of each truss shown in Fig.3.6.4 and Indicate if the
members are in Tension or compression. (You can also check your answers using Sap 2000
however manual calculations are required for at least 2-nodes)
↑
3m
Fig.3.6.4
B
C
D
E
4 m
4 m
80kN
15kN
(Identify the member with the greatest tension force and check if a L6x6x 3/8 its sufficient to
carry the the tension load assuming 1 row- 3 5/8" diameter bolts. Fy=36ksi, Fu=60ksi
Part 2 (60+)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The data in Table 1.5.3 were obtained from a tensile test of a metal specimen with a rectangular cross section of 0.2011in.2 in area and a gage length (the length over which the elongation is measured) of 2.000 inches. The specimen was not loaded to failure. a. Generate a table of stress and strain values. b. Plot these values and draw a best-fit line to obtain a stress-strain curve. c. Determine the modulus of elasticity from the slope of the linear portion of the curve. d. Estimate the value of the proportional limit. e. Use the 0.2 offset method to determine the yield stress.arrow_forwardA column in a building is subjected to the following load effects: 9 kips compression from dead load 5 kips compression from roof live load 6 kips compression from snow 7 kips compression from 3 inches of rain accumulated on the roof 8 kips compression from wind a. If lead and resistance factor design is used, determine the factored load (required strength) to be used in the design of the column. Which AISC load combination controls? b. What is the required design strength of the Column? c. What is the required nominal strength of the column for a resistance factor of 0.90? d. If allowable strength design is used, determine the required load capacity (required strength) to be used in the design of the column. Which AISC load combination controls? e. What is the required nominal strength of the column for a safety factor of 1.67?arrow_forwardDetermine the smallest value of yield stress Fy, for which a W-, M-, or S-shape from Part 1 of the Manual will become slender. To which shapes does this value apply? What conclusion can you draw from your answer?arrow_forward
- A tensile test was performed on a metal specimen having a circular cross section with a diameter 0. 510 inch. For each increment of load applied, the strain was directly determined by means of a strain gage attached to the specimen. The results are, shown in Table: 1.5.1. a. Prepare a table of stress and strain. b. Plot these data to obtain a stress-strain curve. Do not connect the data points; draw a best-fit straight line through them. c. Determine the modulus of elasticity as the slope of the best-fit line.arrow_forwardCompute the nominal shear strength of an M107.5 of A572 Grad 65 steel.arrow_forwardUse the composite beam tables and select a W-shape and stud anchors for the following conditions: Span length = 18 6 Beam spacing = 9 ft Total slab thickness = 51 2 in. (the slab and deck combination weighs 57 psf). Lightweight concrete with a unit weight of 115 pcf is used Construction load = 20 psf Partition load = 20 psf Live load = 225 psf Fy=50 ksi and fc=4 ksi A cross section of the formed steel deck is shown in Figure P9.8-9. The maximum live-load deflection cannot exceed L/360 (use a lower-bound moment of inertia). a. Use LRFD. b. User ASD.arrow_forward
- How is modulus of elasticity represented in engineering formulas?arrow_forwardHow does a tensile stress differ from a compressive stress?arrow_forwardA beam must be designed to the following specifications: Span length = 35 ft Beam spacing = 10 ft 2-in. deck with 3 in. of lightweight concrete fill (wc=115 pcf) for a total depth of t=5 in. Total weight of deck and slab = 51 psf Construction load = 20 psf Partition load = 20 psf Miscellaneous dead load = 10 psf Live load = 80 psf Fy=50 ksi, fc=4 ksi Assume continuous lateral support and use LRFD. a. Design a noncomposite beam. Compute the total deflection (there is no limit to be checked). b. Design a composite beam and specify the size and number of stud anchors required. Assume one stud at each beam location. Compute the maximum total deflection as follows: 1. Use the transformed section. 2. Use the lower-bound moment of inertia.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Steel Design (Activate Learning with these NEW ti...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337094740Author:Segui, William T.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Steel Design (Activate Learning with these NEW ti...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337094740Author:Segui, William T.Publisher:Cengage Learning Architectural Drafting and Design (MindTap Course...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781285165738Author:Alan Jefferis, David A. Madsen, David P. MadsenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Architectural Drafting and Design (MindTap Course...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781285165738Author:Alan Jefferis, David A. Madsen, David P. MadsenPublisher:Cengage Learning Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305084766Author:Saeed MoaveniPublisher:Cengage Learning
Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305084766Author:Saeed MoaveniPublisher:Cengage Learning Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning
Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals Of Construction EstimatingCivil EngineeringISBN:9781337399395Author:Pratt, David J.Publisher:Cengage,
Fundamentals Of Construction EstimatingCivil EngineeringISBN:9781337399395Author:Pratt, David J.Publisher:Cengage,

Steel Design (Activate Learning with these NEW ti...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337094740
Author:Segui, William T.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Architectural Drafting and Design (MindTap Course...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781285165738
Author:Alan Jefferis, David A. Madsen, David P. Madsen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Materials Science And Engineering Properties
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781111988609
Author:Charles Gilmore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305084766
Author:Saeed Moaveni
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305086272
Author:William P. Spence, Eva Kultermann
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals Of Construction Estimating
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337399395
Author:Pratt, David J.
Publisher:Cengage,