
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
I want to correct answer
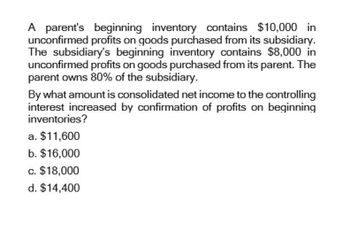
Transcribed Image Text:A parent's beginning inventory contains $10,000 in
unconfirmed profits on goods purchased from its subsidiary.
The subsidiary's beginning inventory contains $8,000 in
unconfirmed profits on goods purchased from its parent. The
parent owns 80% of the subsidiary.
By what amount is consolidated net income to the controlling
interest increased by confirmation of profits on beginning
inventories?
a. $11,600
b. $16,000
c. $18,000
d. $14,400
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 69. A parent owns 80% of its subsidiary, and sells merchandise to its subsidiary at a 25% markup on cost. The subsidiary's ending inventory includes $750,000 purchased from the parent. The subsidiary's beginning inventory includes $825,000 purchased from the parent. What is the effect of the above on the parent's equity in net income of the subsidiary for the current year? a. P15,000 increase b. 70 Yukon C. P15,000 decrease d. no effect rod 75% porcent of the voting common stock of Ontario Corn on January 1 P12,000 increasearrow_forwardin following question solutionarrow_forwardA parent company regularly sells merchandise to its 80%-owned subsidiary. Which of the following statements describes the computation of non-controlling interest income? a. (The subsidiary’s net income + unrealized profits in the ending inventory – unrealized profits in the beginning inventory) x 20% b. The subsidiary’s net income times 20% c. The subsidiary’s net income x 20%) + unrealized profits in the beginning inventory- unrealized profits in the ending inventory d. The subsidiary’s net income + unrealized profits in the beginning inventory – unrealized profits in the ending inventory) x 20%arrow_forward
- A parent company regularly sells merchandise to its 70%-owned subsidiary. Which of the following statements describes the computation of noncontrolling interest share? A. (The subsidiary's net income × 30%) + unrealized profits in the beginning inventory - unrealized profits in the ending inventory B. (The subsidiary's net income + unrealized profits in the ending inventory - unrealized profits in the beginning inventory) × 30% C. (The subsidiary's net income + unrealized profits in the beginning inventory - unrealized profits in the ending inventory) × 30% D. The subsidiary's net income times 30%arrow_forwardkak.3arrow_forwardA subsidiary sold goods costing P1.2 million to its parent for P1.4 million. All of the inventory is held by the parent at year-end. The subsidiary is 80% owned and the parent and subsidiary operate in different tax jurisdictions. The parent pays taxation at 30% and the subsidiary pays taxation at 30%. Calculate any deferred tax asset that arises on the sale of the inventory to the parent. a. P 60,000 c. P48,000 b. P200,000 d. P80,000arrow_forward
- K Company owns 100% of E Company. During the year, Kianapurchased inventory from Elyssa at a mark-up of 20% based on cost.How should the group compute for consolidated cost of sales?a. Cost of Sales of K + Cost of Sales of E– intercompany sales + Realized profit in beginning inventory – Unrealized profit in ending inventory.b. Cost of Sales of K + Cost of Sales of E – intercompany sales – Realized profit in beginning inventory + Unrealized profit in ending inventory.c. Cost of Sales of Kiana + Cost of Sales of Elyssa – Intercompany sales d. Cost of Sales of K + Cost of Sales of Earrow_forwardWhat is the amount of pre-acquisition earnings on the acquisition date consolidated income statement if the parent acquires 90 percent of the subsidiary’s stock and the following income statement accounts exist at the acquisition date? Parent Subsidiary Sales P250,000 P60,000 Cost of Goods Sold 120,000 12,000 Depreciation Expense 10,000 5,000 Operating Expenses 40,000 8,000 Income Tax Expense 32,000 14,000 2. Using the same information in No. 1, what is the imputed value of a subsidiary if the parent pays P56,000 for 80 percent of the subsidiary’s stock? Use the following information for question 3 and 4: Marksman acquired 100 percent of Tribal Transit for P275,000. At the date of acquisition, Fast Transit…arrow_forwardDuring 20x9, PP Corporation recorded sales of inventory costing P500,0000 to SS Company, its wholly owned subsidiary, on the same terms as sales made to third parties. At December 31,20x9, SS held one-fifth of this goods inventory. The following information pertains to PP and SS’s sales for 20x9: (see image below) In its 20x9 consolidated income statement, what amount should PP report as cost of sales?arrow_forward
- 2. Martindale Company, a 100% owned subsidiary of Weisman Corporation, sells inventory to Weisman at a 20% profit on selling price. The following data are available pertaining to inter-company purchases by Weisman: Inter-company sales: Unsold at year end (based on selling price): 2020: $18,000 2020: $4,000 2021: $19,400 2021: $6,000 2022: $21,500 2022: $8,000 Martindale's profit numbers were $125,000, $142,000 and $265,000 for 2020, 2021, and 2022, respectively. Weisman received dividends from Martindale of $25,000 for 2020 and 2021, and $30,000 for 2022. Assume Weisman uses the equity method to account for its investment in Martindale. What is the balance in pre-consolidation Income (loss) from subsidiary for 2022? Select one: A. $268,600 B. $235,000 C. $265,400 D. $264,600arrow_forwardThe non-controlling interest in consolidated income when the selling affiliate isan 80% owned subsidiary is calculated by multiplying the non-controllingminority delete minority ownership percentage by the subsidiary’s reported netincome. A. Plus realized profit in ending inventory less realized profit in beginning inventory B. Less unrealized profit in ending inventory plus realized profit in beginning inventory C. Less realized profit in ending inventory plus realized profit in beginning inventory. D. Plus unrealized profit in ending inventory less unrealized profit in beginning inventoryarrow_forward3. Set out below are the draft income statements of P and its subsidiary S for the year ended 31 December 20X7. On the 1 January 20X6 P purchased 75% of the ordinary shares in S. Revenue Cost of sales and expenses Gross profit Operating expenses Profit from operations Finance costs Profit before taxation Tax Profit for the year P $000 300 (180) 120 (47) 73 73 (25) 48 S $000 150 (70) 80 P values non-controlling interest using the fair value method. (23) 57 (2) 55 (16) 39 During the year S sold goods to P for $20,000, making a mark up of one third. Only 20% of these goods were sold before the end of the year, the rest were still in inventory. Prepare the consolidated income statement for the year ended 31 December 20X7arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education