
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A uniform 37.0 kg scaffold of length 6.2 m is supported by two light cables, as shown below. An 82.0 kg painter stands 1.0 m from the left end of the scaffold, and his painting equipment is 1.6 mfrom the right end. If the tension in the left cable is twice that in the right cable, find the tensions in the cables (in N) and the mass of the equipment (in kg). (Due to the nature of this problem, do not use rounded intermediate values in your calculations).
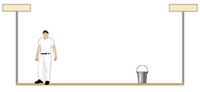
Transcribed Image Text:The image depicts a person standing on a platform. Toward the right side of the platform, there is a bucket. The platform is enclosed by two vertical posts with horizontal beams at the top, possibly representing a setup for a physical demonstration or experiment. The scene appears simple and might be used to explain concepts in physics, such as balance, forces, or motion. The person is dressed in white with a cap, and the setting looks like an indoor or controlled environment.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 24.0 kg beam of length L = 35.1 m is attached at an angle of θ = 36.40 to the side of a building. If the beam is holding up a mass M = 64.4 kg and is supported by a horizontal wire that is attached at location X = 24.5 m (measured along the beam from the building to the wire attachment point), what is the force the building is putting on the beam? What is the Direction of force (measured as an angle off of the side of the building (think west of north)arrow_forwardA 16.0-m uniform ladder weighing 510 N rests against a frictionless wall. The ladder makes a 57.0° angle with the horizontal. (a) Find the horizontal and vertical forces the ground exerts on the base of the ladder when an 850-N firefighter has climbed 3.90 m along the ladder from the bottom. Horizontal force: magnitude direction Vertical force: magnitude direction towards the wall up N ✓✓ N (b) If the ladder is just on the verge of slipping when the firefighter is 8.70 m from the bottom, what is the coefficient of static friction between ladder and ground?arrow_forwardAsap plzzzzzarrow_forward
- The uniform boom shown below weighs 644 N, and the object hanging from its right end weighs 416 N. The boom is supported by a light cable and by a hinge at the wall. 45° 20° 416 N Calculate the tension in the cable and the force by the hinge on the boom (both in N). (Enter the magnitudes.) tension in the cable 787.738 N force by the hinge 812.122 Narrow_forwardb) Determine the horizontal and vertical components of the force acting on the hing 3. A uniform 4.0 m long beam with a mass of 15 kg rests on a pivot at one end and is kept horizontal by a cable at the other end. The beam is supporting a 25 kg mass as shown. What is the tension in the cable? pluct 15 kg beam 2.5m - Fird ferce or support) сп вест of 25 kg -1.5 m 55⁰ 55° weight of beam = middle weight of dhject = pa te middle onarrow_forwardA uniform 37.0 kg scaffold of length 6.4 m is supported by two light cables, as shown below. An 82.0 kg painter stands 1.0 m from the left end of the scaffold, and his painting equipment is 1.3 m from the right end. If the tension in the left cable is twice that in the right cable, find the tensions in the cables (in N) and the mass of the equipment (in kg). I don't understand how to find mass of the equipment.arrow_forward
- A 1204-N uniform beam is attached to a vertical wall at one end and is supported by a cable at the other end A 1515-N crate hangs from the far end of the beam. Find the magnitude of the tension in the wire. The angle theta (9) is 29 degrees and the angle phi () is 53 degrees. The length of the beamis L Вeam ROUND OFF FINAL ANSWER TO THE NEAREST WHOLE NUMBER. INPUT THE SYMBOL OF THE UNIT. NO SPACE BETWEEN THE NUMBER AND THE UNIT.arrow_forwardA uniform 50-kg scaffold of length 7.0 m is supported by two light cables, as shown below. A 61-kg painter stands 1.0 m from the left end of the scaffold, and his paint bucket is 1.5 m from the right end. If the tension in the left cable is twice that in the right cable, find the tensions in the cables and the mass of the bucket. m bucket = kg T (left) = N T (right) = Narrow_forwardThe two children shown in the figure below are balanced on a seesaw of negligible mass. The first child has a mass of 27.3 kg and sits 1.24 m from the pivot. The second child has a mass of 33 and sits 1.00 m from the pivot. Use the second condition for equilibrium (net r= 0) to calculate F, the supporting force (in N) exerted by the pivot. (Enter the magnitude.) m₂ m₂ W₂arrow_forward
- 38. A uniform horizontal strut weighs 400.0 N. One end of the strut is attached to a hinged support at the wall, and the other end of the strut is attached to a sign that weighs 200.0 N. The strut is also supported by a cable attached between the end of the strut and the wall. Assuming that the entire weight of the sign is attached at the very end of the strut, find the tension in the cable and the force at the hinge of the strut. 30° Restaurantarrow_forwardA uniform drawbridge must be held at a 37° angle abovethe horizontal to allow ships to pass underneath. The drawbridge weighs45,000 N and is 14.0 m long. A cable is connected 3.5 m from thehinge where the bridge pivots (measured along the bridge) and pullshorizontally on the bridge to hold it in place. What is the tension in the cable?arrow_forward4. A uniform beam of mass m, and length L is supported as shown below. There is a pin in theb bottom end of the beam and a mass of mass m, hanging from the top end of the beam. Find the magnitude of the tension in the wire attaching the beam to the ground and force from the pin on the beam.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON