
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Consider the reaction between acetone and hydrogen cyanide to produce acetone cyanohydrin:
(c) If 2.5 g of acetone and 1.0 g of hydrogen cyanide react, how many moles of acetone
cyanohydrin (ACH) should form?
(e) Imagine that the reaction in part (c) produced 3.0 g of ACH, all of which was used in another
reaction to produce 6.0 g of C4H9NO5S. These 6.0 g of C4H9NO5S react with excess CH3OH to
form methyl methacrylate (C5,H8O2) according to the chemical equation below. What is the
theoretical yield of methyl methacrylate (in grams)?
C4 H9 NO5 S + CH3 OH → C5 H8 O2 + NH+4 + HSO-4
(f) If 3.1 g of methyl methacrylate are collected, what is the percent yield for the reaction in
part (e)?
Thank you!!
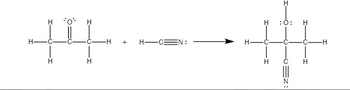
Transcribed Image Text:**Formation of Cyanohydrins**
In the image provided, a chemical reaction depicting the formation of cyanohydrins from an aldehyde and hydrogen cyanide is shown. Here is a detailed breakdown of the reaction:
### Reactants:
1. **Acetaldehyde (CH₃CHO)**
- Structural Formula:
```
H H H
| | |
H-C-C-C-H
| || |
H O H
```
2. **Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN)**
- Structural Formula:
```
H-C≡N
```
### Reaction Process:
- Acetaldehyde reacts with hydrogen cyanide to yield a cyanohydrin.
### Product:
- **Cyanohydrin**
- Structural Formula:
```
H H H
| | |
H-C-C-C-C-H
| | |
H O H
|
C≡N
```
### Reaction Mechanism:
1. **Initial Molecule:** Acetaldehyde (CH₃CHO) possesses a carbonyl group (C=O) attached to two hydrogen atoms and one methyl group.
2. **Addition of Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN):** The cyanide group (CN⁻) from HCN adds to the carbonyl carbon of acetaldehyde, converting the double-bonded oxygen (C=O) into a hydroxyl group (OH).
3. **Formation of Cyanohydrin:** The resulting molecule has an OH group and a CN group attached to the same carbon atom, forming cyanohydrin.
### Detailed Diagram Explanation:
- The diagram illustrates a chemical reaction taking place where each reactant and product is structurally depicted with all bonds and atoms clearly shown.
- The arrow indicates the direction of the chemical reaction, moving from left (reactants) to right (product).
This reaction is significant in organic chemistry as cyanohydrins are versatile intermediates in the synthesis of various important compounds.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In one experiment, 12.0 g of PCl5 was slowly added to 15.0 g of H2O according to the following balanced chemical equation: Pcl5(s)+4H2O(l) ---> H3PO4 (aq) + 5HCl (g) The molar masses for each compounds in the equation are as follows; PCl5: 208.224 g/mol H2O: 18.015 g/mol H3PO4: 97.994 g/mol HCl; 36.45 g/mol What is the limiting reagent in this scenario? Your answer should be an explanation! You're not solving anything. Note! Make an accurate claim: The limiting reagent in this scenario is _____. Provide additional details and use subject specific language. Cite evidence from what's given to you in the problem that supports your answer, hint: look at that equation!. Lastly! Fully connect the evidence to the claim/your answer to the question. Include subject specific language in your reasoning. The two images attached are examples of how your response SHOULD look.arrow_forward6.24 Ethanol, used in alcoholic beverages, can be produced by the fermentation of sucrose, which is found in sugar cane and other plants. The balanced equation for the fermentation process is C12H„0,(s) + H,0(1) – (a) What mass of ethanol, C,H,OH, would be produced when 2.50 g sucrose reacts by this process? (b) What mass of CO, would also be produced? 4C,H,OH() + 4CO,(g)arrow_forwardBe sure to answer all parts. TCDD, also called dioxin (C H,Cl,O2, molar mass 322.0 g/mol), is a potent poison. The average lethal dose in humans is estimated to be 3.0 x 10- mg per kg of body weight. (a) How many grams constitute a lethal dose for a 91-kg individual? (b) How many molecules of TCDD does this correspond to? (a) X 10 g dioxin (b) x 10 moleculesarrow_forward
- In a reaction, 0.77 kg of V,O, are reacted with 0.88 kg of Ca as the following chemical Equation: V2O5 + Ca V+ Cao aBalanced the reaction equation. b-Caleulate the moles of given reactants. CCalculate the moles of product V. d-calculate the mass of V formed in grams. eWhich of the reactants is the limiting reagent? Given that:- (V=50.94g/mol, Ca = 40 g/mol, O = 16 g/mol).arrow_forwardIf 100 grams of CH4 is made to react with 200 grams of O2, what mass of CO2 (in grams) is formed?arrow_forward5. 2Fe(OH);(s) + 3H,SO4(ag) → Fe2(SO4);(ag) + 6H;0(I) classify: If 2.4 g Fe(OH)3 and 3.3 g H2SO4 react and make 4.5 g Fe2(SO4)3, g H20 are made also. Find theoretical yield of Fe2(SO4)3 in a reaction of 24.1 mol Fe(OH)3 and 30.5 mol H2SO4 : The 24.1 mol Fe(OH)3 are enough to form mol Fe2(SO4)3. The 30.5 mol H,SO4 are enough to form mol Fe2(SO4)3. The limiting reagent in the mixture is The theoretical yield of Fe2(SO4)3 is moles If only 8.2 mol Fe2(SO4)3 Was isolated, the percent reaction yield is %arrow_forward
- 0 3.76 Consider the mixture of propane, C,Hg, and O2 shown below. (a) Write a balanced equation for the combustion reaction that Occurs between propane and oxygen. (b) Which reactant is the limiting reactant? (c) How many molecules of CO, H2O, C;Hs, and O, will be present if the reaction goes to completion?arrow_forwardComplete combustion of propane (C3H8) produces carbon dioxide and water as products. C3H8(g) + 5O2(g) --> 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(g) Incomplete combustion produces some carbon monoxide (CO) in place of carbon dioxide (CO2). What is the limiting reactant for incomplete combustion? (A) There is no way to tell (B) Water (C) Propane (D) Oxygenarrow_forwardThe combustion of gasoline produces carbon dioxide and water. Assume gasoline to be pure octane (C8H18)(C8H18) and calculate how many kilograms of carbon dioxide are added to the atmosphere per 4.2 kgkg of octane burned. ( HintHint: Begin by writing a balanced equation for the combustion reaction.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY