
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
A single-piece bicycle crank is shown below under the following load: the rider pedals forward with a vertical force Fp = 500 N on the left pedal and no force on the right pedal. The chain exerts a force Fc on the chainring. The spindle is a solid cylinder with a diameter d = 16 mm.
1. Find the maximum normal stress and shear stress at cross-section y-y in image. Indicate the locations on the given cross section view where they act.
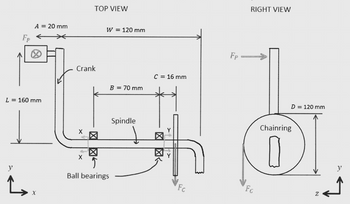
Transcribed Image Text:A = 20 mm
L = 160 mm
X
Crank
X
TOP VIEW
X
W = 120 mm
Ĵ
Ball bearings
B = 70 mm
Spindle
C = 16 mm
Y
FC
Fp
RIGHT VIEW
FC
D = 120 mm
Chainring
Z
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 8 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. A loaded bicycle pedal crank is shown below. q 750N (2 direction) 72/ A @ Top 8 yo B@ Top d = 15 mm x₁ = 125 mm x2 = 24 mm y₁ = 60 mm у2=X2 a. Sketch elements A and B and show the stress states. Clearly label the coordinate axes on the elements. Make sure you calculate the normal (o) and shear stresses (T). Do not neglect Tv. Find the principal stresses for each element using Mohr's Circle. b.arrow_forwardPlease use principle stresses, Tresca failure criterior and Von Mises Yield Criteror to solve for this problemarrow_forwardThe cantilever beam with a rectangular cross-section is under the loading P as shown in the figure. P Part A At an arbitrary cross-section, a - a the state of stress is obtained at various points (point 1 - 5, where point 3 is the midpoint). Select all that describe the stress at the cross-section a - a correctly. O The cross-section a-a has three internal loadings, i.e., shear force, normal force, and bending moment. O The normal stress by bending moment at point 5 is zero. O The maximum shear stress by shear force occurs at the same point as the maximum normal stress by bending moment. O The maximum shear stress by shear force occurs at point 3. O Point 1 develops compressive normal stress by bending moment. O The shear stress by shear force at point 1 is zero. Submit Request Answerarrow_forward
- 7.2-5 The stresses acting on element A on the web of a train rail (see figure part a) are found to be 6500 psi tension in the horizontal direction and 18,500 psi com- pression in the vertical direction (see figure part b). Also, shear stresses with a magnitude of 3800 psi act in the directions shown. Determine the stresses acting on an element ori- ented at a counterclockwise angle of 30° from the horizontal. Show these stresses on a sketch of an ele- ment oriented at this angle. Can Stock Photo Inc./corepics Cross Section PROBLEM 7.2-5 Can Stock Photo Inc./scanrail A Side View Sa A 18,500 psi T (b) 16500 psi 3800 psiarrow_forwardThe horizontal pipe shown in Figure 2 has a hollow circular cross section of 38mm inner- diameter and 50mm outer-diameter. Determine the principle stresses (Gmax and omin) and maximum shear stress (Tmax) at points A and B on the cross section of the pipe at section a-a. As shown in Figure 2, point A is located on y- axis and the inner surface of the pipe while point B is located on z-axis and the outer surface of the pipe. 19 mm E=200 N 25 mm Section a-a 250 mm 300 mmarrow_forwardSolve pleasearrow_forward
- Additional problem: A solid rod with a radius of 10 mm is subjected to a combined loading with two forces and one torque, as shown in the figure below (T-5 Nm). Compute the normal stress o, and shear stress at point H and K. C K H 300 mm SAN-m Z 700 N 250 N Xarrow_forwardı need solutionarrow_forwardCalculate non-zero stress components (normal and shear) at points A, B and C. Point C is located at the center of the cross section attached to the wall. Calculate non-zero strain components at point B. Neglect shear stress due to shear force. Given: loading F = 400 N, P-2000 N, and T = 75 N·m, Young's modulus E = 70 GPa, Poisson's ratio v = 0.25 15-mm D. -100 mmarrow_forward
- Example 2 : 200N Pi-40ON SONUTION: o mm • Dete mine an equivalent force-couple syster at the center of the transverse section passing through H. Evaluate the normal and shearing stresse at H/ 250 mm D. 30 mm 100 m • Betermine the principal planes and calculate the principal stresses. A single horizontal force P,of 600N magnitude soppliad to endD of lever ABD. Determine (a) the normal and shearing stresses on an element at point H having sides parallel to the x and y axes, (b) the principal planes and principal stresses at the point H. mchr's cin' mohr's arclearrow_forwardHow do I calculate for sigma seam? Thank youarrow_forwardA round beam of length 14-in is simply supported at A and D. The beam is loaded in torsion and with transverse loads. The diameter of the beam is 1.5in. Calculate the principal stresses and the max shear stress at the mostcritical point in the beam. solve from tan theta = 4/3 then theta =tan inverse(4/3) = 53.13 degree solve from theta for other force of 600 lb is theta = 45 degrees Then solve for each reactions, bending moment My, bending moment Mz and the maximum bending moment and maximum stress along x axis. And also calucalate the principle stresses and the maximum shear stress at the most crictical point in the beam. Show everything with proper digaram with step by step solution and give me right answer. And I will surely upvote for you and subscribe it.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY