
Entrepreneurial Finance
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337635653
Author: Leach
Publisher: Cengage
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
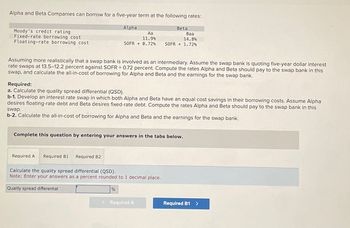
Transcribed Image Text:Alpha and Beta Companies can borrow for a five-year term at the following rates:
Moody's credit rating
Fixed-rate borrowing cost
Floating-rate borrowing cost
Alpha
Beta
Aa
11.9%
SOFR +0.72%
Baa
14.8%
SOFR +1.72%
Assuming more realistically that a swap bank is involved as an intermediary. Assume the swap bank is quoting five-year dollar interest
rate swaps at 13.5-12.2 percent against SOFR + 0.72 percent. Compute the rates Alpha and Beta should pay to the swap bank in this
swap, and calculate the all-in-cost of borrowing for Alpha and Beta and the earnings for the swap bank.
Required:
a. Calculate the quality spread differential (QSD).
b-1. Develop an interest rate swap in which both Alpha and Beta have an equal cost savings in their borrowing costs. Assume Alpha
desires floating-rate debt and Beta desires fixed-rate debt. Compute the rates Alpha and Beta should pay to the swap bank in this
swap.
b-2. Calculate the all-in-cost of borrowing for Alpha and Beta and the earnings for the swap bank.
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
Required A
Required B1
Required B2
Calculate the quality spread differential (QSD).
Note: Enter your answers as a percent rounded to 1 decimal place.
Quality spread differential
%
< Required A
Required B1 >
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Alpha and Beta Companies can borrow for a five year term at the following rates: Alpha Beta Moody's credit rating Aa Baa Fixed rate borrowing cost 12.5% 16.0% Floating rate borrowing cost SOFR+0.72% SOFR+1.72% Required: a. Calculate the quality spread differential (QSD). b-1. Develop an interest rate swap in which both Alpha and Beta have an equal cost savings in their borrowing costs. Assume Alpha desires floating rate debt and Beta desires fixed rate debt. No swap bank is involved in this transaction. What rate should Alpha pay to Beta? b-2. What rate will Beta pay to Alpha? b-3. Calculate the all-in cost of borrowing for Alpha and Beta, respectively.arrow_forward(Motivation for Interest rate swap) National Bank has a $200b Adjustable Rate Mortgage (ARM) as a liability on its balance sheet. The interest rate on the ARM is 2.34%+Libor. As a result, the bank will have to pay floating interest. The bank is considering hedging the risk in the interest payment to the ARM with a three-year interest rate swap. What will be the Bank's net interest rate of payment if it chooses the right swap? Answer: ____________%. Euro-€ Swiss franc U. S. dollar Japanese yen Years Bid Ask Bid Ask Bid Ask Bid Ask 2 3.08 3.12 1.68 1.76 5.43 5.46 0.45 0.49 3 3.25 3.29 2.41 2.68 5.78 6.02 0.56 0.59arrow_forwardA bank today makes $100 in 3-year loans with a 16% fixed annual interest rate. It funds the loans today with $100 in 1-year CDs that currently have a 7% annual interest rate. It has the option of entering an interest rate swap contract. The contract includes a variable rate of 4.5% and a fixed rate of 7.5%. If the bank chooses to hedge its interest rate risk using a $100 notional value swap contract, what is the bank's expected net interest income in the first year if all interest rates remain the same throughout the year? A) $9 OB) 12 OC) $7 OD) $16 O E) $6arrow_forward
- A Credit Default Swap is structured like the one below for a protection of $100 million. If payments are made annually, what are the cash flows from A to B if there is a default after 2 years and 2 months and recovery rate is 40%? And what are the cash flows from B to A? 70 bps per year Default Default Protection Protection Buyer, A Seller, B Payoff if there is a default by reference entity=100(1-R)arrow_forwardPLease use actuarial science work to solve this question. The answer is (a) 0.1774, (b) 0.2124, (c) 0.3020 Thank you so much.arrow_forwardSuppose a bank enters a repurchase agreerment in which it agrees to sell Treasury securities to a correspondent bank at a price of $9.99,838 with the promise to buy them back at a price of $10.000,073. Calculate the yield on the repo if it has a 6-day maturity. (write your answer in percentage and round it to 2 decimal places)arrow_forward
- Consider a one-year interest rate swap with semi-annual payments, based on 30/360 day count convention. The term structure of LIBOR spot rates is given as follows: 6-month LIBOR at 7.2%, and 12-month LIBOR at 8.0%. What is the annualized fixed rate on the swap? A. 7.42%. B. 7.93% C. 7.84%. D. 7.56%.arrow_forwardWhat should be the current interest rate on this financial accounting question?arrow_forwardSuppose you purchase a T-bills that is 125 days from maturity for $9,765. The T-bills has a face value of $10,000.a. Calculate the T-bills’s quoted discount rate. b. Calculate the T-bills’s annualized rate.c. Who are the major issuers of and investors in money market securities?arrow_forward
- Use the data from Q5, and given the following annualized interest rates: r(30) = 4.0%; r(120) = 4.5%; r(210) = 5.0%, and; r(300) = 5.5% sixty days after the initiation of the pay-fixed swap. If the pay-fixed and receive-floating swap is to mark-to-the-market now, who pays whom and how much? Use $5m notional principal. Pay-fixed leg pays $24,214.41 to pay-floating leg. Pay-floating leg pays $24,214.41 to pay-fixed leg. Pay-fixed leg pays $25,455.45 to pay-floating leg. Pay-floating leg pays $25,455.45 to pay-fixed leg.arrow_forward2. Assume that you are a swap dealer and have just acted as a counterparty in an interest rate swap. The notional principal for the swap was $8 million and you are now obligated to make 6 annual payments of 4% interest. The floating rate that you will receive annually is LIBOR + 1%. The LIBOR is expected to be 2.6% for year 1, 2.8% for year 2, and 3.5% thereafter. Compute the net present value of your swap agreement at a discount rate of 6%?arrow_forwardSuppose Home Depot issues 30-year bonds on which it pays a 4.00% (nominal) interest rate. Further, suppose that both Home Depot and the purchasers of its bonds anticipate inflation will average 2.00% during the life of the loan. Now suppose the inflation rate after the loan is made (i.e. after the bond is purchased) is actually 1.00% per annum. It follows that the actual real rate of interest is and, ceteris paribus, are (is) better off than anticipated as a result of the difference between the anticipated and the actual rate of inflation. Select one: a. 2.00%, Bondholders b. 2.00%, Home Depot O c. 3.00%, Bondholders d. 3.00%, Home Depotarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning


Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...
Finance
ISBN:9781337395083
Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher:Cengage Learning