Question
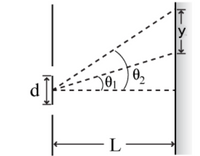
A laser beam is incident on two slits with separation d = 0.032 mm. A screen is placed L = 3.8 m from the slits. The wavelength of the laser light is λ = 5250 Å. θ1 and θ2 are the angles to the first and second bright fringes above the center of the screen
Part (a) Express sin(θ1) in terms of d and λ.
sin(θ1) =?
Part (b) Express sin(θ2) in terms of d and λ.
sin(θ2) = ?
Part (c) Express the distance between the two bright fringes on the screen, y, in terms of θ1, θ2 and L.
y =?
Part (d) Solve for the numerical value of y in meters.
y =?
Transcribed Image Text:L-
kーy
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A perfectly flat piece of glass (n = 1.50) is placed over a perfectly flat piece of black plastic (n = 1.20) as shown in the figure a. They touch at A. Light of wavelength 600 nm is incident normally from above. The location of the dark fringes in the reflected light is shown on the sketch of figure b. (a) How thick is the space between the glass and the plastic at B? (b) Water (n = 1.33) seeps into the region between the glass and the plastic. How many dark fringes are seen when all the air has been displaced by water? (The straightness and equal spacing of the fringes is an accurate test of the flatness of the glass.) (a) (b) A Glass =1.50 Plastic n=1.20 Barrow_forwardA flat piece of glass is held stationary and horizontal above the highly polished, flat top end of a 9.00-cm-long vertical metal rod that has its lower end rigidly fixed. The thin film of air between the rod and glass is observed to be bright by reflected light when it is illuminated by light of wavelength 515 nm. As the temperature is slowly increased by 25.5°C, the film changes from bright to dark and back to bright 200 times. What is the coefficient of linear expansion of the metal?arrow_forwardIn the figure, two isotropic point sources S1 and S2 emit light in phase at wavelength A and at the same amplitude. The sources are separated by distance 2d = 3.0O A. They lie on an axis that is parallel to an x axis, which runs along a viewing screen at distance D = 20.0 A. The origin lies on the perpendicular bisector between the sources. The figure shows two rays reaching point Pon the screen, at position Xp. (a) At what value of xp do the rays have the minimum possible phase difference? (b) What multiple of A gives that minimum phase difference? (c) At what value of xp do the rays have the maximum possible phase difference (show "-1" if infinity)? What multiple of A gives (d) that maximum phase difference and (e) the phase difference when xp = 3.00 A? P Screen D S1 (a) Number i Units (b) Number i Units (c) Number i Units (d) Number i Units (e) Number i Unitsarrow_forward
- Two antennas located at points A and B are broadcasting radio waves of frequency 96.0 MHz, perfectly in phase with each other. The two antennas are separated by a distance d= 6.20 m. An observer, P, is located on the x axis, a distance x= 84.0 m from antenna A, so that APB forms a right triangle with PB as hypotenuse. What is the phase difference between the waves arriving at P from antennas A and B? A P X B 4.594x10-¹ rad Computer's answer now shown above. You are correct. Your receipt no. is 158-6031 > Previous Tries Now observer P walks along the x axis toward antenna A. What is P's distance from A when he first observes fully destructive interference between the two waves? 1.203 m As P gets closer A, the path length difference gets larger. What's the smallest path length difference that gives destructive interference? Submit Answer Tries 0/6 Submit Answer Incorrect. Tries 1/6 Previous Tries If observer P continues walking until he reaches antenna A, at how many places along the x…arrow_forwardYou measure three segments of the distance between a diffraction slit an the screen on which the pattern forms: x1 = (15.8 ± 0.2) cm, x2 = (6.7 ± 0.1) cm, and x3 = (11.3 ± 0.1). What is the uncertainty of the total distance x1 + x2 + x3? Group of answer choices 0.4 cm 0.5 cm 0.2 cm 0.3 cm 0.1 cmarrow_forwardWhat visible wave length will be reflected in this scenario: A 700 nm thick soap film floats on a plate. From the air, white light is struck onto the film at a normal incidence. the wavelength of visible light to air is 400 nm to 700 nm. The index of the soap film is 1.74 and 1.58 for the plate.arrow_forward
- Two antennas located at points A and B are broadcasting radio waves of frequency 104.0 MHz. The signals start in phase with each other. The two antennas are separated by a distance d = 8.7 m. An observer is located at point P on the x axis, a distance x = 110.0 m from antenna A. The points A, P, and B form a right triangle. Now observer P walks along the x axis toward antenna A. What is P's distance from A when they first observe fully constructive interference between the two waves?arrow_forwardA flat piece of glass is held stationary and horizontal above the highly polished, flat top end of a 12.0-cm-long vertical metal rod that has its lower end rigidly fixed. The thin film of air between the rod and glass is observed to be bright by reflected light when it is illuminated by light of wavelength 490 nm. As the temperature is slowly increased by 21.5°C, the film changes from bright to dark and back to bright 200 times. What is the coefficient of linear expansion of the metal? °C-1arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios