
A pathologist has been studying the frequency of bacterial colonies within the field of a microscope using samples of throat cultures from healthy adults. Long-term history indicates that there is an average of 2.98 bacteria colonies per field. Let r be a random variable that represents the number of bacteria colonies per field. Let O represent the number of observed bacteria colonies per field for throat cultures from healthy adults. A random sample of 100 healthy adults gave the following information.
| r | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 or more |
| O | 13 | 13 | 27 | 18 | 21 | 8 |
| e−??r |
| r! |
| P(0) | = |
| P(1) | = |
| P(2) | = |
| P(3) | = |
| P(4) | = |
| P(5 or more) | = |
Compute the expected number of colonies E = 100P(r) for r = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 or more. (Round your answers to one decimal place.)
| E(0) | = |
| E(1) | = |
| E(2) | = |
| E(3) | = |
| E(4) | = |
| E(5 or more) | = |
Compute the sample statistic
|
|||
and the degrees of freedom. (Round your test statistic to three decimal places.)
| d.f. | = |
| ?2 | = |
Hello
According to Bartleby Guidelines we are supposed to answer only first three sub parts so for rest of solution kindly post it again or with specific instructions.
Thank you.
Part (a):
The probability mass function for Poisson distribution is as follows:
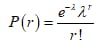
Here, λ is 2.98 it is the average number of bacteria colonies per field.
Step by stepSolved in 10 steps with 8 images

- The average worker at a local brake manufacturer produces 10 brakes per day (other statistical information was not known). An industrial psychologist was hired to increase worker productivity and a new assembly method was designed and tested in a sample of workers. Identify the appropriate test. Select one: a. independent samples t test b. z test c. single sample t test d. paired samples t testarrow_forwardMagnetic surveying is one technique used by archaeologists to determine anomalies arising from variations in magnetic susceptibility. Unusual changes in magnetic susceptibility might (or might not) indicate an important archaeological discovery. Let x be a random variable that represents a magnetic susceptibility (MS) reading for a randomly chosen site at an archaeological research location. A random sample of 120 sites gave the readings shown in the table below. Magnetic Susceptibility Readings,centimeter-gram-second ✕ 10−6 (cmg ✕ 10−6) Comment MagneticSusceptibility Number ofReadings EstimatedProbability "cool" 0 ≤ x < 10 30 30/120 = 0.25 "neutral" 10 ≤ x < 20 54 54/120 = 0.45 "warm" 20 ≤ x < 30 24 24/120 = 0.20 "very interesting" 30 ≤ x < 40 6 6/120 = 0.05 "hot spot" 40 ≤ x 6 6/120 = 0.05 Suppose a "hot spot" is a site with a reading of 40 or higher. (c) What is the probability that you will need more than five readings to find the first…arrow_forwardRothamsted Experimental Station (England) has studied wheat production since 1852. Each year many small plots of equal size but different soil/fertilizer conditions are planted with wheat. At the end of the growing season, the yield (in pounds) of the wheat on the plot is measured. Suppose for a random sample of years, one plot gave the following annual wheat production (in pounds): 3.81 2.97 5.19 3.40 3.05 2.40 4.35 3.00 4.89 5.23 3.37 4.00 3.84 5.42 5.09 5.03 For this plot, the sample variance is . Another random sample of years for a second plot gave the following annual wheat production (in pounds): 3.53 3.65 3.89 4.19 3.44 3.42 3.58 3.83 3.46 4.32 3.58 3.45 3.77 3.54 3.48 4.07 For this plot, the sample variance is . Test the claim using that the population variance of annual wheat production for the first plot is larger than that for the second plot. Find (or estimate) the P-value of the sample…arrow_forward
- Magnetic surveying is one technique used by archaeologists to determine anomalies arising from variations in magnetic susceptibility. Unusual changes in magnetic susceptibility might (or might not) indicate an important archaeological discovery. Let x be a random variable that represents a magnetic susceptibility (MS) reading for a randomly chosen site at an archaeological research location. A random sample of 120 sites gave the readings shown in the table below. Magnetic Susceptibility Readings,centimeter-gram-second ✕ 10−6 (cmg ✕ 10−6) Comment MagneticSusceptibility Number ofReadings EstimatedProbability "cool" 0 ≤ x < 10 36 36/120 = 0.30 "neutral" 10 ≤ x < 20 48 48/120 = 0.40 "warm" 20 ≤ x < 30 12 12/120 = 0.10 "very interesting" 30 ≤ x < 40 18 18/120 = 0.15 "hot spot" 40 ≤ x 6 6/120 = 0.05 Do the probabilities shown in the table add up to 1? Do the probabilities need to total to 1 a. Yes, they do add to 1. The probabilities must total to…arrow_forwardRothamsted Experimental Station (England) has studied wheat production since 1852. Each year many small plots of equal size but different soil/fertilizer conditions are planted with wheat. At the end of the growing season, the yield (in pounds) of the wheat on the plot is measured. Suppose for a random sample of years, one plot gave the following annual wheat production (in pounds): 3.06 4.97 5.01 4.13 5.02 2.91 3.88 2.55 2.91 5.18 3.68 4.54 2.65 4.14 5.11 3.19 Use a calculator to verify that the sample variance for this plot is s^2=0.923. Another random sample of years for a second plot gave the following annual wheat production (in pounds): 3.61 3.50 3.81 3.89 3.84 3.50 3.53 3.62 3.67 4.05 3.82 4.12 3.75 3.92 4.05 4.01 Use a calculator to verify that the sample variance for this plot is s^2=0.042. Suppose that we test the claim using a=0.01 that the population variance of annual wheat production for the…arrow_forwardMagnetic surveying is one technique used by archaeologists to determine anomalies arising from variations in magnetic susceptibility. Unusual changes in magnetic susceptibility might (or might not) indicate an important archaeological discovery. Let x be a random variable that represents a magnetic susceptibility (MS) reading for a randomly chosen site at an archaeological research location. A random sample of 120 sites gave the readings shown in the table below.arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





