
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
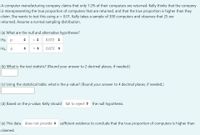
Transcribed Image Text:### Statistical Hypothesis Testing Example
A computer manufacturing company claims that only 7.2% of their computers are returned. Kelly suspects that the company is underreporting and believes the true proportion is higher. She decides to test this hypothesis at a significance level (\(\alpha\)) of 0.01. Kelly samples 300 computers and finds that 25 are returned. Assume a normal sampling distribution.
#### (a) Null and Alternative Hypotheses
- **Null Hypothesis (\(H_0\))**: \(p = 0.072\)
- **Alternative Hypothesis (\(H_A\))**: \(p > 0.072\)
#### (b) Test Statistic
Kelly calculates the test statistic, which should be rounded to two decimal places.
#### (c) p-value
Using a statistical table, she finds the p-value, rounded to four decimal places.
#### (d) Decision Based on p-value
Kelly decides to "fail to reject" the null hypothesis based on the p-value.
#### (e) Conclusion
The data "does not provide" sufficient evidence to conclude that the true proportion of computers returned is higher than the company claims.
This exercise illustrates the process of hypothesis testing in statistics, emphasizing the importance of understanding how to interpret statistical data to make informed decisions.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A Gallup survey based on telephone and face-to-face interviews with 4,220 adults in China, aged 15 and older suggests that 30% smoke regularly or occasionally. The following is also noted "one can say with 95% confidence that the maximum margin of sampling error is 2.2 percentage points". Which of the following is true based on the results of this survey? a. We are 95% confident that 27.8 % to 32.2 % of all Chinese adults smoke. b. If the sample size was larger, the margin of error would be larger as well. c.We are 95% confident that 25.6% to 34.4% of all Chinese adults smoke. d. Exactly 30% of all Chinese adults smoke. e. If we were to randomly sample another group of 4,220 Chinese adults we would find that exactly 30% of them smoke as well.arrow_forwardAfter the political ad campaign, pollsters check the mayor's positives. They test the hypothesis that the ads produced no change against the alternative that the positives are now above 47% and find a P-value of 0.283. Which conclusion is appropriate? Explain. Choose the correct answer below. O A. There is a 28.3% chance that natural sampling variation could produce poll results at least as far above 47% as these if there is really no change in public opinion. There is a 28.3% chance that the poll they conducted is correct. O B. O C. There is a 71.7% chance that the ads worked. O D. There is a 28.3% chance that the ads worked.arrow_forward#1arrow_forward
- 1. In a study of perception, 110 men are tested and 24 are found to have red/green color blindness (based on data from USA Today). Assume that this was done in a simple random manner. A 95% confidence interval estimate of the proportion of all men with red/green color blindness was found to be 0.14 to 0.30. If we learn that the actual population proportion of men with red/green colorblindness is equal to 0.12, then what can we conclude? A. The confidence interval was wrong. B. We would need to see the sample data to make any conclusions Pick either answer A or B as your answer and show your work to go with itarrow_forwardViolation of which assumption below for the two-factor ANVOA is not a cause for concern with large sample sizes? a. The populations from which the samples are selected must have equal variances. b. The populations from which the samples are selected must be normal. c. A violation of any assumption below would be a concern, even with large sample sizes. d. The observations within each sample must be independent.arrow_forwardA computer manufacturing company claims that only 7.2% of their computers are returned. Kelly thinks that the company is misrepresenting the true proportion of computers that are returned, and that the true proportion is higher than they claim. She wants to test this using a = 0.01. Kelly takes a sample of 255 computers and observes that 23 are returned. Assume a normal sampling distribution. (a) What are the null and alternative hypotheses? Но: р 0.072 + HA: p 0.072 + (b) What is the test statistic? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places, if needed.) (c) Using the statistical table, what is the p-value? (Round your answer to 4 decimal places, if needed.) (d) Based on the p-value, Kelly should fail to reject + the null hypothesis. (e) This data does not provide + sufficient evidence to conclude that the true proportion of computers is higher than claimed.arrow_forward
- A sociologist is studying the age of the population in Blue Valley. Ten years ago, the population was such that 19% were under 20 years old, 14% were in the 20- to 35-year-old bracket, 33% were between 36 and 50, 23% were between 51 and 65, and 11% were over 65. A study done this year used a random sample of 210 residents. This sample is given below. At the 0.01 level of significance, has the age distribution of the population of Blue Valley changed?Under 20 20 - 35 36 - 50 51 - 65 Over 6529 27 67 65 22(i) Give the value of the level of significance. State the null and alternate hypotheses.H0: The population 10 years ago and the population today are independent.H1: The population 10 years ago and the population today are not independent.H0: The distributions for the population 10 years ago and the population today are the same.H1: The distributions for the population 10 years ago and the population today are different. H0: Time ten years ago and today are independent.H1: Time ten years…arrow_forwardAssuming that other factors are held constant, which approach would tend to increase the likelihood of rejecting the null hypothesis? a. Decrease the sample mean difference. b. Increase the sample variance. c. Increase the sample mean difference. d. Decrease the sample size.arrow_forwardIn a survey of 180 females who recently completed high school, 75% were enrolled in college. In a survey of 160 males who recently completed high school,70 % were enrolled in college. At a=.009, can you reject the claim that there is no difference in the proportion of college enrollees between the two groups? Assume the random samples are independent. Complete parts (a) through (e).arrow_forward
- State the null and alternate hypothesis. Will you use a left tail, right tail or 2 tailed test? Identify the sampling distribution to be used: standard normal, Student’s t or chi squared. Find the value of the test statistic. Find the P-Value. Based on your answers, shall we reject or accept the null hypothesis? Write the conclusion in the context of the problem.arrow_forwardI need the solution for (d) pleasearrow_forwardYou are deciding whether to employ a z procedure or a t procedure to test hypotheses about the mean of a population using a significance level of 0.05 for a sample size of 50. Which of the following statements is correct? Question 17 options: You should not use the t procedure, because the population does not have a Normal distribution. You may use the z procedure, but only if you use the sample standard deviation. You may not use the z procedure because you know the population standard deviation. You should use the t procedure, provided you do not know the population standard deviation.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman