
A researcher wants to perform a hypothesis test to determine whether the
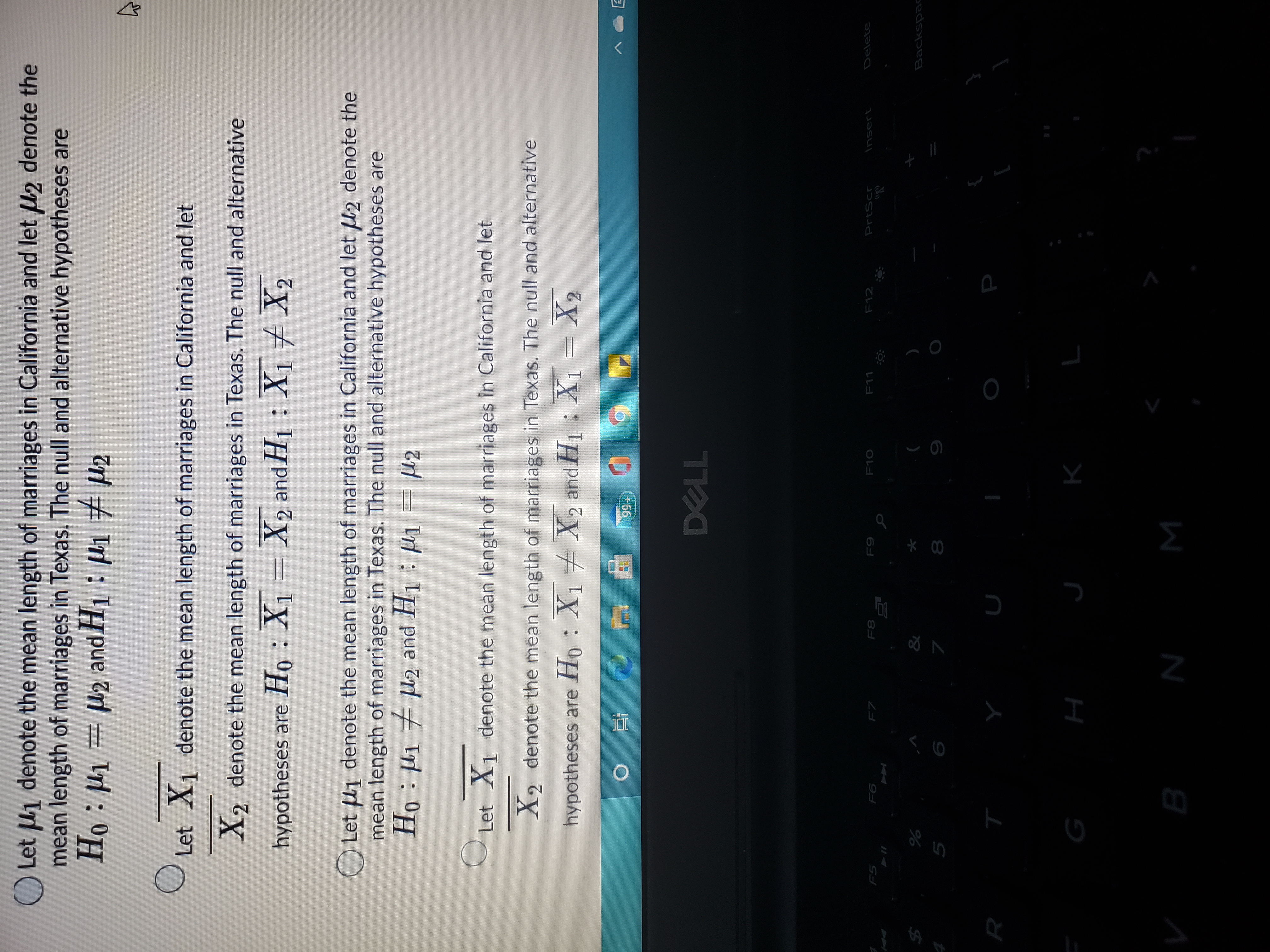
A. Let U1 denote the mean length of marriages in California and let U2 denote the mean length of marriages in Texas. The null and alternative hypotheses are H0:U1=U2 and H1:U1 does not equal U2
B. Let X1 denote the mean length of marriages in California and let X2 denote the mean length of marriages in Texas. The null and alternative hypotheses are H0:X1=X2 and H1:X1 does not equal X2
C. Let U1 denote the mean length of marriages in California and let U2 denote the mean length of marriages in Texas. The null and alternative hypotheses are H0:U1 does not equal U2 and H1:U1=U2
D. Let X1 denote the mean length of marriages in California and let X2 denote the mean length of marriages in Texas. The null and alternative hypotheses are H0:X1 does not equal X2 and H1:X1=X2
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- Monthly telephone charges for cell phone in the United States are normally distributed with a mean of $62 for a single user. Coach Keefer thinks that leasing smart phones has increased the monthly cell phone bill for a single user. O Ho : µ = 62 H : μ> 62 u > O Ho: µ= 62 Ha : µ# 62 OHo: = 62 Ha: 62 O Ho: p = 62 Ha:µ262 ASUS VivoBookarrow_forwardDogsled drivers, known as mushers, use several different breeds of dogs to pull their sleds. One proponent of Siberian Huskies believes that sleds pulled by Siberian Huskies are faster than sleds pulled by other breeds. He times 4040 teams of Siberian Huskies on a particular short course, and they have a mean time of 7.77.7 minutes. The mean time on the same course for 4747 teams of other breeds of sled dogs is 6.26.2 minutes. Assume that the times on this course have a population standard deviation of 1.51.5 minutes for teams of Siberian Huskies and 1.61.6 minutes for teams of other breeds of sled dogs. Let Population 1 be sleds pulled by Siberian Huskies and let Population 2 be sleds pulled by other breeds. Step 1 of 2 : Construct a 95%95% confidence interval for the true difference between the mean times on this course for teams of Siberian Huskies and teams of other breeds of sled dogs. Round the endpoints of the interval to one decimal place, if necessary.arrow_forwardExpress the alternative hypothesis in symbolic form. A psychologist claims that the mean amount of time (in hours) that females spend in talk therapy is more than that of men. Assume that two samples are independent. Let the female talk therapy times be the first population and the male talk therapy times be the second population.arrow_forward
- The mean number of sick days an employee takes per year is believed to be about 10.5. Members of a personnel department do not believe this figure. They randomly survey ten employees. The number of sick days they took for the past year are as follows: 12; 4; 15; 3; 11; 8; 6; 8; 2; 9. Let x = the number of sick days they took for the past year. Should the personnel team believe that the mean number is ten?arrow_forwardAn online instructor wants to estimate the mean amount of time that students spend in the online homework system on a particular homework assignment. The instructor takes a random sample of 30 students and looks up the amount of time recorded by the system for that assignment.arrow_forwardDoes the type of instruction in a college statistics class (either lecture or self-paced) influence students’ performance, as measured by the number of quizzes successfully completed during the semester? Twelve students were recruited for the study. Students received the lecture instruction or a self-paced instruction. The total number of quizzes completed during teach type of instruction appear below.arrow_forward
- According to previous studies, the mean distance each visitor in Greenspan National Park hikes during their visit is 30 kilometers. The park recently closed its shuttle system, which used to transport hikers to many of the park's most popular hiking trails. Because of this, an administrator at the park suspects the mean distance, u, is now less than 30 kilometers. The administrator chooses a random sample of 45 visitors. The mean distance hiked for the sample is 27.2 kilometers. Assume the population standard deviation is 9.9 kilometers. Can the administrator conclude that the mean distance hiked by each visitor is now less than 30 kilometers? Perform a hypothesis test, using the 0.10 level of significance. (a) State the null hypothesis H, and the alternative hYpothesis H,. Oarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardAt a local food processing plant, it used to take an average of 90 minutes for new workers to learn a food processing job. Recently the company installed a new food processing machine. The supervisor at the company wants to find if the mean time taken by new workers to learn the food processing procedure on this new machine is different from 90 minutes. A sample of 20 workers showed that it took, on average, 85 minutes for them to learn the food processing procedure on the new machine. It is known that the learning times for all new workers are normally distributed with a population standard deviation of 7 minutes. Use a significance level of 0.01 to test the claim that the mean time is different from 90 minutes. What is the decision? A) Reject Ho because the test statistic is in the critical region and the p-value is greater than the significance level. B) Reject Ho because the test statistic is not in the critical region and the p-value is greater than the significance level.…arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosarrow_forward_ios
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





