
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A traffic light hangs from a structure as shown. The uniform aluminum pole AB is 7.5 m long and has a mass of 8.0 kg. The mass of the traffic light is 12.0 kg. Determine the tension in the horizontal, massless cable CD, and the vertical and horizontal components of the force exerted by the pivot A on the aluminum pole
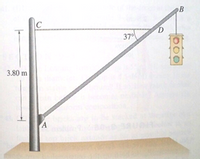
Transcribed Image Text:B
37
3.80 m
A
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- a. A 1200-N uniform boom of length 2.00 m is supported by a cable, as shown in the figure. The boom is pivoted at the bottom, and a 2000-N weight hands from its top. Find the tension in the cable and the components of the reaction force exerted on the boom by the floor. For the next two parts you can assume that the 2000-N weight is concentrated at the top end of the boom. b. Determine the total moment of inertia of the boom/weight system around the pivot point. c. The cable now breaks, and the boom pivots until the right end hits the floor. Determine the velocity of the right end at the instant before it hits the floor.arrow_forwardA 14.0 m uniform ladder weighing 510 N rests against a frictionless wall. The ladder makes a 59.0°-angle with the horizontal. A. Find the horizontal and vertical forces (in N) the ground exerts on the base of the ladder when an 810-N firefighter has climbed 4.10 m along the ladder from the bottom. B. If the ladder is just on the verge of slipping when the firefighter is 9.40 m from the bottom, what is the coefficient of static friction between ladder and ground? C. If oil is spilled on the ground, causing the coefficient of static friction to drop to half the value found in part (b), what is the maximum distance (in m) the firefighter can climb along the ladder from the bottom before the ladder slips?arrow_forwardA ladder of length 2L and mass M is positioned on level ground leaning against a wall such that the angle between the ladder and the horizontal is a. The coefficient of static friction between the ladder and the wall and between the ladder and the ground is jistatic = 0.66. The centre of mass ofthe ladder is halfway along it. Draw a diagram indicating all the forces acting on the ladder, and state what each force represents. Also show the direction of the a- and y-axes you will use.arrow_forward
- A 355 N uniform ladder of length L= 8.00 m leans against a smooth (frictionless) wal The ladder mnakes an angle of 50.0° angle with the horizontal ground and the force of static friction keeps the ladder from sliding to the left. An 875 N firefighter has climbed d = 6.30 m along the ladder trom the bottom. What is the force of static friction f, between the ladder and the ground? 50.0 O 119 N O 480 N O 727 N O 567 N command eptienarrow_forwardA 7-kg mass (m1) hangs from a cord that runs through a pulley and back down to attach to a 6-kg mass (m2) that is hanging from the other side. The pulley has a mass of 5.00-kg and a diameter of 20-cm. Find: A) the tension in the cord supporting m1 and the tension in the cord supporting m2; B) the tension in the cord supporting the pulley. C) Why is the answer to B) not equal to the sum of tensions in A)? Why is it not equal to the sum of the three weights?arrow_forwardA uniform 37.0 kg scaffold of length 6.2 m is supported by two light cables, as shown below. An 82.0 kg painter stands 1.0 m from the left end of the scaffold, and his painting equipment is 1.6 mfrom the right end. If the tension in the left cable is twice that in the right cable, find the tensions in the cables (in N) and the mass of the equipment (in kg). (Due to the nature of this problem, do not use rounded intermediate values in your calculations).arrow_forward
- A uniform drawbridge must be held at a 38o angle above the horizontal to allow ships to pass underneath. The drawbridge weights 55000 N and is 15.0 m long. A cable is connected 3.5 m from the hinge where the bridge pivots (measured along the bridge) and pulls horizontally on the bridge to hold it in place. What is the tension in the cable? Find the magnitude and direction of the force the hinge exerts on the bridge. If the cable suddenly breaks, what is the magnitude of the angular acceleration of the drawbridge just after the cable breaks? What is the angular speed of the drawbridge as it becomes horizontal? What is the velocity of the drawbridge, just before it “hits” (i.e. goes horizontal)?arrow_forwardA 6.0 m long ladder AB leans against a smooth wall making an angle of 60º with the floor (Figure 3). The ladder is uniform and has a mass of 20.0 kg.(a) Determine the forces exerted on the ladder by the floor and the wall (i.e. at A and B, respectively).(b) Determine the minimum value of the coefficient of static friction to prevent the ladder from slipping.arrow_forwardThe figure below shows a beam of uniform density with a mass of 35.5 kg and a length t5.95 m. It is suspended from a cable at a distance d 1.20 m from its left end, while its right end is supported by a vertical column. (a) What is the tension (in N) in the cable? (b) What is the magnitude of the force (in N) that the column exerts on the right end of the beam? Need Help? Read Page 20arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON