
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Answer the following questions by analysing the T-accounts given below.
- a) Purchases of direct material
- b) The cost of direct material used
- c) Why does direct labor account has a credit balance of $5000? Explain
- d) Direct labor costs assigned to production
- e) The
overhead as a percentage of direct labor costs
- f) Total
manufacturing costs charged to the Work in Process Inventory account during the current year
- g) The cost of finished goods manufactured
- h) The year-end balance in the Work in Process Inventory account
- i) The cost of goods sold
- j) The total amount of inventory listed in the hear-end
balance sheet - k) Manufacturing overhead assigned to production
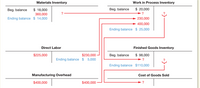
Transcribed Image Text:Materials Inventory
Work in Process Inventory
$ 20,000
$ 18,000
360,000
Beg. balance
Beg. balance
+ 230,000
+ 400,000
Ending balance $ 14,000
Ending balance $ 25,000
Direct Labor
Finished Goods Inventory
$225,000
$230,000
Beg. balance
$ 98,000
Ending balance $ 5,000
Ending balance $110,000
Manufacturing Overhead
Cost of Goods Sold
$400,000
$400,000
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- please answer within the format by providing formula the detailed workingPlease provide answer in text (Without image)Please provide answer in text (Without image)Please provide answer in text (Without image)arrow_forward0 jor pro se Used Balances: Direct Materials Work-in-Process Inventory Finished Goods Inventory Data table Direct Materials Used: Direct Materials Used Print Other information: Depreciation, plant building and equipment Direct materials purchases Insurance on plant Sales salaries Repairs and maintenance-plant Indirect labor Direct labor Administrative expenses Manufacturing Overhead: Cost of Goods Manufactured Beginning Ending $ Done Total Manufacturing Overhead Total Manufacturing Costs incurred during the Year Total Manufacturing Costs to Account For Requirements 1. Use the information to prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured. 2. What is the unit product cost if Clark manufactured 4,380 lamps for the year? 57,000 $ 22,000 103,000 67,000 50,000 52,000 $ 4 Clark, Corp. Schedule of Cost of Goods Manufactured Year Ended December 31, 2024 11,000 155,000 23,000 43,000 13,000 40,000 125,000 53,000 - Xarrow_forwardA manufacturer reports the information below. Finished goods inventory, beginning Finished goods inventory, ending Depreciation on factory equipment Direct labor Indirect labor Factory utilities Selling expenses Direct materials used Indirect materials used Office rent expense Work in process inventory, beginning Work in process inventory, ending Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required A Required B Compute cost of goods sold for the period. Goods available for sale Cost of goods sold $ 8,200 9,140 4,800 84,000 36,700 3,200 750 55,900 700 1,200 1,600 2,400 $ 0arrow_forward
- Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] The following data is provided for Garcon Company and Pepper Company for the year ended December 31. Finished goods inventory, beginning Work in process inventory, beginning Raw materials inventory, beginning Rental cost on factory equipment Direct labor Finished goods inventory, ending Work in process inventory, ending Raw materials inventory, ending Factory utilities General and administrative expenses Indirect labor Repairs-Factory equipment Raw materials purchases Selling expenses Sales Cash Accounts receivable, net Garcon Company $ 12,500 16,100 7,400 34,750 19,800 21,800 26,200 7,200 12,600 27,000 14,750 4,940 41,500 58,000 296,220 26,000 13,600 Pepper Company $ 17,350 22,050 9,450 25,150 39,400 14,600 20, 200 8,000 15,750 43,000 14,320 3,750 60,500 46,000 388,450 18,700 21,950 1. Prepare income statements for both Garcon Company and Pepper Company. 2. Prepare the current assets section of…arrow_forwardComplete the information in the cost computations shown here: Raw materials Beginning inventory Purchases Materials available for use Ending inventory Materials used in production Work in process inventory Beginning inventory Materials used in production Direct labor Overhead applied Manufacturing costs incurred Ending inventory Cost of goods manufactured Finished goods inventory Beginning inventory Cost of goods manufactured Goods available for sale Ending inventory Cost of goods sold $341 1,533 323 $931 1,536 $22,450 936 $25,008 $21,792arrow_forwardAccounting records for Antoinette Designs (AD) for November show the following (each entry is the total of the actual entries for the account for the month): Account Titles Work-in-Process Inventory (Direct Labor) Wages Payable Direct Materials Inventory Accounts Payable Finished Goods Inventory Work-in-Process Inventory Cost of Goods Solda Finished Goods Inventory Debit 7,200 122,130 136,800 131,400 Credit 7,200 Required: a. What was the finished goods inventory balance on November 30? b. How much manufacturing overhead was applied for November? c. What was the manufacturing overhead rate for November? d. How much manufacturing overhead was incurred for November? e. What was the Work-in-Process Inventory on November 1? f. What was the Work-in-Process Inventory on November 30? 122,130 136,800 131,400 aThis entry does not include any over- or underapplied overhead. Over- or underapplied overhead is written off to Cost of Goods Sold once for the month. For November, the amount written…arrow_forward
- Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] The following data is provided for Garcon Company and Pepper Company for the year ended December 31. Finished goods inventory, beginning Work in process inventory, beginning Raw materials inventory, beginning Rental cost on factory equipment Direct labor Finished goods inventory, ending Work in process inventory, ending Raw materials inventory, ending Factory utilities General and administrative expenses Indirect labor Repairs-Factory equipment Raw materials purchases Selling expenses Sales Cash Accounts receivable, net Garcon Company $ 12,700 16,800 8,700 30,250 24,600 20,600 24,100 Required 1 5,800 12,600 24,500 14,900 5,660 40,000 Required 2 59, 200 283,890 34,000 14,200 Pepper Company $ 19,300 22,800 12,600 23,500 43,800 13,600 16,400 7,600 14,750 53,000 14,400 2,250 67,500 48,700 1. Compute the total prime costs for both Garcon Company and Pepper Company. 2. Compute the total conversion…arrow_forward22 Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Use the following selected account balances of Delray Manufacturing for the year ended December 31. Sales Raw materials inventory, beginning Work in process inventory, beginning Finished goods inventory, beginning Raw materials purchases Direct labor Indirect labor Repairs Factory equipment Rent cost of factory building Selling expenses General and administrative expenses Raw materials inventory, ending Work in process inventory, ending Finished goods inventory, ending Sales Cost of goods sold: Finished goods inventory, beginning Cost of goods manufactured DELRAY MANUFACTURING Income Statement For Year Ended December 31 Goods available for sale Less: Finished goods inventory, ending Cost of goods sold Gross profit Selling expenses Prepare an income statement for Delray Manufacturing (a manufacturer). Assume that its cost of goods manufactured is $1,372,000. $ 2,650,000 110,000 143,000 Work in…arrow_forward*need help with C please *arrow_forward
- Make an income statementarrow_forwardJustine Industries is calculating its Cost of Goods Manufactured at year-end. The company's accounting records show the following: The Raw Materials Inventory account had a beginning balance of $17,000 and an ending balance of $12,000. During the year, the company purchased $55,000 of direct materials. Direct labor for the year totaled $121,000, while manufacturing overhead amounted to $151,000. The Work in Process Inventory account had a beginning balance of $22,000 and an ending balance of $21,000. Assume that Raw Materials Inventory contains only direct materials. Compute the Cost of Goods Manufactured for the year. (Hint: The first step is to calculate the direct materials used during the year.) ~arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education