
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
a) Using the following graph state the
b) State the conditions that establish the market structure monopoly, and the conditions needed for
(image attached)
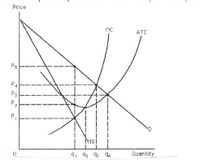
Transcribed Image Text:Price
MC
ATC
P5
P4
P3
P2
P,
MRİ
2 4 14
Quantity
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 7arrow_forwardQUESTION 2 Consider the following graph: Price P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 Q5 Q302 01 04 Curve D Curve A Market efficient quantity Market efficient price Curve C Curve A = MR, Curve B = Demand, Curve C = ATC, Curve D = MC Match the correct values to the descriptions: ▾ Monopoly profit maximizing quantity Curve B Monopoly profit maximizing price Quantity A. P1 B. P2 C. P3 D. P4 E. P5 F. Q1 G. Q2 H. Q3 I. Q4 J. Q5arrow_forwardssume there is no price discrimination: Matthew, Rachel, Janice, and Mandy own the only ice company in town (they have a monopoly on the ice market). Matthew wants to sell as much ice as possible without losing money. Rachel wants the ice company to bring in as much revenue as possible. Janice wants to maximize total surplus and Many wants to make the largest possible profit. Use ONE clearly-labelled graph of the ice company’s marginal revenue, demand, and cost curves to show the price and quantity (i.e., ice) each person desires. Provide explanation.arrow_forward
- Which of the following situations would likely result in the formation of a natural monopoly? Question 21Select one or more: a. There is very low demand for the product, i.e., there’s a small market b. Firms have large fixed costs and a constant marginal cost of production c. Due to return to scale, one large firm can produce at a lower cost than many small firms d. The government issues liquor licenses, which are required for businesses to sell alcohol e. Doctors can only practice medicine if they are accredited by the American Medical Association f. The government issues a patent for a new inventionarrow_forwardExplain how a monopoly arises and distinguish between a single-price monopoly and a price-discriminating monopoly.arrow_forwardv THE VIRTUAL MONOPOLY OF EPIPENS BY THE APLIA ECONOMICS CONTENT TEAM In 2007, as part of a $6.7 billion deal with Merck & Co., Inc., one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world, Mylan N.V., an American generic and specialty pharmaceuticals company, acquired the EpiPen, an epinephrine injection device used to treat the potentially fatal allergic reaction known as anaphylaxis. At the time, EpiPen was not a household brand that everyone knew, but efforts by Mylan's CEO Heather Bresch changed the landscape for this device. According to Jen Wieczner, in an article in Fortune: "She poured marketing resources into the product, and embarked on an awareness and political campaign to get more EpiPens into schools and other public institutions. Today, 47 states have laws about making epinephrine auto-injectors available at school in case of an anaphylaxis incident, largely as a result of Bresch's efforts" (Jen Wieczner, "Mylan CEO Blamed Obama Care for EpiPen Sticker Shock,"…arrow_forward
- 1. Calculate the profit-maximizing quantity and price for the non-student market. (attached Figure A: Non-Students) 2. Calculate the profit-maximizing quantity and price for the student market. (attached Figure B: Students) 3. Calculate the profit if the firm charges both the non-students and students the same price of $20. (attached Figure A: Non-Students and Figure B: Students) 4. Calculate the profit if the monopoly firm perfectly price discriminates. (attached Figure A: Non-Students and Figure B: Students)arrow_forwardTo answer this question, you will want to work out the answer using a graph on a piece of scratch paper (not turned in). You are going to compare the outcomes in the case where there is perfect competition to the monopoly case. So, as an intermediate step, you will need to compute the equilibrium outcomes under competition and monopoly. Suppose that you have the following information about the demand for oil. Price ($/barrel) 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 Suppose that the marginal cost to produce a barrel of oil is $20. What is the deadweight loss if the oil market is a monopoly? Quantity demanded(# barrels) 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12arrow_forwardThe accompanying graph depicts a hypothetical monopoly. Follow instuctions 1−3 below to identify the monopoly's profits. Place point E at the monopoly's profit maximizing price and quantity. Move the average total cost (ATC) curve to a position that depicts the monopoly earning a positive profit. Place the area labeled Profit in the area of the graph that represents the monopoly's profit.arrow_forward
- What is the difference between a monopoly's marginal revenue curve and a perfect competitor's marginal revenue curve? Please explain the difference in these markets by drawing the graphs.arrow_forwardQuestion 3arrow_forwardb) The Fundamental cause of monopoly is barriers to entry. Discuss the main causes of Monopoly.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education