
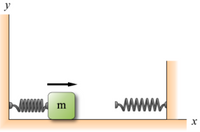
A box of mass m = 0.12 kg is set against a spring with a spring constant of k1 = 595 N/m which has been compressed by a distance of 0.1 m. Some distance in front of it, along a frictionless surface, is another spring with a spring constant of k2 = 158 N/m. The box is not connected to the first spring and may slide freely.
How far, d2 in meters, will the second spring compress when the box runs into it?
How fast, v in meters per second, will the box be moving when it strikes the second spring?
Now assume that the surface is rough (that is, not frictionless). You perform the experiment and observe that the second spring only compresses a distance d2/2. How much energy, in joules, was lost to friction?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

- Two forces, 1 = (−6.55î + 4.75ĵ) N and 2 = (−4.05î + 6.40ĵ) N, act on a particle of mass 2.20 kg that is initially at rest at coordinates (+2.30 m, +4.10 m). In what direction is the particle moving at t = 10.1 s? What displacement does the particle undergo during the first 10.1 s? What are the coordinates of the particle at t = 10.1 s?arrow_forwardA 100 kg skier starts from rest at the top of a ski slope that is 50 m long. If his final speed at the bottom of the slope is 10 m/s, where the bottom of the slope is 20 m below the top, what is the approximate average force of friction between the skis and the slope? 20 m 50 m O 300 N O 1500 N ○ 600 N ○ 750 N O 150 Narrow_forward50 X 10 X 18.710 7. An airplane of mass 1.5x104 kg moves horizontally at a speed of 60.0 m/s. The pilot then increases the engine's thrust to 7.50 x104 N. The air resistance is 4.00x104 N. Find the speed of the airplane after it has traveled 5.00x10² m horizontally while maintaining a constant altitude.arrow_forward
- The figure shows a block of mass m resting on a 20° slope. The block has coefficients of friction μs = 0.64 and μk = 0.54 with the surface of the slope. It is connected using a very light string over an ideal pulley to a hanging block of mass 2.0 kg. The string above the slope pulls parallel to the surface. What is the minimum mass m so the system will remain at rest when it is released from rest?arrow_forwardA small block slides down a frictionless track whose shape is described by y = (x^2) /d for x<0 and by y = -(x^2)/d for x>0. d = 3.25 m. You start the block on the track at rest, somewhere to the left of x = 0. You then release the block from rest and let it slide down. What is the maximum value of x (that is, what is the closest to the origin) from which you can release the block from rest and have it leave the track at x = 0 and go into freefall? -1.63 m -1.15 m -1.39 m -1.52 marrow_forwardA hockey puck with mass 0.166 kg is pushed across the ice with a constant force of 0.89 N. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the puck and the ice is 0.22. After a distance of 2.6 m, what is the puck's speed in m/s?arrow_forward
- A man pushing a crate of mass m = 92.0 kg at a speed of v = 0.860 m/s encounters a rough horizontal surface of length ℓ = 0.65 m as in the figure below. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and rough surface is 0.360 and he exerts a constant horizontal force of 279 N on the crate. A man pushes a crate labeled m, which moves with a velocity vector v to the right, on a horizontal surface. The horizontal surface is textured from the right edge of the crate to a horizontal distance ℓ from the right edge of the crate. (a) Find the magnitude and direction of the net force on the crate while it is on the rough surface. magnitude N direction (b) Find the net work done on the crate while it is on the rough surface. J(c) Find the speed of the crate when it reaches the end of the rough surface. m/sarrow_forwardA 13 gg plastic ball is thrown horizontally at 15 m/sm/s from xx = 0 mm. It experiences an increasing headwind that exerts a drag force Fx=−(2.0×10−3N/m)xFx=−(2.0×10−3N/m)x.How far does the ball travel before reversing direction and being blown backward?arrow_forwardA man pushing a crate of mass m = 92.0 kg at a speed of v = 0.875 m/s encounters a rough horizontal surface of length ℓ = 0.65 m as in the figure below. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and rough surface is 0.350 and he exerts a constant horizontal force of 297 N on the crate. A man pushes a crate labeled m, which moves with a velocity vector v to the right, on a horizontal surface. The horizontal surface is textured from the right edge of the crate to a horizontal distance ℓ from the right edge of the crate. (a) Find the magnitude and direction of the net force on the crate while it is on the rough surface. magnitude ______N direction ---Select--- (b) Find the net work done on the crate while it is on the rough surface._____ J(c) Find the speed of the crate when it reaches the end of the rough surface._____m/sarrow_forward
- A heavy ball with a weight of 150 N (m = 15.3 kg) is hung from the ceiling of a lecture hall on a 4.6-m-long rope. The ball is pulled to one side and released to swing as a pendulum, reaching a speed of 5.6 m/s as it passes through the lowest point. What is the tension in the rope at that point?arrow_forwardsadasdasdasdasarrow_forwardA bead with mass 1.80 × 10-2 kg is moving along a wire in the positive direction of an x axis. Beginning at time t = 0, when the bead passes through x = 0 with speed 12.0 m/s, a constant force acts on the bead. The figure indicates the bead's position at times t0 = 0.00 s, t1 = 1.00 s, t2 = 2.00 s, and t3 = 3.00 s. The bead momentarily stops at t = 3.00 s. What is the kinetic energy of the bead at t = 10.0 s?arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





