
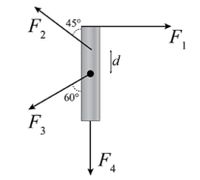
A uniform thin rod of mass m = 3.2 kg and length L = 1.7 m can rotate about an axle through its center. Four forces are acting on it as shown in the figure. Their magnitudes are F1 = 3.5 N, F2 = 4.5 N, F3 = 15 N and F4 = 17 N. F2 acts a distance d = 0.21 m from the center of mass.
Calculate the magnitude τ1 of the torque due to force F1, in newton meters.
τ1 =
Calculate the magnitude τ2 of the torque due to force F2 in newton meters.
τ2 =
Calculate the magnitude τ3 of the torque due to force F3 in newton meters.
τ3 =
Calculate the magnitude τ4 of the torque due to force F4 in newton meters.
τ4 =
Calculate the
α =
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

- Two wheels A and B in the figure are connected by a belt that does not slip. The radius of B is 6.03 times the radius of A. What would be the ratio of the rotational inertias IA/IB if the two wheels had (a) the same angular momentum and (b) the same rotational kinetic energy?arrow_forwardA carousel has a radius of 1.65 m and a moment of inertia of 118 kg· m2. A girl of mass 49.0 kg is standing at the edge of the carousel, which is rotating with an angular speed of 3.40 rad/s. Now the girl walks toward the center of the carousel and stops at a certain distance from the center d. The angular speed of the carousel is now 5.4 rad/s. How far from the center, in meters, did the girl stop?arrow_forwardThe distance from the fisherman's hand to the tip of the rod is L = 1.94 m. A fish is on the line, and it pulls the line with a force of F = 110 N at an angle 37.0° below the horizontal. What is the magnitude of the torque (in N · m) exerted by the fish about an axis perpendicular to the page and passing through the fisherman's handarrow_forward
- Each propeller on a King Air twin-engine airplane consists of three blades, each of mass 21 kg and length 121 cm. The blades may be treated approximately as uniform, thin rods. What is the rotational inertia of the propeller, and if the propeller is driven by an engine that develops a torque of 2650 N⋅m, how long will it take to change the propeller's angular speed from 1250 rpm to 1850 rpm?arrow_forwardA force of F (2.00i+3.00j) N is applied to a rigid object that is pivoted about a fixed axis aligned along the z coordinate axis. The force is applied at a point located at r(4.00i+5.00j) m relative to the axis. Find the torque T applied to the object.arrow_forwardA torque of 35.6 N · m is applied to an initially motionless wheel which rotates around a fixed axis. This torque is the result of a directed force combined with a friction force. As a result of the applied torque the angular speed of the wheel increases from 0 to 9.9 rad/s. After 5.80 s the directed force is removed, and the wheel comes to rest 59.8 s later.arrow_forward
- The figure below shows a fisherman with a fishing pole that makes an angle of 20.0° above the horizontal. The distance from the fisherman's hand to the tip of the pole is L = 1.89 m. A fish is on the line, and it pulls the line with a force of F = 119 N at an angle 37.0° below the horizontal. What is the magnitude of the torque (in N · m) exerted by the fish about an axis perpendicular to the page and passing through the fisherman's hand?arrow_forwardA 4kg ball with a 0.45-meter radius is initially at rest begins to roll and accelerate at a uniform rate to a velocity of 10 rad/s in 5 seconds. The rotational inertia of the ball is 0.243 kg*m^2. Calculate the magnitude of the torque on the ball. Answer must use the correct SI units.arrow_forwardYou stand on a frictional platform that is rotating at 1.6 rev/s. Your arms are outstretched, and you hold a heavy weight in each hand. The moment of inertia of you, the extended weights, and the platform is 7.9 kg · m2. When you pull the weights in toward your body, the moment of inertia decreases to 3.7 kg · m2. (a) What is the resulting angular speed of the platform?(b) What is the change in kinetic energy of the system?(c) Where did this increase in energy come from? (Select all that apply.) -your internal energy -gravity -kinetic energy of the platform -mass of the weights -air resistancearrow_forward
- A picture frame is hanging out from a wall as shown. You choose the origin to be where the picture frame touches the wall and counter-clockwise to be the positive torque direction. If the tension in the string between the wall and the picture frame is Twp = 67.3 N, theta = 121.6 degrees, h = 0.47 m, and phi = 14.8 degrees, what is the torque about the origin due to the tension in the string on the picture frame?arrow_forwardA man ties one end of a strong rope 9.18 m long to the bumper of his truck, 0.561 m from the ground, and the other end to a vertical tree trunk at a height of 3.30 m. He uses the truck to create a tension of 8.17 102 N in the rope. Compute the magnitude of the torque on the tree due to the tension in the rope, with the base of the tree acting as the reference point. N · marrow_forwardTwo blocks are connected by massless string that is wrapped around a pulley. Block 1 has a mass m1=6.00 kg, block 2 has a mass m2=2.00 kg, while the pulley has a mass of 1.00 kg and a radius of 18.0 cm. When the pulley turns, there is friction in the axel that exerts a torque of magnitude 0.410 N m. If block 1 is released from rest at a height h=1.40 m, how long does it take to drop to the floor?arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





