
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
a) Draw a phylogenetic tree based on characters 1-5 in the table below. Place hatch marks on the tree to indicate the origin of characters 1-6.
b) Assume that tuna and dolphins are sister species and redraw the phylogenetic tree accordingly. Use hatch marks to indicate the origin of characters 1-6.
c) How many evolutionary changes are required in each tree? Which tree is most parsimonious?
Use figure 20.5 and 20.12 from the Campbell, Biology in focus.
Can you pls explain this to me?
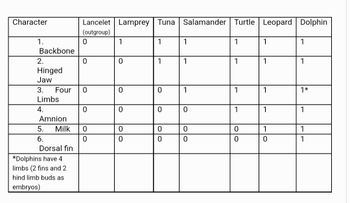
Transcribed Image Text:Character
1.
Backbone
2.
Hinged
Jaw
3. Four
Limbs
4.
Amnion
5.
6.
Milk
Dorsal fin
*Dolphins have 4
limbs (2 fins and 2
hind limb buds as
embryos)
Lancelet Lamprey Tuna Salamander
(outgroup)
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
lo
0
0
0
Turtle
1
1
1
1
0
0
Leopard
1
1
1
1
1
0
Dolphin
1
1
1*
1
1
1
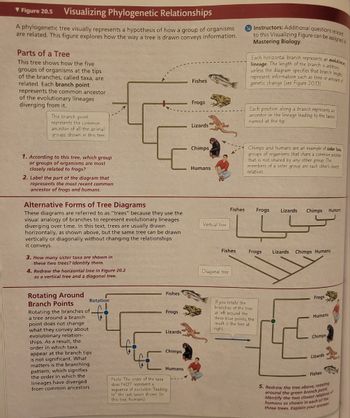
Transcribed Image Text:▼Figure 20.5 Visualizing Phylogenetic Relationships
A phylogenetic tree visually represents a hypothesis of how a group of organisms
are related. This figure explores how the way a tree is drawn conveys information.
Parts of a Tree
This tree shows how the five
groups of organisms at the tips
of the branches, called taxa, are
related. Each branch point
represents the common ancestor
of the evolutionary lineages
diverging from it.
This branch point
represents the common
ancestor of all the animal
groups shown in this tree.
1. According to this tree, which group
or groups of organisms are most
closely related to frogs?
2. Label the part of the diagram that
represents the most recent common
ancestor of frogs and humans.
Alternative Forms of Tree Diagrams
These diagrams are referred to as "trees" because they use the
visual analogy of branches to represent evolutionary lineages
diverging over time. In this text, trees are usually drawn
horizontally, as shown above, but the same tree can be drawn.
vertically or diagonally without changing the relationships
it conveys.
3. How many sister taxa are shown in
these two trees? Identify them.
4. Redraw the horizontal tree in Figure 20.2
as a vertical tree and a diagonal tree.
Rotating Around
Branch Points
Rotation
f
Rotating the branches of
a tree around a branch
point does not change
what they convey about
evolutionary relation-
ships. As a result, the
order in which taxa
appear at the branch tips
is not significant. What
matters is the branching
pattern, which signifies
the order in which the
lineages have diverged
from common ancestors.
Fishes
Frogs
Lizards
Chimps
Humans
Note: The order of the taxa
does NOT represent a
sequence of evolution "leading
to" the last taxon shown (in
this tree, humans).
Fishes
Frogs
Lizards
Chimps
Humans
Vertical tree
Fishes
Fishes
Diagonal tree.
Instructors: Additional questions related
to this Visualizing Figure can be assigned in
Mastering Biology.
evolutionary
Each horizontal branch represents an
lineage. The length of the branch is arbitrary
unless the diagram specifies that branch lengths
represent information such as time or amount of
genetic change (see Figure 20.13).
Each position along a branch represents an
ancestor in the lineage leading to the taxon
named at the tip.
Chimps and humans are an example of sister taxa
groups of organisms that share a common ancestor
that is not shared by any other group. The
members of a sister group each other's closest
relatives.
Frogs Lizards Chimps
If you rotate the
branches of the tree
at left around the
three blue points, the
result is the tree at
right.
Frogs Lizards Chimps Humans
Frogs
Humans
Chimps
Humans
Lizards
Fishes
5. Redraw the tree above, rotating
around the green branch point.
Identify the two closest relatives o
s of
humans as shown in each of the
three trees. Explain your answer.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Examine the image of the relatedness of vertebrates represented in this phylogenetic tree. Which statements are correctly inferred from this tree? Select all that apply. A) The mammals are the outgroup in this tree. B) Birds and dinosaurs share a recent common ancestor. C) Mammals and birds are more closely related than any other species. D) Turtles are equally as diverged from lizards and snakes as they are from crocodiles. E) Lizards and snakes are more recently diverged from each other than they are from crocodiles.arrow_forwardFor the first phylogenetic tree, if we assume absolute time is NOT represented, can we say that the species in circle B are more closely related than the species in Circle A? For the second phylogenetic tree (if we hold the same assumptions), can we say that B and C are more closely related than A and C?arrow_forwardSketch the generated phylogenetic tree below and color the branches of the generated phylogenetic tree according the the island: 1) Anolis sheplani 2) Anolis cybotes 3) Anolis olssoni 4) Anolis celestinus 5) Anolis occultus 6) Anolis cristatellus 7) Anolis puchellus 8) Anolis evermanni Hispaniola Species - Blue Puerto Rico Species - Red 1) What can you conclude about the relatedness of anole lizards living on these two islands?arrow_forward
- Which of the following is true regarding vestigial traits? A) They represent transitional character states for example between the presence or absence of a feature. B) They help to support proposed phylogenetic placement. C) They are likely present because there is no fitness cost to their retention or because they are in the process of being removed due to light selective pressure. D) All of the above. E) None of the above.arrow_forwardSequence data from OTUs are provided in the table below with values provided as (percentage distance x 1000) measurements. Determine the phylogenetic tree from the data in the table below using the UPGMA procedure mentioned in class. Berenstain Bear Berentstain Bear Care Bear Gummi Bear Paddington Bear Care Bear 160 Gummi Bear 150 40 Paddington Bear 80 130 120 Place each OTU in the correct box on the appropriate tree below. Do not label the incorrect tree. Care Bear Gummi Bear Berenstain Bear Paddington Beararrow_forwardTo test evolutionary hypotheses, you make a phylogeny of a group of organisms based on six traits: A B 1 2 E 5 2 1= singing 2= nest-building 3 = short legs 4 = hollow snout 5= crest J L M 6 = tree dwelling a) Based on your phylogeny, did hollow snouts evolve to allow singing? Explain your answer. b) Your friend wants to put all of the species that have hollow snouts into a single taxonomic group. Is this a good taxonomic group? Explain your answer. 4.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education