
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Draw the structural formulas for the major product(s) resulting from the following reaction
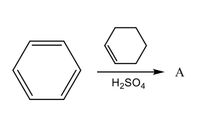
Transcribed Image Text:### Conversion of Benzene to Cyclohexane
**Chemical Reaction:**
The displayed diagram is a schematic representation of a chemical reaction where benzene is converted into another compound labeled as 'A' in the presence of sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄).
**Structural Representation:**
1. **Reactant:**
- The structure on the left is benzene, represented by a hexagonal ring consisting of alternating double bonds, illustrating its aromatic property.
2. **Reagent:**
- Beneath the arrow, the reagent used is sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄).
3. **Product:**
- The structure on the right demonstrates another ring structure with no double bonds, indicating it's cyclohexane. This is labeled as compound 'A'.
**Process Explanation:**
- **Benzene (C₆H₆)** is an aromatic hydrocarbon with accessible delocalized electrons in its π-bond system.
- **Sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄)** often acts as a catalyst or acid in organic reactions.
**Reaction Type:**
This transformation suggests the hydrogenation of benzene to cyclohexane. The presence of sulfuric acid typically indicates an acidic environment which could facilitate such a reaction, although hydrogen (H₂) would also be commonly involved in a practical scenario to provide the additional H atoms needed for full saturation of the benzene ring.
In conclusion, this explains the conversion of benzene (a stable aromatic compound) to cyclohexane (a saturated, non-aromatic compound) when subjected to sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Draw the structure(s) of the major organic product(s) of the following reaction. aqueous H₂SO + KCNarrow_forwardGive the alkene and reagent that are needed to synthesize the following compoundarrow_forwardGive the main organic product that would form after the following reaction. OMe OMe H₂O H*arrow_forward
- Draw a structural formula for the substitution product of the reaction shown below. Br A CH3 CH₂CH₂OHarrow_forwardProvide the structure of the major product which results from the following reaction.arrow_forward6. Complete the following reactions by providing the intermediate(s) and product(s). CH3OH, Harrow_forward
- Complete the following reactions. Only include the major products and any byproducts (H2O) but no minor products. Please use either full structural diagrams, don't use Skeletal/line diagrams.arrow_forwardAnswer the question below the reaction. H3C H3C H3C OH H3C In the second step of the reaction mechanism, which of the following is formed? CH3 CH3 CH3 + Excess NH4Cl CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 H₂SO4 CH3 CI ха +H2Oarrow_forward6. What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction? Brzarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY