
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
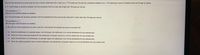
Transcribed Image Text:Assume that females have pulse rates that are normally distributed with a mean of μ = 75.0 beats per minute and a standard deviation of σ = 12.5 beats per minute. Complete parts (a) through (c) below.
a. If 1 adult female is randomly selected, find the probability that her pulse rate is less than 78 beats per minute.
The probability is ⬜.
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
b. If 16 adult females are randomly selected, find the probability that they have pulse rates with a mean less than 78 beats per minute.
The probability is ⬜.
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
c. Why can the normal distribution be used in part (b), even though the sample size does not exceed 30?
⬜ A. Since the distribution is of sample means, not individuals, the distribution is a normal distribution for any sample size.
⬜ B. Since the mean pulse rate exceeds 30, the distribution of sample means is a normal distribution for any sample size.
⬜ C. Since the distribution is of individuals, not sample means, the distribution is a normal distribution for any sample size.
⬜ D. Since the original population has a normal distribution, the distribution of sample means is a normal distribution for any sample size.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 19 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- a. b. In a normal distribution, a = -2, z = 6. This tells you (right or left) of the mean. O A. left OB. right 67 U that x = -2 is standard deviations to thearrow_forwardRefer to the figure at the right. At a =0.10, can you reject the claim that the proportion of 18 to 24-year-olds living in their parents' homes in 2000 was the same for men and women? Assume the survey included a random sample of 248 men and 244 women. Percentage of 18-to 24-year olds living in parents' homes 70- 51.5% 41.2% 46.6% 44.3% 0- 2012 I Women 2000 Men Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. Choose the correct answer below. O A. Ho: P1 #P2 Ha: P1 = P2 O B. Ho: P, P2 c. Họ: P1 = P2 Ha: P1 #P2 O D. Ho: P1 >P2 Ha: P1 SP2 Find the critical value(s). The critical value(s) is(are) ±1.65. (Round to two decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) Find the standardized test statistic. (Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardRefer to the figure at the right. At a = 0.10, can you reject the claim that the proportion of 18 to 24-year-olds living in their parents' homes in 2000 was the same for men and women? Assume the survey included a random sample of 270 men and 278 women. Percentage of 18- to 24-year olds living in parents' homes 70,60.4% 54.6% 50.3% 45% 2000 2012 I Men IWomen Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. Choose the correct answer below. O B. Ho: P1 + P2 A. Ho: P1= P2 Hg: P1 P2 H: P1 =P2 OD. Ho: P,> P2 OC. Ho: P1 P2 Hg: P, SP2 Find the critical value(s). The critical value(s) is(are) +1.65. (Round to two decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) Find the standardized test statistic. z= 3.61 (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Can you reject the claim that the proportion of 18 to 24-year-olds living in their parents' homes was the same for men and women in 2000? . at the 10% significance level, there is v evidence to v the claim.arrow_forward
- Assume that a randomly selected subject is given a bone density test. Those test scores are normally distributed with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. Find the probability that a given score is between 2.15 and 3.81 and draw a sketch of the region. Sketch the region. Choose the correct graph below O A. -2.15 3.81 O B. -2.15 3.81 O C. -2.15 3.81 O D. 2.15 3.81arrow_forwardA variable is normally distributed with a mean of 17 and a standard deviation of 8. Use your graphing calculator to find each of the following areas. Write your answers in decimal form. Round to the nearest thousandth as needed.a) Find the area to the left of 20. b) Find the area to the left of 11. c) Find the area to the right of 14. d) Find the area to the right of 21. e) Find the area between 11 and 26arrow_forwardThe amount of time a service technician needs to change the oil in a car is uniformly distributed between 11 and 21 minutes. Let X = the time needed to change the oil on a car. c. Find the 50th percentile. Round to the nearest minute.arrow_forward
- c. Identify the mean and standard deviation of x. Choose the correct answer below. O A. µ and О В. н аnd o C. and O D. and o 이들arrow_forwardAssume that the readings on the thermometers are normally distributed with a mean of 0 degrees and standard deviation of 1.00degrees C. Assume 2.4% of the thermometers are rejected because they have readings that are too high and another 2.4% are rejected because they have readings that are too low. Draw a sketch and find the two readings that are cutoff values separating the rejected thermometers from the others. A. The cutoff values are degrees. (Use a comma to separate answers as needed. Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardCompute the standard deviation of each of the two data sets A and B below. Then subtract the Standard Deviation of the data set A from the Standard Deviation of data set B. State your result as a decimal value with one digit after the decimal point (e.g. 3.0). Data set A: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 Data set B: 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26arrow_forward
- Assume that thermometer readings are normally distributed with a mean of 0degrees°C and a standard deviation of 1.00degrees°C. A thermometer is randomly selected and tested. (The given values are in Celsius degrees.) Between -1.47and 1.76arrow_forwardAssume that adults have IQ scores that are normally distributed with a mean of u= 100 and a standard deviation g= 15. Find the probability that a randomly selected adult has an IQ less than 118. Click to view page 1 of the table. Click to view page 2 of the table. The probability that a randomly selected adult has an IQ less than 118 is (Type an integer or decimal rounded to four decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardAssume that the readings at freezing on a batch of thermometers are normally distributed with a mean of 0°C and a standard deviation of 1.00°C. A single thermometer is randomly selected and tested. Find P30, the 30-percentile. This is the temperature reading separating the bottom 30% from the top 70%.P30 = °C(Round answer to three decimal places)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman