
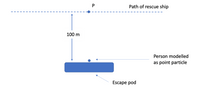
A 70 kg space voyager is stranded on a 700 kg escape pod that has left the main spacecraft and is floating in free space (you may assume its velocity is 0 m/s). A rescue ship is approaching and will pass within 100 m of the escape pod. The space voyager plans to push herself away from the escape pod towards the point by which the rescue ship will pass (point P in the diagram). The space voyager knows that she can apply a constant force of 100 N while she pushes for the 0.50 s it takes her to straighten her arms.
(a) What will her velocity be after she has finished pushing against the rescue pod?
(b) How long before the rescue ship is due to arrive a point P should the space voyager begin her push?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 10 images

- In the figure below, a box of Cheerios (mass mc = 1.5 kg) and a box of Wheaties (mass mw = 2.7 kg) are accelerated across a horizontal surface by a horizontal force F applied to the Cheerios box. The magnitude of the frictional force on the Cheerios box is 2.0 N, and the magnitude of the frictional force on the Wheaties box is 4.1 N. If the magnitude of F is 12 N, what is the magnitude of the force on the Wheaties box from the Cheerios box? |---Select--- mc Mwarrow_forwardA bowl of apples is resting on a table. The bowl is not moving (it is not accelerating) even though the Earth is pulling down on the bowl. This gravitational force on the bowl is half of a pair of forces that are related by Newton's Third Law. We call a pair of forces like this a third law pair. Which, if any, of the following choices is the other half of that third law pair? O The force the bowl exerts on the table. O The force the table exerts on the bowl. O The force the apples exert on the bowl. O The force the bowl exerts on the apples. O None of the above is the other half of the pair.arrow_forwardA 1090 kg boat is traveling at 92 km/h when its engine is shut off. The magnitude of the frictional force ?→?f→k between boat and water is proportional to the speed v of the boat: fk = 85v, where v is in meters per second and fk is in newtons. Find the time required for the boat to slow to 46 km/h.arrow_forward
- A mysterious force acts on all particles along a particular line and always points towards a particular point P on the line. The magnitude of the force on a particle increases as the cube of the distance from that point, that is, F∝ r3, if the distance from the P to the position of the particle is r. It has been determined that the constant of proportionality is 0.23 N/m3, i.e. the magnitude of the force on a particle can be written as 0.23r3, when the particle is at a distance r from the force center. Find the magnitude of the potential energy, in joules, of a particle subjected to this force when the particle is at a distance 0.21 m from point P assuming the potential energy to be zero when the particle is at P. PE= ?arrow_forwardA block with a mass of m = 16 kg rests on a frictionless surface and is subject to two forces acting on it. The first force is directed in the negative x-direction with a magnitude of F1 = 8.5 N. The second has a magnitude of F2 = 19.5 N and acts on the body at an angle θ = 11° measured from horizontal, as shown. a.) Write an expression for the component of net force, Fnet,x, in the x-direction, in terms of the variables given in the problem statement. b.) Write an expression for the magnitude of the normal force, FN, acting on the block, in terms of F2 and the other variables of the problem. Assume that the surface it rests on is rigid. c.) Find the block's acceleration in the x-direction, ax, in meters per second squared.arrow_forwardDetermine the force Q-> when the block moves with constant velocity. Express your answer in vector form.arrow_forward
- The high-speed winds around a tornado can drive projectiles into trees, building walls, and even metal traffic signs. In a laboratory simulation, a standard wood toothpick was shot by pneumatic gun into an oak branch. The toothpick mass was 0.14 g, its speed before entering the branch was 221 m/s, and its penetration depth was 17 mm. If its speed was decreased at a uniform rate, what was the magnitude of the force of the branch on the toothpick?arrow_forwardA particle of mass m moving along the x-axis experiences the net force Fx=ct, where c is a constant. The particle has velocity v0x at t = 0. Find an algebraic expression for the particle's velocity vx at a later time t. Express your answer in terms of the variables c, t, v0x, and m.arrow_forwardUnder the influence of its drive force, a snowmobile is moving at a constant velocity along a horizontal patch of snow. When the drive force is shut off, the snowmobile coasts to a halt. The snowmobile and its rider have a mass of 139 kg. Under the influence of a drive force of 180 N, it is moving at a constant velocity whose magnitude is 5.43 m/s. The drive force is then shut off. Find (a) the distance in which the snowmobile coasts to a halt and (b) the time required to do so. (a) S = (b) t = i iarrow_forward
- On a horízontal air track, a glider of mass m carries a l-shaped post. The post supports a small dense sphere, also of mass m, hanging just above the top of the glider on a cord of length L. The glider and sphere are initially at rest with the cord vertical. (Figure a below shows a cart and a sphere similarly connected.) A constant horizontal force of magnitude F is applied to the glider, moving it through displacement x;; then the force is removed. During the time interval when the force is applied, the sphere moves through a displacement with horizontai component x2. (a) Find the horizontal component of the velocity of the center of mass of the glider-sphere system when the force is removed. (Use the following as necessary: F, x1, x2, and m.) F(x, +x2) VCM 2m (b) After the force is removed, the glider continues to move on the track and the sphere swings back and forth, both without friction. Find an expression for the largest angle the cord makes with the vertical. (Use any variable…arrow_forward(Figure 1) shows a F = 6.4 N force pushing two gliders along an air track. The 170 g spring between the gliders is compressed. Assume the force Facts and the whole system moves in the same direction. The spring does not sag. Figure F A 400 g m B 600 g 1 of 1 Part A How much force does the spring exert on glider A? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. F = Submit Part B F = O Submit Value Request Answer How much force does the spring exert on glider B? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. μA Value Units Request Answer ? Units ?arrow_forwardUnder the influence of its drive force, a snowmobile is moving at a constant velocity along a horizontal patch of snow. When the drive force is shut off, the snowmobile coasts to a halt. The snowmobile and its rider have a mass of 143 kg. Under the influence of a drive force of 220 N, it is moving at a constant velocity whose magnitude is 4.38 m/s. The drive force is then shut off. Find (a) the distance in which the snowmobile coasts to a halt and (b) the time required to do so. (a) s= (b) t = i i + +arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





