
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
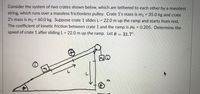
Transcribed Image Text:**Problem Statement:**
Consider the system of two crates shown below, which are tethered to each other by a massless string, which runs over a massless frictionless pulley. Crate 1’s mass is \( m_1 = 35.0 \, \text{kg} \) and crate 2’s mass is \( m_2 = 60.0 \, \text{kg} \). Suppose crate 1 slides \( L = 22.0 \, \text{m} \) up the ramp and starts from rest. The coefficient of kinetic friction between crate 1 and the ramp is \( \mu_k = 0.205 \). Determine the speed of crate 1 after sliding \( L = 22.0 \, \text{m} \) up the ramp. Let \( \theta = 31.7^\circ \).
**Diagram Description:**
- The diagram depicts a ramp inclined at an angle \( \theta = 31.7^\circ \).
- Crate 1 with mass \( m_1 \) is on the inclined ramp.
- Crate 2 with mass \( m_2 \) hangs vertically off the edge of the ramp, attached to crate 1 via a pulley system.
- The ramp shows the direction of motion for crate 1 with an arrow pointing upwards along the ramp.
- The distance \( L = 22.0 \, \text{m} \) is marked along the ramp, indicating the length crate 1 travels.
- A pulley is illustrated at the top of the ramp, connected to both crates.
**Objective:**
Calculate the speed of crate 1 after it has slid 22.0 meters up the ramp, taking into account the effects of kinetic friction and gravity.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 24 kg box is tied to a 14 kg box with a horizontal rope. The coefficient of friction between the box and the floor is 0.32. You pull the larger box forward with a force of 1.8 x 102 N at an angle of 250 above horizontal. a. Calculate the acceleration of the boxes. b. Calculate the tension in the rope?arrow_forwardThe system shown below is on verge of starting to move up the incline. Each block weight 55 N and an incline angle is 36 °. The friction force acting on the block M is: O 105 N O 110. N O 122 N O 116 N O 119 Narrow_forwardesc Download DRA.jpeg Two objects are positioned and moving as shown. m₁ = 7.4 kg, m₂ = 8.4 kg, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between object 1 and the tabletop is μ = 0.13. Find the acceleration of object 2 (assuming up is the positive direction) as well as the tension in the string. motion m₁ 7 m₂ 13. Acceleration of Object 2 A. 3.021_m/s² D. B. 3.274 m/s² E. C. 4.613_m/s² F. 1--1 14. Tension in String A. 48.18 N D. B. 32.89 N E. C. 56.79 N F. 1--1 MacBook Pro & Pigshow.jpeg C $ A Pig show.jpeg G Search or type URL % 3.518 m/s² 8.692 m/s² 8.998 m/s² 43.57 N 76.22_N 68.75 N * + ( ( Sign in Showarrow_forward
- In (Figure 1), the man has a mass of 90 kg and the crate has a mass of 160 kg. The coefficient of static friction between his shoes and the ground is μ = 0.4 and between the crate and the ground is μ = 0.3. Figure t Part A Determine if the man is able to move the crate using the rope-and-pulley system shown. The man can move the crate. The man cannot move the crate. Submit ✓ Correct Part B F, Fmax = Previous Answers Prove your answer to part A by calculating the static frictional force F between the man's shoes and the ground required to move the crate and the maximum static frictional force Fmax which can be developed. Express your answers in newtons to three significant figures separated by a com_ma. 15| ΑΣΦ41 Submit Provide Feedback Request Answer vec Review N Next >arrow_forwardA block with mass m1 = 7.5 kg rests on the surface of a horizontal table which has a coefficient of static friction of μs = 0.63. This block is connected by a pulley system to another block which hangs vertically. The hanging block has mass m2. a. What is the minimum mass, m2,min, in kilograms, that will cause the system to move? b. A second block with mass of 10 kg is placed on top of the first block. What is the new hanging mass, m2,min', in kilograms, that will cause the system to move? c. The table is inclined at an angle, θ, relative to the horizontal in such a way that the pulley is at the highest point and the 10 kg is removed from m1. Write an equation for the magnitude of the normal force, FN, of the block. d. Write an equation for the tension, T, in terms of mass m1 just before the block begins to slide. Note that the angle θ is not so large that the block would slide down the table under its own weight (i.e. if the tension acting on mass m1 were removed, the block would…arrow_forwardTwo blocks with masses m1 = 15.0 kg and m2= 10.0 kg are connected by a massless string across a massless, frictionless pulley as shown in the figure below. Block 1 sits on a frictionless plane inclined at an angle θ = 30.0° above the horizontal. When both blocks are released, block 1 begins sliding up the plane as block 2 falls. What is the acceleration of both blocks after they have been released?arrow_forward
- Asap plzzzarrow_forwardA disk between vertebrae in the spine is subjected to a shearing force of 625 N. Find its shear deformation, taking it to have a shear modulus of 1.30 x 10° N/m². The disk is equivalent to a solid cylinder 0.550 cm high and 2.50 cm in diameter. Question Credit: OpenStax College Physics shear deformation: marrow_forwardmust be used? Ans: 39 N Question 12. A skier is pulled up a slope at a constant velocity by a tow bar. The slope is inclined at 24.2° with respect to the horizontal. The force applied to the skier by the tow bar is parallel to the slope. The skier's mass is 56.7 kg, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the skis and the snow is 0.140. Find the magnitude of the force that the tow bar exerts on the skier. Ans: 299 N What is thearrow_forward
- Two blocks are supported by a pulley along an incline as shown. The lower block B has a weight of 30 lbs and the higher block A has a weight of 20 lbs. Assume that there is friction between the blocks with Hs = 0.15 and assume no friction between block Band the incline. Determine the angle z for which motion is impending. 201b 301b A Tension in block A as a function of z can be written as TA %3D Tension in block B as a function of z can be written as Tây Thus, impending motion is at z = degrees.arrow_forwardProblem 2. Consider the system shown in Figure 1 with m,= 12.5 kg, m, = 20.0 kg. Object m, is resting on the floor, and object m, is 4.00 m above the floor when it is released from rest. The pulley axis is frictionless. The cord is light does not stretch, and does not slip on the pulley a. What is the magnitude %3D %3D the acceleration of the object. b. Calculate the time interval required for m, to hit the floorarrow_forwardA box with mass 13.0 kg moves on a ramp that is inclined at an angle of 55.0∘ above the horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the ramp surface is μk = 0.300. a. Calculate the magnitude of the acceleration of the box if you push on the box with a constant force 150.0 N that is parallel to the ramp surface and directed down the ramp, moving the box down the ramp. b. Calculate the magnitude of the acceleration of the box if you push on the box with a constant force 150.0 N that is parallel to the ramp surface and directed up the ramp, moving the box up the ramp.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON