
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
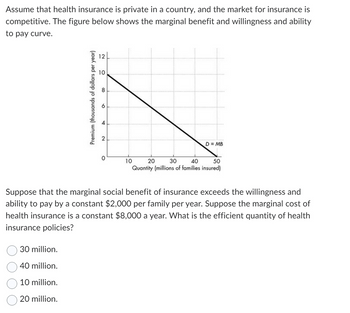
Transcribed Image Text:Assume that health insurance is private in a country, and the market for insurance is
competitive. The figure below shows the marginal benefit and willingness and ability
to pay curve.
Premium (thousands of dollars per year)
30 million.
40 million.
10 million.
20 million.
12
O
10
CO
6
2
O
10
D = MB
50
20 30 40
Quantity (millions of families insured)
Suppose that the marginal social benefit of insurance exceeds the willingness and
ability to pay by a constant $2,000 per family per year. Suppose the marginal cost of
health insurance is a constant $8,000 a year. What is the efficient quantity of health
insurance policies?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 7) The graph below depicts the social loss from the existence of health insurance in the presence of moral hazard. Price Demand curve with partial coinsurance Quantity a. What is the cause of the social loss? Briefly explain. b. Why do we have health insurance if social loss is created as a result of health insurance? ( Social lossarrow_forwardAdverse selection arises in the market for health insurance because Moral hazard arises in the market for health insurance because OA. for many people, the price of health insurance is beyond their ability to pay for it; the marginal social benefit of healthcare exceeds the marginal benefit perceived by its consumers OB. people optimistically underestimate the health risks that they face; people take too short a view of the benefits of healthcare OC. O D. some of the healthiest people choose to not buy insurance; once insured, a person has less incentive to adopt a healthy lifestyle once insured, a person has less incentive to adopt a healthy lifestyle; some of the healthiest people choose to not buy insurance;arrow_forward12 Demand elasticity and social loss. Consider two vaccines for difffferent viruses χ and Ω Assume that the marginal cost of producing both drugs is constant and that the fixed cost is small. In other words, assume that the supply curve for both drugs is flat. a Suppose that demand for vaccine χ is price elastic, whereas demand for vaccine Ω is relatively inelastic. Plot the private demand curve for both drugs on separate axes. b For the sake of example, assume that both viruses have the same externality. Plot the social demand curve for both drugs and label the social loss in each case. c Explain intuitively why, all else equal, social loss is greater in the case of elastic demand than it is in the case of inelastic demand.arrow_forward
- 2 Premium (thousands of dollars per year 6 $80 million. $160 billion. $80 billion. $160 million. 10 8 4 N HA 10 wom D = MB 30 40 50 20 Quantity (millions of families insured) Suppose that the marginal social benefit of insurance exceeds the willingness and ability to pay by a constant $2,000 per family per year. Suppose the marginal cost of health insurance is a constant $8,000 a year. If the government decides to provide public health insurance, how much will taxpayers have to pay?arrow_forwardAssume that health insurance is private in a country, and the market for insurance is competitive. The figure below shows the marginal benefit and willingness and ability to pay curve. Premium (thousands of dollars per year) $160 billion. $80 billion. $160 million. $80 million. 12 10 8 606 4 2 0 D = MB 10 20 30 40 50 Quantity (millions of families insured) Suppose that the marginal social benefit of insurance exceeds the willingness and ability to pay by a constant $2,000 per family per year. Suppose the marginal cost of health insurance is a constant $8,000 a year. If the government decides to provide public health insurance, how much will taxpayers have to pay?arrow_forwardBeatrix Hoffman argues that the influential role of private profit-making companies in the US health care system has historically led to... O Lower costs O Higher costs but a more patient-friendly system O Better health outcomes relative to other wealthy nations O Higher costs and a more fragmented and complex systemarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education