
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
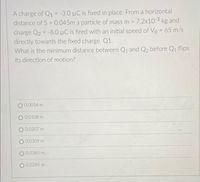
Transcribed Image Text:A charge of Q1 = -3.0 µC is fixed in place. From a horizontal
distance of S = 0.045m a particle of mass m 7.2x103 kg and
charge Q2 = -8.0 µC is fired with an initial speed of Vo = 65 m/s
directly towards the fixed charge Q1.
What is the minimum distance between Q1 and Q2 before Q1 flips
%3D
its direction of motion?
O 0.0054 m
O 0.0108 m
O 0.0207 m
O 0.0309 m
0.0385 m
O 0.0285 m
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Given:
Solution:
We know that, from the conservation of energy we have:
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two small metallic spheres, each of mass m = 0.30 g, are suspended as pendulums by light strings from a common point as shown in the figure below. The spheres are given the same electric charge, and it is found that they come to equilibrium when each string is at an angle of 0 = 8.2° with the vertical. If each string has length L = 40.0 cm, what is the magnitude of the charge on each sphere? L m nCarrow_forwardA small sphere of mass m = 6.60 g and charge q1 = 31.0 nC is attached to the end of a string and hangs vertically as in the figure. A second charge of equal mass and charge q2 = −58.0 nC is located below the first charge a distance d = 2.00 cm below the first charge as in the figure. A rope hangs vertically down from a ceiling with positive charge q1 at its end. Negative charge q2 is a distance d directly below q1. (a) Find the tension in the string. Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. N(b) If the string can withstand a maximum tension of 0.180 N, what is the smallest value d can have before the string breaks? cmarrow_forwardneed help with this problemarrow_forward
- A point charge q1=5.00μC is held fixed in space. From a horizontal distance of 8.00 cmcm, a small sphere with mass 4.00×10^−3 kg and charge q2=+2.00μC is fired toward the fixed charge with an initial speed of 45.0 m/sm/s. Gravity can be neglected. What is the acceleration of the sphere at the instant when its speed is 22.0 m/sm/s?arrow_forwardA small sphere of mass m = 6.20 g and charge q₁ = 30.4 nC is attached to the end of a string and hangs vertically as in the figure. A second charge of equal mass and charge q₂ = -58.0 nC is located below the first charge a distance d = 2.00 cm below the first charge as in the figure. 91 92 (a) Find the tension in the string. N (b) If the string can withstand a maximum tension of 0.180 N, what is the smallest value d can have before the string breaks? cmarrow_forward23.46 CP A point charge q1 = +5.00 µC is held fixed in space. From a horizontal distance of 6.00 cm, a small sphere with mass 4.00 × 10³ kg and charge q2 = +2.00 μC is fired toward the fixed charge with an initial speed of 40.0 m/s. Gravity can be neglected. What is the acceleration of the sphere at the instant when its speed is 25.0 m/s?arrow_forward
- Two parallel plates are separated ?=0.00375 mx=0.00375 m and have a potential difference of ?=1610 V.V=1610 V. A small ball with mass ?=9.10×10−12 kgm=9.10×10−12 kg is placed between the two plates and remains motionless and floating between the plates. From the overall charge on the ball, determine the number of electrons ?ene the ball has gained or lost. The acceleration due to gravity is ?=9.81 m/s2,g=9.81 m/s2, and the elementary unit of charge is ?=1.60×10−19 C.arrow_forwardThe ball of mass m = 2.00 g has a drag coefficient of D = 0.500 and a radius of r = 1.00 cm, and carries a charge of 3.75 µC. The density of air surrounding the ball is ) = 1.20 kg/m. Divide your group in two and have one subgroup solve part (a) and the other part (b). (a) Group (i): The wind blows to the right in the figure at a speed of 10.0 m/s. What angle (in degrees) does the string make with the vertical? (b) Group (ii): The wind shifts so that it blows into the page at the same speed. Now what angle (in degrees) does the string make with the vertical? Now gather your group together again and answer the following. (c) In part (b), what angle (in degrees) does the string make with the plane of the page when looking at the figure?arrow_forwardHow much work is required to set up the four-charge configuration of the figure if q = 3.59 pC, a = 74.0 cm, and the particles are initially infinitely far apart and at rest? +1 -9 +qarrow_forward
- Now it's your turn Four charged particles are placed so that each particle is at the corner of a square. The sides of the square are 15 cm. The charge at the upper left corner is +3.0 µC, the charge at the upper right corner is -6.0 μC, the charge at the lower left corner is -2.4 µC, and the charge at the lower right corner is -9.0 μC. a. What is the net electric force on the +3.0 µC charge? b. What is the net electric force on the -6.0 µC charge? c. What is the net electric force on the-9.0 uC charge?arrow_forwardTwo identical small spheres of mass 1.10 g each carry equal charge (sign and magnitude) and are placed 3.60 cm apart. When released, each sphere experiences an instantaneous acceleration of 419 m/s². Determine the magnitude of the charge on one of the spheres. Report your answer in nC. (1 nC = 1.00×10-⁹ C and k = 8.99x10⁹ Nm²/C²)arrow_forwardAs stated in picarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON