
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
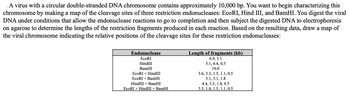
Transcribed Image Text:A virus with a circular double-stranded DNA chromosome contains approximately 10,000 bp. You want to begin characterizing this
chromosome by making a map of the cleavage sites of three restriction endonucleases: EcoRI, Hind III, and BamHI. You digest the viral
DNA under conditions that allow the endonuclease reactions to go to completion and then subject the digested DNA to electrophoresis
on agarose to determine the lengths of the restriction fragments produced in each reaction. Based on the resulting data, draw a map of
the viral chromosome indicating the relative positions of the cleavage sites for these restriction endonucleases:
Endonuclease
EcoRI
HindIII
BamHI
EcoRI + HindIII
EcoRI + BamHI
HindIII+ BamHI
EcoRI + HindIII + BamHI
Length of fragments (kb)
6.9, 3.1
5.1, 4.4, 0.5
10.0
3.6, 3.3, 1.5, 1.1, 0.5
5.1, 3.1, 1.8
4.4, 3.3, 1.8, 0.5
3.3, 1.8, 1.5, 1.1, 0.5
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For a restriction enzyme that recognizes the restriction site GGCC, Which of the following statements is/are true?arrow_forwardDescribe the process for shotgun sequencing of a genome. Practice aligning the two sets of sequenced fragments below, to determine the order of the fragments and the complete sequence.arrow_forwardb. After molecular cloning and confirming you properly cloned stripes into the vector shown, you transform bacteria with the plasmid and select out bacteria that contain the plasmid. Now, you want to these transformed bacteria to express the STRIPES. Under what conditions would we need to grow bacteria transformed with this plasmid so that they express STRIPES? Explain your answer, and be sure to describe the important regulatory regions on the plasmid above and what interacts with these regulatory regions in the conditions you have indicated.arrow_forward
- A 2.0kb bacterial plasmid ‘BS1030’ is digested with the restriction endonuclease Sau3A; the plasmid map is depicted in the diagram below and the Sau3A (S) restriction sites are indicated. Which of the following DNA fragments do you expect to see on an agarose gel when you run Sau3A-digested plasmid ‘BS1030’ DNA? a. 250 bp, 450 bp, 550 bp, 1.1 kb, 1.5 kb and 2.0 kb b. 2.0kb c. 250 bp, 400 bp, 450 bp, 500 bp and 550 bp d. 100 bp, 200 bp, 250 bp, 400 bp, 500 bp and 550 bparrow_forwardAssume that a plasmid is 4700 base pairs in length and has restriction sites for a given restriction enzyme at the following locations: 800, 1400, 2900, and 3600. List the fragments by size that are ! expected when the plasmid is fully digested the restriction enzyme.arrow_forwardWhy would you NOT expect a restriction endonuclease to exist that would recognize the site AAGGAA?arrow_forward
- Below is shown a plasmid map from a recombinant DNA experiment you have performed. You inserted your gene of interest (labeled gene on the map) into the lac Z reporter gene via a Hind III site. If you digested this recombinant DNA with HindIII what is the size of the DNA fragment(s) you would obtain on a DNA gel electrophoresis? The plasmid alone is 4000 bp. I have attached the image below.arrow_forwardRestriction endonucleases are bacterial enzymes that cleave duplex (double-stranded) DNA at specific nucleotide sequences. The mode of replication of the animal virus SV40 has been investigated by using restriction endonucleases that cleave SV40 DNA into a number of unique segments. Like most viruses, SV40 DNA is circular. The map positions of the 11 fragments produced by a pair of restriction endonucleases are shown on the next page. Immediately following a 5 or 10 minute pulse of radioactively labeled thymidine, labeled SV40 molecules that have completed replication during the pulse are isolated. These newly replicated DNA molecules are digested by the restriction endonucleases and the resulting fragments are analyzed for the relative amounts of pulse label they contain. The results are in the table below. Assume that at the time the label was added there was a random population of replicating SV40 DNA molecules in all possible stages of synthesis. From the information given below,…arrow_forwardNucleosomes can be assembled onto defined DNA segments. When a particular 225-bp segment of human DNA was used to assemble nucleosomes and then incubated with micrococcal nuclease, which digests DNA that is not located within the nucleosome, uniform fragments 147 bp in length were generated. Subsequent digestion of these fragments with a restriction enzyme that cuts once within the original 225-bp sequence produced two well-defined bands at 37 bp and 110 bp. Why do you suppose two well-defined fragments were generated by restriction digestion, rather than a range of fragments of different sizes? How would you interpret this result?arrow_forward
- Consider the ends of the DNA fragments shown below. They have been produced by digestion of a single sequence of DNA using a number of restriction endonucleases. 1. 5'A 3' 3'TTCGA5' 2. 5'G 3' 3'CAGCT5' 3. 5'AATTC3' 3' G5 4. 5'TCGAC3' 3' G5' 5. 5'GGG 3' 3'CCC 5' Which of these ends are capable of annealing and being joined by DNA ligase?arrow_forwardMany of the gene products involved in DNA synthesis wereinitially defined by studying mutant E. coli strains that could notsynthesize DNA. Question: The dnaE gene encodes the a subunit of DNA polymeraseIII. What effect is expected from a mutation in this gene?How could the mutant strain be maintained?arrow_forwardNow that you’ve isolated the gene and made lots of copies, you need to insert the gene into something you can manipulate and move into your lab strain of E. coli. You have access to the following vectors, either pBR322 or pUC19 (look them up here to see a map https://www.neb.com/products/dna-plasmids-and-substrates Please note the restriction sites in BOLD appear only once in the plasmid). You may use either vector. What is a vector? Which vector did you choose? Explain why you made that choice. What enzyme(s) will you use to place your fragment into the vector? Explain why you chose these enzymes. How will you move this construct into coli? What phenotype will tell you if the coli have taken up the plasmid? What phenotype will tell you if the coli have taken up the plasmid with the gasP gene?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education