
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
As a material scientist, you have been requested by an engineer to list down a possible
cylindrical rod alloy to be used in your next project. Each cylindrical rod having a
dimension of 100 mm long and a diameter of 10.0 mm is to be deformed using a tensile
load of 27,500 N. It must not experience either plastic deformation or a diameter
reduction of more than 7.5 × 10−3 mm. Based on materials listed in Table 2, which are
possible candidates? Justify your choice(s).
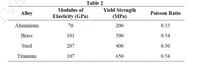
Transcribed Image Text:Table 2
Yield Strength
(MPa)
Modulus of
Alloy
Poisson Ratio
Elasticity (GPa)
Aluminium
70
200
0.33
Brass
101
300
0.34
Steel
207
400
0.30
Titanium
107
650
0.34
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A cylindrical rod 380 mm long and having a diameter of 10.0 mm is to be deformed using a tensile load of 22 KN. It must not experience either plastic deformation or a diameter reduction of more than 0.01 mm. Of the materials listed as follows, which are possible candidates? Show your solution Aluminum E-70GPa, Yield Strength 255 MPa, Poisson's ration 0.33 Brass E=105GPa, Yield Strength 345 MPa, Poisson's ration 0.34 Steel E=207GPa, Yield Strength 450 MPa, Poisson's ration 0.30 Copper E=110GPa, Yield Strength 250 MPa, Poisson's ration 0.33arrow_forwardDetermine the material property of the materials from the following website. Material Property Data (www.matweb.com) Material: Carbon Steel C1018 (AISI 1018) Hot Rolled 1 in. round Property: Young's Modulus (psi) 11300arrow_forwardFatigue accounts for ~90% of mechanical engineering failures. Please list 4 measures that may be taken to increase the resistance to fatigue of metallic materials. Please also briefly explain how each of these measures improves fatigue performance.arrow_forward
- You have been given the following test sample data following mechanical testing of 15 test pieces of a transformation toughened zirconia. What is the Weibull modulus of this material? Would you advise the use of this material over one with a Weibull Modulus of 25.4 and a mean failure stress of 235 MPa, if you anticipate that the peak stress on the material could be 220 MPa? (Since this question has two parts, you must select the two correct options from the list below) Test Sample Failure Stress (MPa) 1 255 2 271 3 260 4 223 5 257 6. 267 7 242 8 230 9. 245 10 225 11 254 12 236 13 238 14 251 15 264 O a. 27.3 O b. 4.5 O c. 6.9 O d. Yes е. 15.2 O f. 18.3 O g. No O O O O O O Oarrow_forwardQ1/A structural part is 1-meter-long and subjected to a 50 KN load in which this part must be deformed elastically without experiencing any permanent deformation. If you know that part is made of steel, brass, aluminum, and Titanium alloys and the yield strengths and densities of these alloys are: 860 MPa, 7.9 g/cm³; 415 MPa, 8.5g/cm³; 310 MPa, 2.7 g/cm³; and 550 MPa, 4.5 g/cm³ respectively. Based on these criteria, rank the alloys from the heaviest to the lightest in weight.arrow_forwardBased on the stress-strain plots, which materials tested are stiff and which are tough? How can you tell the difference? * we tested (Steel HR250)and (Aluminium 5251)in this experimentarrow_forward
- You are given three metal test samples, with the same chemical composition and differing grain sizes: A: 5.0, B: 10.0 and C: 20.0 microns. Samples A and B have been tested and have yield stresses of 142.4 MPa and 135.8 MPa (all numbers are rounded off to the 1st decimal point). Based on this information, which of the following values do you think will be the closest to the yield stress of Sample C? In calculating the answer, use the Hall-Petch relation between yield stress of a metal o vield and the grain size of the metal d, which is Oyield = 00 + kd¬1/2 where k and og are constants. (This question has only one correct answer) а. 100.6 MPa b. 131.1 MPa С. 152.4 MPa O d. 115.8 MPa е. 128.1 MPaarrow_forwardNeed help on part A,C,and D engineering of materials Part C - Angle of twist of B with respect to E Determine the angle of twist of B with respect to E. Express your answer to four significant figures and include the appropriate units. ϕB/E = Part D - Angle of twist of A with respect to F Determine the angle of twist of A with respect to F. Express your answer in radians to four significant figures. ϕA/F =arrow_forwardAn investigation of mechanical properties and microstructures of aluminium alloy 201.arrow_forward
- Determine the material property of the materials from the following website. Material Property Data (www.matweb.com) e Material: Carbon Steel C1045 (AISI 1045) Cold Drawn 1 in. round Property: Ultimate Tensile Strength (psi) 49,900arrow_forwardDefine a homogeneous material?arrow_forwardIn designing a ceramic part for a jet engine, to ensure that the part does not fail, we plan to ensure that the maximum applied stress is only one-third of the yield strength. The yield strength of this CMC part for a jet engine is 520 MPa, and its plane strain fracture toughness is 5.5 MPa√?. We utilize a nondestructive test to find any internal faults that are longer than 1.27 mm. Does our non-destructive test have the requisite sensitivity if Y = 1.4? Explain.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY