
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
15th Edition
ISBN: 9781337408332
Author: Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
PLEASE tell me what each pedigree diagram is. so which one is most likely to show a family with Haemophilia A? most likely to show a family with Gaucher Disease? most likely to show a family with Sickle Cell Anaemia? most likely to show a family with Achondroplasia? most likely to show a family with Goltz Syndrome?
What is the most likely inheritance pattern shown in image B, below?
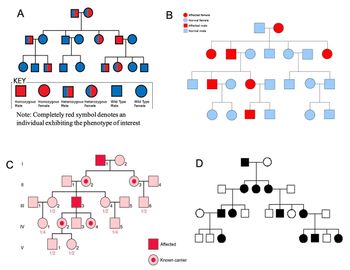
Transcribed Image Text:A
KEY_
Homozygous Homozygous Heterozygous Heterozygous Wild Type
Male
Female
Male
Female
Male
Wild Type
Female
Note: Completely red symbol denotes an
individual exhibiting the phenotype of interest
CI
III
=
IV
1/4
>
B
Affected female
Normal female
Affected male
Normal male
O
D
2
3
5
1/2
1/2
1/2
1/2
4
1/4
1/2
Affected
Known carrier
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- ✔Listen 10 11 17 I Sex linked recessive Autosomal recessive Sex linked dominant Autosomal dominant {i 15 $arrow_forwardKlinefelter syndrome (XXY) can most be easily diagnosed by _______. a. pedigree analysis. b. aneuploidy c. karyotyping d. phenotypic treatmentarrow_forwardA couple was referred for genetic counseling because they wanted to know the chances of having a child with dwarfism. Both the man and the woman had achondroplasia (MIM 100800), the most common form of short-limbed dwarfism. The couple knew that this condition is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait, but they were unsure what kind of physical manifestations a child would have if it inherited both mutant alleles. They were each heterozygous for the FGFR3 (MIM 134934) allele that causes achondroplasia. Normally, the protein encoded by this gene interacts with growth factors outside the cell and receives signals that control growth and development. In achrodroplasia, a mutation alters the activity of the receptor, resulting in a characteristic form of dwarfism. Because both the normal and mutant forms of the FGFR3 protein act before birth, no treatment for achrondroplasia is available. The parents each carry one normal allele and one mutant allele of FGRF3, and they wanted information on their chances of having a homozygous child. The counsellor briefly reviewed the phenotypic features of individuals with achondroplasia. These include facial features (large head with prominent forehead; small, flat nasal bridge; and prominent jaw), very short stature, and shortening of the arms and legs. Physical examination and skeletal X-ray films are used to diagnose this condition. Final adult height is approximately 4 feet. Because achondroplasia is an autosomal dominant condition, a heterozygote has a 1-in-2, or 50%, chance of passing this trait to his or her offspring. However, about 75% of those with achondroplasia have parents of average size who do not carry the mutant allele. In these cases, achondroplasia is due to a new mutation. In the couple being counseled, each individual is heterozygous, and they are at risk for having a homozygous child with two copies of the mutated gene. Infants with homozygous achondroplasia are either stillborn or die shortly after birth. The counselor recommended prenatal diagnosis via ultrasounds at various stages of development. In addition, a DNA test is available to detect the homozygous condition prenatally. What is the chance that this couple will have a child with two copies of the dominant mutant gene? What is the chance that the child will have normal height?arrow_forward
- A couple was referred for genetic counseling because they wanted to know the chances of having a child with dwarfism. Both the man and the woman had achondroplasia (MIM 100800), the most common form of short-limbed dwarfism. The couple knew that this condition is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait, but they were unsure what kind of physical manifestations a child would have if it inherited both mutant alleles. They were each heterozygous for the FGFR3 (MIM 134934) allele that causes achondroplasia. Normally, the protein encoded by this gene interacts with growth factors outside the cell and receives signals that control growth and development. In achrodroplasia, a mutation alters the activity of the receptor, resulting in a characteristic form of dwarfism. Because both the normal and mutant forms of the FGFR3 protein act before birth, no treatment for achrondroplasia is available. The parents each carry one normal allele and one mutant allele of FGRF3, and they wanted information on their chances of having a homozygous child. The counsellor briefly reviewed the phenotypic features of individuals with achondroplasia. These include facial features (large head with prominent forehead; small, flat nasal bridge; and prominent jaw), very short stature, and shortening of the arms and legs. Physical examination and skeletal X-ray films are used to diagnose this condition. Final adult height is approximately 4 feet. Because achondroplasia is an autosomal dominant condition, a heterozygote has a 1-in-2, or 50%, chance of passing this trait to his or her offspring. However, about 75% of those with achondroplasia have parents of average size who do not carry the mutant allele. In these cases, achondroplasia is due to a new mutation. In the couple being counseled, each individual is heterozygous, and they are at risk for having a homozygous child with two copies of the mutated gene. Infants with homozygous achondroplasia are either stillborn or die shortly after birth. The counselor recommended prenatal diagnosis via ultrasounds at various stages of development. In addition, a DNA test is available to detect the homozygous condition prenatally. Should the parents be concerned about the heterozygous condition as well as the homozygous mutant condition?arrow_forwardA couple was referred for genetic counseling because they wanted to know the chances of having a child with dwarfism. Both the man and the woman had achondroplasia (MIM 100800), the most common form of short-limbed dwarfism. The couple knew that this condition is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait, but they were unsure what kind of physical manifestations a child would have if it inherited both mutant alleles. They were each heterozygous for the FGFR3 (MIM 134934) allele that causes achondroplasia. Normally, the protein encoded by this gene interacts with growth factors outside the cell and receives signals that control growth and development. In achrodroplasia, a mutation alters the activity of the receptor, resulting in a characteristic form of dwarfism. Because both the normal and mutant forms of the FGFR3 protein act before birth, no treatment for achrondroplasia is available. The parents each carry one normal allele and one mutant allele of FGRF3, and they wanted information on their chances of having a homozygous child. The counsellor briefly reviewed the phenotypic features of individuals with achondroplasia. These include facial features (large head with prominent forehead; small, flat nasal bridge; and prominent jaw), very short stature, and shortening of the arms and legs. Physical examination and skeletal X-ray films are used to diagnose this condition. Final adult height is approximately 4 feet. Because achondroplasia is an autosomal dominant condition, a heterozygote has a 1-in-2, or 50%, chance of passing this trait to his or her offspring. However, about 75% of those with achondroplasia have parents of average size who do not carry the mutant allele. In these cases, achondroplasia is due to a new mutation. In the couple being counseled, each individual is heterozygous, and they are at risk for having a homozygous child with two copies of the mutated gene. Infants with homozygous achondroplasia are either stillborn or die shortly after birth. The counselor recommended prenatal diagnosis via ultrasounds at various stages of development. In addition, a DNA test is available to detect the homozygous condition prenatally. What if the couple wanted prenatal testing so that a normal fetus could be aborted?arrow_forwardPlease draw it out so I understand how it's suppose to be drawnarrow_forward
- Classes SBI3C1-2 rr x rr Meet - rz pQLSeUir31BTTSeUl8EYpVNYpajrmzBg_g0n6oMivineMfM4k0w/viewform rr x Rr Classwork O Rrx Rr ORR X Rr Genet X SBI3C1-2 Genetics Two parents were known to be right-handed. Assuming that right-handed (R) is dominant to left-handed (r), what would be the genotypes of the parents if their son is left-handed? Google M Post Atte Sp * 1 poirarrow_forward70 T 꿈 ㅁ ㅁ 이어어어어어어 In the pedigree shown, indicate whether each of the following inheritance patterns is possible by selecting YES or NO from the appropriate drop down menu. Y-linked Autosomal Recessive Autosomal Dominant X-linked Recessive X-linked Dominant ()arrow_forwardHelparrow_forward
- Match the following with their appropriate descriptor: 1. Homozygous Dominant hh xhy 2. Heterozygous Dominant 3. Homozygous Recessive HH Hh 4. Sex-Linked >arrow_forwardUnaffected father Camier mother XY Unaffected Afected Carrier Unaffeded Unaffected daugkter U.S. National Lbrany of Mediche Carrier Affected son daughter son In humans, as well as in many other animals and some plants, the sex of the individual is determined by sex chromosomes. The sex chromosomes are one pair of non-homologous chromosomes: XX represents a female, while XY represents a male. When a gene for a specific trait is attached to the X or Y chromosome, we say it is sex-linked, and when it is attached to the X chromosome, we say it is X-linked. Alleles for these linked traits, such as hemophilia or color blindness, crosses, may be recessive or dominant. Hemophilia is an X-linked, recessive trait. The recessive allele for hemophilia is actually a mutated version of the normal alllele but it can still be passed on through generations. Imagine a female is a carrier for hemophilia; her genotype is Xx She is married to a man who does not have hemophilia. What conclusion is NOT valid…arrow_forward40arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...
Biology
ISBN:9781337408332
Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...
Biology
ISBN:9781305073951
Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning
