
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780133594140
Author: James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
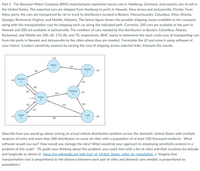
Transcribed Image Text:Part 1. The Bavarian Motor Company (BMC) manufactures expensive luxury cars in Hamburg, Germany, and exports cars to sell in
the United States. The exported cars are shipped from Hamburg to ports in Newark, New Jersey and Jacksonville, Florida. From
these ports, the cars are transported by rail or truck to distributors located in Boston, Massachusetts; Columbus, Ohio; Atlanta,
Georgia; Richmond, Virginia; and Mobile, Alabama. The below figure shows the possible shipping routes available to the company
along with the transportation cost for shipping each car along the indicated path. Currently, 200 cars are available at the port in
Newark and 300 are available in Jacksonville. The numbers of cars needed by the distributors in Boston, Columbus, Atlanta,
Richmond, and Mobile are 100, 60, 170, 80, and 70, respectively. BMC wants to determine the least costly way of transporting cars
from the ports in Newark and Jacksonville to the cities where they are needed. Formulate the LP and solve it using software of
your choice. Conduct sensitivity analysis by varying the cost of shipping across selected links. Interpret the results.
+100
Boston
$30
Newark
$50
-200
1
Columbus
3
+60
$40
$40
$35
Richmond
+80
$30
Atlanta
+170
$25
$45
$50
$35
Mobile
J'ville
7
+70
|-300
$50
Describe how you would go about solving an actual vehicle distribution problem across the domestic United States with multiple
seaports of entry and more than 300 distributors to cover all cities with a population of at least 100 thousand residents. What
software would you use? How would you manage the data? What would be your approach to employing sensitivity analysis in a
problem of this scale? (To guide your thinking about this problem, you could start with a list of cities and their locations by latitude
and longitude as shown in https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List of United States cities by_population. e Imagine that
transportation cost is proportional to the distance between each pair of cities and demand, cars needed, is proportional to
population.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Use the MO diagram (below) to calculate the bond order for BN. лp .πp Op Os ПР Question 34 of 50 Jp 1 4 7 +/- 2 5 3 6 8 9 0 Submit X C x 100 +arrow_forwardProblem FedEx must transport packages from a central warehouse to various destinations (hubs) using a road network. Each road segment has an associated cost, representing the transportation cost per kilometer. Problem Facts 1. Central warehouse at node A, with four destinations (nodes B, C, D, and E).2. Transportation costs per kilometer between nodes: -A to B: $5 USD-A to C: $3 USD-A to D: $8 USD-B to E: $2 USD-C to B: $2 USD-C to D: $2 USD-D to E: $4 USD Detail: - Network representation and explanation of its construction.- Implementation details in python with networkx and results. Explanation of the differences between the implementation of the Dijkstra and Bellman-Ford algorithms.- Analysis of the shortest paths and associated costs.arrow_forwardPlease answer the question as quickly as possiblearrow_forward
- Sherman Company employs 400 production, maintenance, and janitorial workers in eight separate departments. In addition to supervising operations, the supervisors of the departments are responsible for recruiting, hiring, and firing workers within their areas of responsibility. The organization attracts casual labor and experiences a 20 to 30 percent turnover rate in employees per year. Employees clock on and off the job each day to record their attendance on time cards. Each department has its own clock machine located in an unattended room away from the main production area. Each week, the supervisors gather the time cards, review them for accuracy and sign and submit them to the payroll department for processing. In addition, the supervisors submit personnel action forms to reflect newly hired and terminated employees. From these documents, the payroll clerk prepares payroll checks and updates the employee records. The supervisor of the payroll department signs the paychecks, which…arrow_forwardQuestion 6. Convert the following CFG into CNF. Show all intermediate steps. A → BAB B& B → 00 €arrow_forwardProblem 4 - NFA to DFA Consider the following NFA 이1 이1 1. Draw the transition table for this NFA 2. Find an DFA equivalent to this NFAarrow_forward
- Given the following case, you are to answer the two questions on the following pages. When completed download this document into the drop box labeled BISI SLO#1 Bob’s Supply (BS) needs to keep track of the parts they have in their inventory. He wants to know the description of each part, the color of each part, how many of each item is in stock [QOH], and how much each part costs him. BS also needs to keep track of who supplies each part, the supplier’s name, contact person, and telephone number. We know that each part in inventory has only one supplier, but some suppliers supply multiple parts to BS. Bob wants each part and each supplier to be assigned a unique identifying number. Table 1: Partsarrow_forwardIn these three examples, we see how a surrogate key may be used as the primary key of a connection.arrow_forwardIn Cybersecurity, explain followings: EXAMPLE 1 → SL-C(Control Center) = { 2 2 0 1 3 1 3 } EXAMPLE 2 → SL-T(Plant DMZ) = { 3 3 2 3 0 0 1 } EXAMPLE 3 → SL-C(RDF, FS-PLC) = 4arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science
Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning
Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education
Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY
Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780133594140
Author:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780124077263
Author:David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781337569330
Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Concepts of Database Management
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781337093422
Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. Last
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Prelude to Programming
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780133750423
Author:VENIT, Stewart
Publisher:Pearson Education

Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781119368830
Author:FITZGERALD
Publisher:WILEY