
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
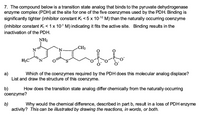
Transcribed Image Text:7. The compound below is a transition state analog that binds to the pyruvate dehydrogenase
enzyme complex (PDH) at the site for one of the five coenzymes used by the PDH. Binding is
significantly tighter (inhibitor constant K < 5 x 10-10 M) than the naturally occurring coenzyme
(inhibitor constant K, < 1x 10-5 M) indicating it fits the active site. Binding results in the
inactivation of the PDH.
NH2
CH3
H3C
N.
а)
List and draw the structure of this coenzyme.
Which of the coenzymes required by the PDH does this molecular analog displace?
transition state analog differ chemically from
b)
coenzyme?
How does
naturally occurring
b)
activity? This can be illustrated by drawing the reactions, in words, or both.
Why would the chemical difference, described in part b, result in a loss of PDH enzyme
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
The given molecular analogue name is Thiamine thiazolone pyrophosphate. It is a transition state analogue. It has high affinity for pyruvate dehydrogenase.
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex causes oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA. It requires five co-factors:- TPP, lipoamide, FAD, NAD+ and coenzyme A.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The catalytic efficiency of many enzymes depends on pH. Chymotrypsin, which has a well-known catalytic mechanism, shows a maximum value of kcat/Km at pH 8.0. A) Draw a pH curve of chymotrypsin activity over the pH range of 5 to 10 and briefly explain the rationale within the context of catalysis for your depiction. In particular, note how kcat and Km may change over this pH range. B) Enzymes of the a-amylase family catalyze a reaction by forming a covalent intermediate analogous to chymotrypsin, but to a conserved aspartate residue. Illustrate a catalytic mechanism containing a tetrahedral intermediate for a glycogen debranching enzyme based upon its potential membership in the a-amylase family. (don’t need to draw a whole glycogen)arrow_forwardThe active site of an enzyme that uses a general acid-base catalytic mechanism contains a Glu and an Asp residue (both of which are essential for catalysis) with pKa values of 5.9 and 4.5, respectively. If the enzyme is found in the lysosome (pH = 5.2), which residue will act as the general acid and which will act as the general base during the initial steps of the reaction?arrow_forwardIdentify each reaction catalyzed by (a) a nucdeotidase; (b) a phosphorylase; (c) a phosphoribosyltransferase. GMP A D E Guanine Guanosine Farrow_forward
- Which of the following statements about de novo purine synthesis is true? (A) Purine nucleotides are formed by separately synthesizing the phosphorylated ribose and the purine ring and then joining them together.(B) GMP is formed first and is used as a precursor to form AMP.(C) The synthesis of AMP from inosinate is driven forward by ATP hydrolysis. (D) GMP synthetase uses NADPH and glutamine to modify the inosinate ring to form GMP.(E) Replacement of the C-1 PPi on PRPP with an amine is required to construct the purine ring on the ribose sugar.arrow_forwardPhosphoglycerate mutase transfers a phosphoryl group from C3 of 3-phosphoglycerate to C2 position to give 2-phosphoglycerate. Why is it important to have the phosphoryl group at position 2 rather than at C3? It was observed that the activity of some preparations of the enzyme could be increased if catalytic (very small) amount of 2, 3-bisphosphoglycerate was added to the enzyme. Give a possible explanation for this observation.arrow_forwardIf G6P is labeled at its C2 position, where will the label appear in the products of the pentose phosphate pathway?arrow_forward
- You are studying the kinetics of a novel competitive inhibitor of ATP-citrate lyase that can be used to prevent obesity. What is likely true about this inhibitor? (A) This inhibitor lowers the Vmax of ATP-citrate lyase. (B) The inhibitor likely looks structurally similar to acetyl CoA. (C) The inhibitor binds to an allosteric region on ATP-citrate lyase and prevents catalysis. (D) You can distinguish between an uninhibited and inhibited enzyme by comparing the x-intercepts on a Lineweaver-Burk plot. (E) This inhibitor lowers the KM of ATP-citrate lyase. Related to this question, you should also be able to: • explain the function of ATP-citrate lyase and why inhibition would prevent obesity • interpret Michaelis-Menten & Lineweaver-Burk plots related to this question • explain the differences between a competitive and non-competitive inhibitorarrow_forwardCoenzyme-dependent enzymes can catalyze the general transformations shown below.What would be the best coenzymes to use for the two steps in the scheme, and why? Then, proposean enzyme-catalyzed method for step A to proceed without a coenzyme. Show this enzymecatalyzed mechanism for step A that does not require the coenzyme. You can abbreviate acidicamino acid residues “Enz–B–H” and basic residues “ B–Enz”.arrow_forwardPLP is a cofactor for a number of enzymes involved in amino acid metabolism. Give an example of reaction in which PLP participates in cleavage of the a, b, and c bonds of an amino acid, as diagrammed in shown Fig.arrow_forward
- Which of the following intermediates of the TCA cycle has 5 carbons? (Hint: You don't need to have memorized specific structures for this question, just recall what molecules the TCA cycle starts with and where in the cycle carbons are lost as CO2 ). a) Fumarate b) None of the above c) Succinyl CoA d) Citrate e) Oxaloacetatearrow_forwardAn enzyme with an unknown reaction mechanism has been isolated and is being investigated in the lab. Based on the information given below, propose one or more specific catalytic strategies (covalent, acid-base, and/or metal ion catalysis) used by the enzyme and predict the role of each catalytic residue in the enzyme's reaction cycle. Explain your reasoning. (a) Mapping of the active site with substrate analog showed that it contains a critical Ser residue. (b) Studies conducted in buffers of varying pH showed that the enzyme is sensitive to pH changes and has two catalytically important residues with pKa values of ~10.5 and ~4.0. (c) Substitution of the Ser residue with Ala resulted in a five-fold increase in the KM but had no effect on the kcat. (d) The reaction rate was insensitive to the addition of metal chelators such as EDTA and EGTA.arrow_forward5arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON