
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
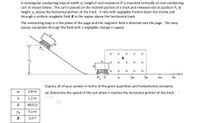
Transcribed Image Text:A rectangular conducting loop of width w, height h and resistance R is mounted vertically on non-conducting
cart as shown below. The cart is placed on the inclined portion of a track and released rest at position P, at
height yo above the horizontal portion of the track. It rolls with negligible friction down the incline and
through a uniform magbetic field B in the region above the hortizontal track.
The conducting loop is in the plane of the page and the magnetic field is directed into the page. The loop
passes competely through the field with a negligible change in speed.
P,
B
Yo
X X
P2
2w
3w
4w
5w
Express all of your answer in terms of the given quantities and fundamental constants.
2.6 m
(a) Determine the speed of the cart when it reaches the horizontal portion of the track.
h
1.2 m
R
40.0 0
Yo
5.1 m
B
2.0 T
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A square conducting loop that measures a = 0.250 m on each side, is placed in a magnetic field. The magnetic field is directed into the page and is perpendicular to the loop. The magnetic field has a magnitude B=2.60 T. The loop is pulled out of the magnetic field region at velocity v=1.60 m/s in the direction shown.arrow_forwardA conducting rod of length / is free to slide on two parallel, horizontal, conducting bars as shown in the figure. Two resistors R,-3R and R-6R are connected across the ends of the bars to form a loop. Apart from the resistors, the loop has negligible resistance. A constant uniform magnetic field of magnitude B is directed perpendicularly into the page everywhere inside the loop. An external agent pulls the rod to the left with a constant speed u. Part A-Find the current through the resistor R. (Answer in terms of R) 1阿 AE中 Submit Request Answer Part B-Find the total power dissipated by the resistors. (Answer in terms of R) 1%AX中 Pearsonarrow_forwardA conducting rectangular loop of mass 0.70kg, resistance 60 Ω, and 2.0m wide is allowed to fall from rest through a uniform magnetic field 6.0 T which is perpendicular to the plane of the loop. The loop accelerates until it reaches a terminal (constant) speed (before the upper end enters the magnetic field). (a) What is the terminal speed?arrow_forward
- Two coplanar and concentric circular loops of wire carry currents of I, = 5.90 A and I, = 2.30 A in opposite directions as in the figure below. Let r, = 12.0 cm and r, = 8.60 cm. (Assume the positive direction along the axis perpendicular to the faces of the loops is out of the screen (towards you) and assume the positive vertical direction is toward the top of the screen.) (a) What is the magnitude of the net magnetic field (in µT) at the center of the two loops? PT (b) What is the direction of the net magnetic field at the center of the two loops? out of the screen O into the screen O toward the top of the screen O toward the bottom of the screen (c) Let r, remain fixed at 12.0 cm and let r, be a variable. Determine the value ofr, (in cm) such that the net field at the center of the loops is zero. cmarrow_forwardA magnetic dipole with a dipole moment of magnitude 0.016 J/T is released from rest in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 58 mT. The rotation of the dipole due to the magnetic force on it is unimpeded. When the dipole rotates through the orientation where its dipole moment is aligned with the magnetic field, its kinetic energy is 0.60 mJ. (a) What is the initial angle between the dipole moment and the magnetic field? _____________°(b) What is the angle between the dipole moment and the magnetic field when the dipole is next (momentarily) at rest? ______________°arrow_forwardA solid conducting bar is free to move across two ends of a conducting U shape of wire that are separated by L=25 cm. On the base of the U shape is a resistor R=20 ohms. The whole apparatus is in a constant magnetic field B=0.7 T pointing out of the page. If the conducting bar has negligent resistance itself and is moved to the right at a constant velocity of 12 m/s, what is the magnitude and direction of the current induced in the loop? a) 0.11 A, clockwise b) 0.11 A, counterclockwise c) 2.1 A, clockwise d) 2.1 A, counterclockwisearrow_forward
- A proton has a velocity of 1.1X10^2 m/s î +1.8X10^2 m/s ĵ and is located in the z=0 plane at x=3.4m, y=3.6m at some time t=T. Find the magnetic field in the z=0 plane at the following at x=1.9m, y=1.9m.arrow_forwardA square loop with side length L carries a current 1, counterclockwise. The loop is placed in uniform magnetic field of magnitude B that points upwards. I< B () In the above problem, in which direction will the loop rotate?arrow_forwardA loop of wire has the shape shown in the drawing. The top part of the wire is bent into a semicircle of radius r = 0.22 m. The normal to the plane of the loop is parallel to a constant magnetic field (φ = 0˚) of magnitude 0.90 T. What is the change ΔΦ in the magnetic flux that passes through the loop when, starting with the position shown in the drawing, the semicircle is rotated through half a revolution?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON