
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
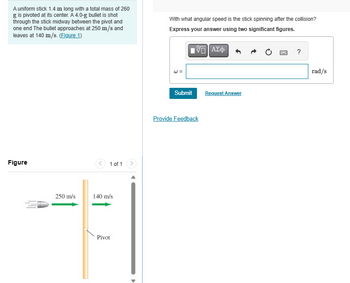
Transcribed Image Text:A uniform stick 1.4 m long with a total mass of 260
g is pivoted at its center. A 4.0-g bullet is shot
through the stick midway between the pivot and
one end The bullet approaches at 250 m/s and
leaves at 140 m/s. (Figure 1)
With what angular speed is the stick spinning after the collision?
Express your answer using two significant figures.
Figure
250 m/s
1 of 1
140 m/s
Pivot
ΜΕ ΑΣΦ
Submit
Request Answer
Provide Feedback
?
rad/s
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two small 0.55-kg masses are attached to opposite ends of a very lightweight rigid rod 0.7 m long. The system is spinning in a horizontal plane around a vertical axis perpendicular to the rod located halfway between the masses. Each mass is moving in a circle of radius 0.35 m at a speed of 0.85 m/s. What is the total angular momentum of this system? kg-m²/s Need Help? Read Itarrow_forwardA 0.02 kg mass red object (bead) is moving at a speed of 10.0 m/s when it sticks to the edge of a uniform solid cylinder. The cylinder is free to rotate about its axis through its center and has a mass of 0.5 kg , a radius of 0.25 m and is initially at rest. I = 1/2MR2^2 a) What is the angular velocity of the system after the collision? b) How much kinetic energy is lost in the collision? c) If the angular position of the Cylinder varies as θ(t)=3.2t-t^2 find the centripetal acceleration of the red object (bead). d) A cord is now wrapped around the cylinder. Use the work energy theorem to find the angular velocity of the cylinder after 5.0m of cord have been removed by a 40N Force. e) If the 40N force on the cord is replaced by a 40-N weight, what is the angular velocity of the cylinder after 5.0m of cord has unwound?arrow_forwardA sanding disk with a rotational inertia of 1.2 x 10-3kgm2 is attached to an electric drill whose motor delivers a torque of 16 Nm. If the torque is applied for 25 ms and the disk starts from rest, what is the magnitude of the angular velocity of the sanding disk? Use the rotational version of the Impulse Momentum Theorem. Take note of the time units.arrow_forward
- Each of the following objects has a radius of 0.168 m and a mass of 2.67 kg, and each rotates about an axis through its center (as in this table) with an angular speed of 40.1 rad/s. Find the magnitude of the angular momentum of each object. a hoop a solid cylinder a solid sphere a hollow spherical shellarrow_forwardA student holds a spinning bicycle wheel while sitting motionless on a stool that is free to rotate about a vertical axis through its center (see the figure below). The wheel spins with an angular speed of 18.6 rad/s and its initial angular momentum is directed up. The wheel's moment of inertia is 0.130 kg. m² and the moment of inertia for the student plus stool is 3.50 kg. m². HINT Lwheel Ⓡ (a) Find the student's final angular speed (in rad/s) after he turns the wheel over so that it spins at the same speed but with its angular momentum directed down. rad/s (b) Will the student's final ang O up down Lwheel entum be directed up or down?arrow_forwardProblem #5: A merry-go-round has a radius of 3.0 m and a moment of inertia 400kg-m2. A boy of mass 40 kg runs tangent to the rim at a speed of 5.0 m/s and jumps on. If the merry-go-round is initially rotating at an. gular velocity of 8 rad/s; a. What is the angular momentum of the merry-go-round before the boy jumps on? b. What is the angular velocity after the boy jumps on? c. What is the final angular momentum of the merry-go-round after the boy jumps on? Attach Filearrow_forward
- A student sits on a freely rotating stool holding two dumbbells, each of mass 2.93 kg (see figure below). When his arms are extended horizontally (Figure a), the dumbbells are 1,09 m from the axis of rotation and the student rotates with an angular speed of 0.745 rad/s. The moment of inertia of the student plus stool is 2.64 kg m² and is assumed to be constant. The student puls the dumbbells inward horizontally to a position 0.307 m from the rotation axis (Figure b) 1 (a) Find the new anguler speed of the student. rad/s (b) Find the kinetic energy of the rotating system before and after he pulls the dumbbells inward. Koefore Kate"arrow_forwardWhat is the angular momentum L, of a 0.300-kg tetherball when it whirls around the central pole at 70.0 rpm and at a radius of 135 cm? L₂= x10 TOOLS kg-m²/sarrow_forwardA lawnmower blade has a length of 0.75 m and a mass of 1.5 kg. The blade rotates around its center at an angular velocity of 500 re. The end of the blade hits a 0.25 kg croquet ball (point mass), and the ball sticks to the blade. min Before the collision, the ball was stationary. After the collision, the ball will be moving at the same angular velocity as the blade at a distance of half of the blade length from the axis of rotation. Treat the blade as a rod rotating around its center. The final angular velocity of the lawnmower blade and croquet ball combo is rad Sarrow_forward
- I need help with this problem. Thanksarrow_forwardA 200-kg, 2.0-m-radius, merry-go-round in the shape of a flat, uniform, circular disk parallel to level ground is rotating at 1.2 cycles/second about an axis through its center of mass and perpendicular to the ground. A 50-kg boy jumps onto the edge of the merry-go round and lands at a fixed point. What is the angular velocity of the merry-go-round after the boy lands on it? Hint: = (1/2)mR2 where m is the mass of the disk and R is the radius of the disk.arrow_forwardPlease refer to the picture to help answer the questions. A ice skater goes into a spin standing vertically with his arms outstretched horizontally. We can crudely model his torso and legs as a cylinder with radius 0.1m and mass 52 kg and each arm is a rod with mass 4 kg and length 0.9 m. The skater will initially spin at 2.0 rad/s. Question 1: what is the moment of inertia of the skater's torso and legs. Please answer in kg m^2. Question 2: What is the moment of inertia of one of the skater's arms? Please answer in kg m^2. Question 3: What is the total moment of inertia of the skater? Please answer in kg m^2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON