
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
- An electron accelerates from rest through an electric field and into a magnetic field as shown in the diagram to the right. The plates have a potential difference of 85 V and the magnetic field has a magnitude of 0.75 T.
(a) Calculate the initial speed of the electron upon entering the magnetic field.
(b) Calculate the magnitude and direction of the magnetic force on the electron.
(c) Calculate the radius of the electron’s circular path.
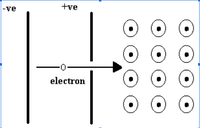
Transcribed Image Text:|-ve
+ve
0-
electron
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A long straight wire carries a 1.5 A current. An electron moves parallel to the wire at speed 3.1 x 104 m/s. The distance between the electron and the wire is 8 cm. Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic force on the electron.(Give your answer in newtons but don't include the units.)arrow_forwardAn electron moves at a velocity of 2.20 x 10^6 m/s in a direction perpendicular to a magnetic field of strength 1.89 T. How much force will the electron experience?arrow_forwardA particle with a charge of 2μC is moving at 3 x 106m/s perpendicularly through a magnetic field with a strength of 0.05T. What is the magnitude of the force on the particle?arrow_forward
- An electric field of 1.51 kV/m and a perpendicular magnetic field of 0.413 T act on a moving electron to produce no net force. What is the electron's speed?arrow_forwardA singularly-charged ion (i.e. a neutral atom which has gained one electron) with kinetic energy of 7x10−15 J follows a circular path of radius 0.6m when placed in a magnetic field of 0.5T. (Note that the charge of an electron is e = 1.6 x 10−19 C.) a) Using the fact that the ion is going in a circular motion in a magnetic field, what is the ion’s momentum (in kg.m/s)? b) What is the ion’s speed (in m/s)? c) What is the ion’s mass (in kg)? d) An electric field is added to the experiment and adjusted so that the ion passes through without any deflection. What is the magnitude of this electric field (in T)?arrow_forwardA proton moves perpendicular to the magnetic field of 0.5 T. The track is observed to be a circular arc of radius 2.0 cm. Find: a) The direction of the force acting on the proton? b) The velocity of the proton c) The kinetic energy of the moving proton d) The magnitude of the force acting on the protonarrow_forward
- A long straight wire carries a 1.5 A current. An electron moves parallel to the wire at speed 1.3 x 104 m/s. The distance between the electron and the wire is 7 cm. Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic force on the electron.(Give your answer in newtons. Don't round your answer.)arrow_forwardA proton moves with a speed of 1.0 x 107 m/s in the directions shown. A 0.50 T magnetic field points in the positive x-direction. For each, what is the magnetic force on the proton? Give your answers as a magnitude and a direction.arrow_forwardWrite down an expression for the force experienced by an electron moving with a velocity, v, in a magnetic field B. By equating this expression to the force required to cause electrons to follow a circular path of radius, r, derive an expression for the ratio, (?⁄?) for an electron in terms of the magnetic field strength, the radius of the circular path and the accelerating potential, V.arrow_forward
- Determine the magnitude of the force on an electron traveling 5.85×105 m/s horizontally to the east in a vertically upward magnetic field of strength 0.20 T . Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. Determine the direction of the force on an electron.arrow_forwardStarting from rest, an electron is accelerated through a region between two oppositely charged plates, as shown in Figure 1. The distance between the plates is 10 cm and the magnitude of the potential difference between them is 100 V. Immediately after exiting the region with the uniform electric field, the electron enters a region with a uniform magnetic field of 0.85 T, directed into the page. (a) Calculate the magnitude of the electric force on the electron. (b) Calculate the work done by the electric force on the electron. (c) Determine the electron's speed when it enters the magnetic field. (d) Determine the magnitude and direction of the magnetic force on the electron when it enters the magnetic field. (e) Suppose that the experiment was repeated with the locations of the positive and negative plates switched, and the electron was replaced with a proton, but nothing else was changed. Calculate R,/R., the ratio of the radius of the proton's path in the magnetic field (R,) to that…arrow_forwardAn electron moves with a speed of 5.0×107 m/s in the directions shown in (Figure 1) and (Figure 2) below. A 0.40 T magnetic field points in the positive x-direction.What is the magnitude of the magnetic force in (Figure 2)?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON