
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
A simply supported beam with a cantilever side is subjected to a uniform load of 15 kN/m and a point load of 5 kN as shown in Figure 1. Assume E= 205 GPa and I=60(10)6 mm4 . (Hint: Consider method of superposition)
1.1 Calculate the reactions at the supports of the beam
1.2 Draw the shear force and bending moment diagrams with critical values
1.3 Calculate the deflection at A using unit load method
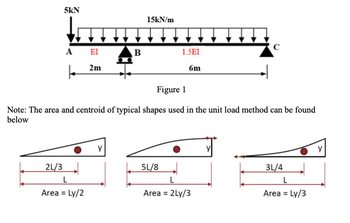
Transcribed Image Text:5kN
2L/3
A EI
k
2m
L
Area = Ly/2
↓↓↓
B
y
15kN/m
Figure 1
Note: The area and centroid of typical shapes used in the unit load method can be found
below
1.5EI
6m
5L/8
с
L
Area = 2Ly/3
3L/4
L
Area = Ly/3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 9 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Rigid bar ABC is supported by bronze rod (1) and stainless steel rod (2) as shown in the figure. A concentrated load of P = 24 kips is applied to the free end of bronze rod (3). Determine the magnitude of the deflection of rod end D after the temperature of all rods has increased by 115 Fo. Use the following dimensions and properties: a = 3.5 ft, b = 7.5 ft. Rod (1): d 1= 1.10 in.,L 1= 12 ft , E 1= 15,200 ksi , a 1= 12.20 × 10 - 6 /Fo. Rod (2): d 2 = 0.65 in. , L 2 = 10 ft , E 2 = 28,000 ksi, a 2 = 9.60 x 10 - 6/Fo. Rod (3): d 3 = 1.15 in. , L 3 = 6 ft, E3 = 15,200 ksi , a 3 = 12.20 x 10 - 6/Fo. (1) L (2) b L2 a Rigid bar A (3) L3 vD = i in.arrow_forwardConsider the cantilever beam in the figure,subject to a concentrated force P = 20kip at Band a concentrated moment Mo = 100k-ft at C.Knowing that a = 5ft, use the conjugate beammethod to calculate the following in terms ofgeneric E and I:(a) The slope of point C(b)The deflection of point Barrow_forward4. A beam is supported by two fixed supports and a spring as shown below. The spring constant is k = 400000 N/m. The beam is loaded by a uniform distributed load and an end moment as shown. The beam has EI = 25000 N-m². 500Nm | 1000 N/m L ↓ Im fr B 1 1 с a. Find the reactions at the three supports. b. Calculate the total deflection of the beam at point D. D COS~²³| 40.51³/arrow_forward
- Q. 4 Determine the slope at the supports for the beam shown below. Also, determine the deflections at B and C. 10 ft I 40 k B 60 k 10 ft 21 E = constant = 29,000 ksi I = 1,000 in.4 10 ft I Q. 4arrow_forwardHere is the follow up,arrow_forwardRigid bar ABC is supported by bronze rod (1) and stainless steel rod (2) as shown in the figure. A concentrated load of P = 16 kips is applied to the free end of bronze rod (3). Determine the magnitude of the deflection of rod end D after the temperature of all rods has increased by 125°F. Use the following dimensions and properties: a = 2.8 ft, b = 6.3 ft. Rod (1): d₁ = 0.90 in., L₁ = 11 ft, E₁ = 15,200 ksi, α₁ = 12.20 × 10-6/°F. Rod (2): d₂ = 0.80 in., L₂ = 9 ft, E2 = 28,000 ksi, a₂ = 9.60 × 10-6/F. Rod (3): d3 = 1.25 in., L3 = 5 ft, E3 = 15,200 ksi, a3 = 12.20 x 10-6/°F. VD = i L in. (1) A a L3 B (3) D b Rigid bar L2arrow_forward
- The beam shown in the figure is subjected to a moment of M = 50 kN.m. Determine the bending stress at point A and B.arrow_forward2. A uniform, simply supported beam, is loaded as shown in Figure 2. Using singularity functions, determine an expression for the bending moment at any point along the beam. Hence, determine the slope of the beam at point, A, and the deflection of the beam at point, B. The bending stiffness of the beam is 3200 Nm². 320 N 200 N/m 1.2m 0.6m Figure 2 2 A 0.4m X * B Darrow_forwardCalculate the value of the deflection at point B due to concentrated load P in the form Calculate the vertical reaction at support D. Calculate the vertical reaction at support A. Find the maximum bending moment in the beam Calculate the magnitude maximum bending stress in the beam.arrow_forward
- For the beam supported at A and B as shown, is carrying two concentrated loads. RA 2 m PĮ 1 m B RB 1.5 m C If P = Q = 66.10 kN and El= 24x10^12 N-mm^2, What is the deflection at C in mm? (Numerical Value only)arrow_forwardDetermine the slope and deflection at point A of the beam shown in the figure.arrow_forwardProblem 2. Consider the frame shown below. Take E constant for all three members, and ignore axial deformations. a) b) Find all reactions. Draw the BMD; identify the magnitude and location of all minima, maxima, and inflection points. Find the horizontal deflection at joint C as a function of EI. 10 m XB 15 m I 21 15 m D I -30 kNarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning