
A
q TC VC FC
0 4
1 8
2 10
3 14
4 20
5 28
6 38
b) Assuming that the market price is p = 8, what are the quantity produced by each firm and the profit it makes?
The variable cost can be calculated by using the below formula:
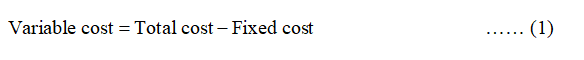
If Q is 1 and TC is 8, then the variable cost can be calculated by using equation (1) as follows:
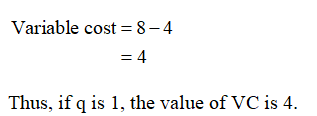
The average variable cost can be calculated by using the below formula:
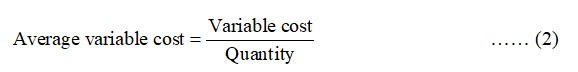
If Q is 1 and VC is 4, then the average variable cost can be calculated by using equation (2) as follows:
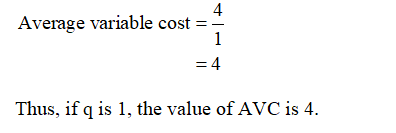
The average total cost can be calculated by using the below formula:
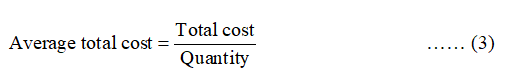
If Q is 1 and TC is 8, then the average total cost can be calculated by using equation (3) as follows:
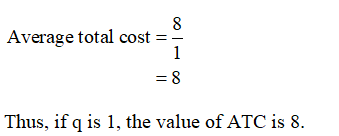
Marginal cost can be calculated by using the below formula:
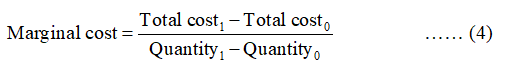
If Q is 1, then the marginal cost can be calculated by using equation (4) as follows:
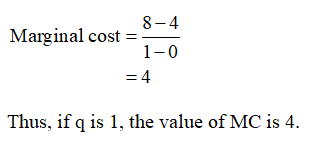
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 10 images

- A perfectly competitive firm will choose to shut down when the average total cost intersects the marginal cost curve below the average variable cost curvearrow_forwarda.Suppose a perfectly competitive firm can produce10000 bushels of corn a year at an output at which marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost. The market price of corn per bushel is $2. The firm's total costs per year are $30000 and fixed costs per year are $15000. Show and explain which of the following is true: In the short run, this firm should a) Produce 20000 bushels to try to increase economic profit. b) Produce 10000 bushels of corn because, although they are losing money, they are losing less than if they shut down. c)Shut down. d) Continue producing until the price of corn increases. b.A perfectly competitive firm, with MC=q operates in a market character,zed by the following market demand and supply conditions: Demand: Q=20000-100P Supply: Q=100P How much output does this competitive firm produce to maximize profit? Show your work graphically and algebraically.arrow_forwardIn competitive markets economic profit becomes zero in the long-run. However, it is also possible for some firms to earn a greater accounting profit and to enjoy a higher producer surplus than other firms. How is it possible?arrow_forward
- QUESTION 6 Use the model of the perfectly competitive firm shown below to fill in the following blanks: $ 8 7 6 сл 5 4 3 2 1 MC If the firm produces Q* units their profit will be $ If the firm shown above shuts down their profit will be $ The profit maximizing firm should In the long run firms will ATC 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 AVC MR Q this market, this will cause market price toarrow_forwardThe cost curves below are for a firm competing in a perfectly competitive industry. If the market price is $7.50, a profit-maximizing firm would: Price and cost 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 2 MC y A A 1 B a 10 11 12 ATC AVC 13 Quantity Produce between 10 and 11, for a positive economic profit Produce about 9, for an economic profit of over $9 Produce between 10 and 11, for an economic profit of about $0 Produce about 9, for an economic profit of less than $9 Produce about 10, for an economic profit of about $20arrow_forwardIn the short run, if a perfectly competitive firm chooses to produce, then its profits are maximized by producing the quantity of output where marginal cost equals marginal revenue. True Falsearrow_forward
- Consider the graph of a firm in a perfectly competitive market to answer the question below: P MC АТС 7 3 MR 10 What is the value of this firm's revenue if it operates where MR=MC? Enter your answer as a number below. Do not include a "$" sign.arrow_forwardConsider the perfectly competitive market for sports jackets. The following graph shows the marginal cost ( MCMC ), average total cost ( ATCATC ), and average variable cost ( AVCAVC ) curves for a typical firm in the industry.arrow_forwardA perfectly competitive firm has total revenue and total cost curves given by: TR = 800Q TC = 4,000 + 12Q + 2 Q2 a. Find the profit-maximizing output for this firm. b. What profit does the firm makearrow_forward
- Use the following table to answer the next question. The table shows the total costs associated with varying levels of output produced by a perfectly competitive firm. Output 0 1 2 3 4 Total Cost $1,400 1,600 2,000 2,600 3,500 4,800 If the product sells for $800 a unit, the firm's profit-maximizing output isarrow_forwardq 53 Suppose jumbo packs of notepads are sold in a perfectly competitive market for 60. To produce jumbo packs of notepads, an individual firm has a cost function of C = 2 + Q2. What is the firm’s profit? a. 798 b 698 c 898 d 998arrow_forwardWhat does (Box A + Box B) represent for this firm? A Marginal Revenue B Marginal Cost C Average Total Cost D Total Revenue E Total Cost F Profitarrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





