
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
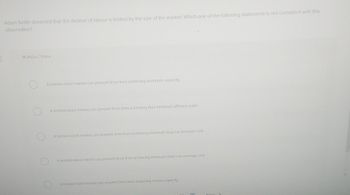
Transcribed Image Text:Adam Smith observed that the division of labour is limited by the size of the market. Which one of the following statements is not consistent with this
observation?
Multiple Choice
A limited-sized market can prevent firms from achieving economic capacity
A limited-sized market can prevent firms from achieving their minimum efficient scale.
A limited-sized market can prevent firms from achieving minimum long-run average cost
A limited-sized market can prevent firms from achieving minimum short-run average cost
A limited-sized market can prevent firms from achieving excess capacity
FER
Next >
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Solve Part C on paperarrow_forwardA competitive firm's production function is given by y = f(K, L) = 8K 1/2 + L 1/4 Assume that the price of the good produced is p = $100, the price of capital is r = $4, and the price of labor is w = $5. Find the profit- maximizing levels of capital and labor (K * and L * ). Find the profit-maximizing level of output (y * ). What is the maximum profit of the firm (π * )?arrow_forwardIf a firm chooses to produce output in the short run, how much output will it produce. Explain why the firm will choose that quantity. Which quantity of output is best for the overall society? Explain why that quantity is so good for society. Will the ideal quantity of output for the firm be the same quantity as the ideal quantity for society? Explain.arrow_forward
- In what way does an economist's measurement of profit differ from an accountant's? Accountants calculate total revenue differently. Accountants do NOT always include all of the opportunity costs when calculating total production costs. Economists calculate higher profits for firms as economic profit generally exceeds accounting profit. Economists do NOT always include all of the opportunity costs when calculating total production costs.arrow_forwardThe table below shows the weekly marginal cost (MC) and average total cost (ATC) for Buddies, a purely competitive firm that produces novelty ear buds. Assume the market for novelty ear buds is a competitive market and that the price of ear buds is $6.00 per pair. Buddies Production Costs Quantity MC ATC of Ear Buds ($) ($) 20 1.00 25 2.00 1.20 30 2.46 1.41 35 3.51 1.71 40 4.11 2.01 45 5.43 2.39 50 5.99 2.75 55 8.47 3.27 Instructions: In part a, enter your answer as the closest given whole number. In parts b-d, round your answers to two decimal places. a. If Buddies wants to maximize profits, how many pairs of ear buds should it produce each week? pairs b. At the profit-maximizing quantity, what is the total cost of producing ear buds? 2$ c. If the market price for ear buds is $6 per pair, and Buddies produces the profit-maximizing quantity of ear buds, what will Buddies profit or loss be per week? 2$arrow_forwardWhich of the following products/markets is most consistent with the perfect competition model? Apple iPhones a bustling farmers' market Kellogg's Frosted Flakes electric utilities automobiles 2 Adam Smith’s “invisible hand” refers to The mechanism that moves market price and quantity to equilibrium The natural tendency of markets to avoid monopolies and ensure competition The market’s incentive to lower price in order to increase quantity sold The lack of government role in the free market due to the market’s ability to self-regulate The tendency of firm’s to seek to merge in order to realize synergies and market dominance 3 A company facing inelastic demand for a product sees an increase in its costs after a worker strike forces a wage increase. What is likely to happen to the price and quantity sold of that product? Price will fall slightly while…arrow_forward
- Vincent Pearson makes dining tables, and he is trying to decide how many tables to produce. He can sell each dining table for $3,000. The cost of the first table is $1,000, for the second it's $1,500. For each additional table he produces, the marginal cost of each table increases by $500. How many dining tables should Vincent produce, and what is the total cost of his production? He will produce five tables at a cost of $10,000. He will produce four tables at a cost of $12,000. He will produce six tables at a cost of $13,500. He will produce seven tables at a cost of $17,500.arrow_forwardFor an economist, a technology is: A method of combining resources to make goods and services. 8 8 8 A computer. A capital-intensive method of production. Any production technique that is patented.arrow_forwardEvaluate and explain the following statement: The market system is a profit-and-loss system.arrow_forward
- Can labor specialization be a source of economies of scale (size) within a production plant? Why or why not? Can labor specialization be a source of diseconomies of scale (size)?arrow_forwardEconomists have a different way of talking about costs than accountants. According to economists, which of the following statements are true? In the long run, economies of scale are always present Monopoly is a very good market structure for consumers In the long run, a firm can change any sort of cost it faces O Monopsony is a very good market structure for sellersarrow_forwardYour average total cost is $30; the price you receive for the good is $15. Should you keep on producing the good? Why? You should produce in the long run as long as you are only earning small economic losses. It is always possible to make up a small loss. Maybe. It depends on whether you are covering average variable costs in the long run. You should not produce in the long run because you are earning an economic loss. All inputs are variable in the long run so you can go out of business. You should continue producing in the long run because you are earning an economic profit.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education