
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A rubber pad is sandwiched between two steel plates subjected to shear force V = 400kN. The dimensions of the plate area, a= 250mm and b = 300mm. The thickness of the rubber is c = 125mm. After the force is applied, the top plate is found to have displaced laterally by δ = 1.5mm along the 300mm length. Determine the shear stress. Determine the shear strain. Determine the shear modulus.
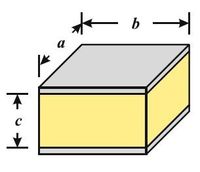
Transcribed Image Text:b
a
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The strain at point A on the bracket has normal components 250x10-6 and 550x10-6 in x and y directions, respectively and shear component -600 x10-6 in x-y plane. Determine the absolute maximum shear strain in 10-6 unit.arrow_forwardThe brake pads for a bicycle tire are made of rubber. If a frictional force of 50 N is applied to each side of the tires, determine the average shear strain in the rubber. Each pad has cross-sectional dimensions of 20 mm and 50 mm.Gr = 0.20 MPa.arrow_forwardThe man has a mass of 84 kg and stands motionless at the end of the diving board. Figure -1.5 m B -2.5 m 30 mm 350 mm 20 mm 10 mm 10 mm 10 mm Part A If the board has the cross section shown, determine the maximum normal strain developed in the board. The modulus of elasticity for the material is E 127 GPa. Assume A is a pin and 13 is a roller. B (Figure 1) C= IVE ΑΣΦ Submit ↓↑ vec Previous Answers Request Answer Ć MADE * Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining Return to Assignment Provide Feedback ? mm/mmarrow_forward
- A strain gage is mounted to the outer surface of a thin-walled boiler. The boiler has an inside diameter of 1820_mm and a wall thickness of 18 mm, and it is made of stainless steel [E = 179 GPa; v = 0.3]. Determine: (a) the internal pressure in the boiler when the strain gage reads 210 µɛ. (b) the maximum shear strain in the plane of the boiler wall. (c) the absolute maximum shear strain on the outer surface of the boiler. Answers: (a) p = i MPа. (b) Ymax in-plane = i prad. (c) Yabs max i prad. =arrow_forwardThe normal strain in a suspended bar of material of varying cross section due to its own weight is given by the expression yy/3E where y = 2.9 lb/in.³ is the specific weight of the material, y = 0.5 in. is the distance from the free (i.e., bottom) end of the bar, L = 5 in. is the length of the bar, and E = 25000 ksi is a material constant. Determine, (a) the change in length of the bar due to its own weight. (b) the average normal strain over the length L of the bar. (c) the maximum normal strain in the bar.arrow_forwardAthin triangular plate PQR forms a right angle at point Q. During deformation, point Q moves to the left by u = 1.0 mm and upward by v=4.1 mm to new position Q'. Determine the shear strain y at corner Q' after deformation. Use c= 670 mm, a= 28%, and 5= 62° 4 R Answer: y= i uradarrow_forward
- The strain at point A on the bracket has normal components 400x10-6 and 550x106 in x and y directions, respectively and shear component -650 x10-6 in x-y plane. Determine the absolute maximum shear strain in 10-6 unit. Aarrow_forwardUse the graphical method to construct the shear-force diagram and identify the magnitude of the largest shear force (consider both positive and negative). The ground reactions at the wall of the cantilever are provided. L1= 14.00 ft L2 = 7.75 ft Vc = 87.00 kips Mc = 621.875 kip-ft 20 kips 70 kips 12 kips/ft 6 kips/ft Mc A В L1 L2 99.00 kips O 110.00 kips O 75.00 kips O 64.00 kips O 87.00 kipsarrow_forwardThe material is subjected to biaxial loading producing uniform normal stress x and y as shown. The strains are Strainx=−0.00065 and Strainy=−0.00040. Use E=30×106 psi and v=0.30. Determine the following: (a) stress at x. Indicate tension or compression. Use 2 decimal places. (b) stress at y. Indicate tension or compression. Use 2 decimal places. (c) Change in the thickness of the material. Indicate elongation or contraction. Use 5 decimal places and scientific notation of ×10−3(Example: _ . _ _ _ _ _ ×10−3)arrow_forward
- A pipe is subjected to a tension force of P = 70 kN. The pipe outside diameter is 32 mm, the wall thickness is 6.0 mm, and the elastic modulus is E = 180 GPa. Determine the normal strain in the pipe. P Select one: O a. 0.001263 mm/mm O b. 0.000535 mm/mm O c. 0.000568 mm/mm O d. 0.000794 mm/mm e. 0.001382 mm/mm O f. Nonearrow_forwardThe thin-walled pipe has an inner diameter of 1.2 cm and a thickness of 0.06 cm. If it is subjected to an internal pressure of 4 MPa and the axial tension and torsional loadings shown, determine the principal stress and the absolute maximum shear stress at a point on the surface of the pipe. (15' in total) 2000 N 2000 N 8 N-m 8 N-m 1.2 cm 0.06 cmarrow_forwardThe 1900-NN load is applied along the centroidal axis of the member. (Figure 1) Determine the magnitude of the resultant internal normal force in the member section a-a. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. 2) Determine the magnitude of the resultant internal shear force in the member section a-a. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY