
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
In muscle cells, when adrenaline binds to beta-adrenergic receptor, it trigger signaling cascade leading to active glycogen phosphorylate breaks up glycogen into glucose subunits (Glycogen -> G1P). Base on following figure, describe this signaling cascade:
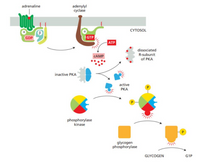
Transcribed Image Text:adrenaline
adenylyl
cyclase
CYTOSOL
GDP
ATP
dissociated
R-subunit
of PKA
CAMP
inactive PKA
active
РКА
phosphorylase
kinase
glycogen
phosphorylase
GLYCOGEN
G1P
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
The cell signalling process is the medium of communicating between different cells in our body and usually the signalling molecule or ligand is the mediator of this pathways.
Usually in the case of water soluble ligand molecules they binds with the cell surface receptor and activates the signaling cascade.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A certain type of tumor results in the overproduction of glucagon. Researchers claim that treatment with insulin can counteract the effects of the excess glucagon on the pathway shown in Figure 2. Provide reasoning to justify the researchers' claim.arrow_forwardI don't understand, can I get help? I have attached a picture of everything that will be needed to be annotated. Numerous signaling molecules work together in order for glucagon to induce the regulated release of glucose into the bloodstream. Construct an annotated list of each of these signaling molecules (as learned in the lecture video). For your annotated list, please use the format below. You will need to use this format for each molecule in the pathway that we learned. Name of Molecule:Type of Molecule:Is activated (or inhibited) by:Activates (or inhibits):arrow_forwardLabel the molecules in this figure showing how IP3 and DAG function as second messengers. Note: not all labels are used. IP3 and calcium activating protein kinase C Activated phospholipase C DAG triggering calcium release Activated G-protein with GTR bound Siy IP3 triggering calcium release Phosphatidyl inositol Ligand bound to receptor DAG and calcium activating protein kinase C Activated G-protein with GDP bound Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. TH ,,arrow_forward
- Insulin signals activate all of the following enzymes except: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) Glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) Protein kinase B (PKB; or Akt) All of the above enzymes are activated by insulin signals Citrate move in and out of mitochondria via a specific transport protein. What would happen if aninhibitor completely inhibited this transport system? Fatty acid biosynthesis would slow down Ketone body synthesis would slow down Both A and B Neither A nor Barrow_forwardEpinephrine stimulates glycogen breakdown by activating glycogen phosphorylase. However, in the research lab, no glycogen breakdown occurred when epinephrine was added to a test tube containing the enzyme and its substrate, glycogen. Explain why glycogen phosphorylase could be activated by epinephrine only when the hormone was added to intact cells in a solution.arrow_forwardWhich of the following steps amplify the epinephrine signal response in cells: receptor activation of G protein, G protein activation of adenylyl cyclase, cAMP activation of PKA, or PKA phosphorylation of glycogen phosphorylase kinase (GPK)? Which change will have a greater effect on signal amplification: an increase in the number of epinephrine receptors or an increase in the number of Gαs proteins?arrow_forward
- 2+ Activation of 5-HT2A Increases cytosolic free Ca²+ Concentration ([Ca²+]) Via a Signaling cascade. At rest, neurons have a cytosolic Ca Concentration of 100nM. The ex- Tra cellular free calcium concentration is typically 1.2m M. Calculate the resting potential (at equilibrium) produced by the neuron as a result of the calcium ion concentration gradient. (Report your answer in mV ).arrow_forwardDetermine if the following statement is true or false. Explain your answer. “Two molecules of insulin must bind to the insulin receptor in order for activation to occur.”arrow_forwardWhich processes are involved in the signaling pathway from insulin to glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) inactivation (select all that apply)? O protein kinase B being activated by a protein kinase known as PDK-1 O activation of insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) by phosphorylation O phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase associating with IRS-1 generates phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate O protein kinase B phosphorylating GSK3, resulting in its activation O insulin binding to a tyrosine kinase receptorarrow_forward
- Please explain the steps in this pathway on the picture.arrow_forwardWhich of the following results are most likely to be observed in liver enzymes following initiation of glucagon signaling? O Enzymes that showed lower activity were unphosphorylated. Enzymes that showed altered activity (higher or lower) were methylated. Enzymes that showed altered activity (higher or lower) were phosphorylated. Enzymes that showed higher activity were sulfonated.arrow_forwardPart A The phosphodiesterase that catalyzes hydrolysis of cyclic AMP is inhibited by caffeine. What overall effect would caffeine have on a signal that is mediated by CAMP? O When caffeine inhibits the enzymatic hydrolysis of cyclic AMP, response to a hormonal signal is decreases. O When caffeine inhibits the enzymatic hydrolysis of cyclic AMP, response to a hormonal signal is prolonged.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education