
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A curved beam is in the form of quarter-circle with straight base as shown in Figure Q3. The beam is subjected to a vertical load of 500 N at point A. The Young’s modulus of elasticity E for the material of the beam and second moment of area I for the cross section of the beam are 200 ×109 N/m2 and 1.3 × 10−7 m4 respectively. Calculate the vertical deflection at point A.
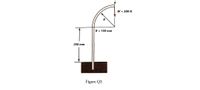
Transcribed Image Text:W = 500 N
R = 150 mm
250 mm
Figure Q3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- helppparrow_forwardQuestion 3 Determine the value of a in meters so that the deflection at point C is equal to the max deflection between A and B. Use E = 200 GPa and I = 5 x 10' mm4. P = 2.3 kN A a 10 marrow_forward2. For the cantilever beam shown in the figure, what will cause zero deflection at A? ANS. P=112.5 N A P M = 400 N-m B 2 m 2 marrow_forward
- Using double integration method, compute the maximum deflection for the beam loaded as shown in the figure. Usee E=10GPa and I =4.5x10^6 mm^4arrow_forwardSolve q4 part both parts c ,d and e plz solve this in maximum 2 hour if u can't solve this u can reject in one hour so that i can't wait of your answer plz..arrow_forwardUse the moment-area method to determine the lateral deflection at point D for the structure shown in Figure 1. 59 kN 100 kN 1m - 1m B D E = 200 GPa I = 1x10-4 m* 4 m A TTTT tarrow_forward
- Obtain the formula for the deformed beam shown below. Indicate the location of where the maximum deflection occurs and its value.Also obtain the deflection at point C and the rotation at point A for the beam using (a) the moment area method and (b) the conjugate method.arrow_forward2. Use the conjugate-beam method to determine the slope and deflection at point B of the beams shown in the figure. 50 kN A 6 m B 90 kN ↓ C 9 m El= constant E = 70 GPa I = 95 (106) mm4 9 m D EXCEarrow_forwardPlease just do figure 10.2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning