
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
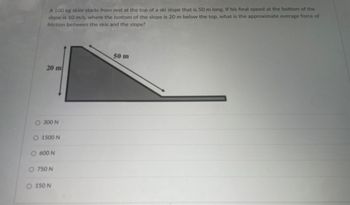
Transcribed Image Text:A 100 kg skier starts from rest at the top of a ski slope that is 50 m long. If his final speed at the bottom of the
slope is 10 m/s, where the bottom of the slope is 20 m below the top, what is the approximate average force of
friction between the skis and the slope?
20 m
50 m
O 300 N
O 1500 N
○ 600 N
○ 750 N
O 150 N
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A 2.1 ✕ 103-kg car starts from rest at the top of a 5.3-m-long driveway that is inclined at 18° with the horizontal. If an average friction force of 4.0 ✕ 103 N impedes the motion, find the speed of the car at the bottom of the driveway. m/sarrow_forwardStarting from rest, a 92-kg firefighter slides down a fire pole. The average frictional force exerted on him by the pole has a magnitude of 710 N, and his speed at the bottom of the pole is 3.5 m/s. How far did he slide down the pole?arrow_forwardA 11 g plastic ball is thrown horizontally at 12 m/s from x = 0 m. It experiences an increasing headwind that exerts a drag force Fx=−(2.0×10−3N/m)x.arrow_forward
- A skier starts going down a rocky hill that is inclined 30 degrees from the horizontal. It is 2 km long, and he starts with an initial speed of 5 m/s down the hill. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between his skis and the hill is 0.7: Does he make it to the bottom? If so, how long does it take?arrow_forwardA girl is swinging on a swing. At the highest point, she is 3.8 meters from the ground. At the lowest point, she is 0.5 meters from the ground. Neglecting friction and air resistance, what will be her maximum speed? 10.4 m 3.8 m 0.5 m O 8.6 m/s O 8.0 m/s O 3.13 m/s O 13.9 m/s Her maximum speed depends on her mass.arrow_forwardA boy shoves his stuffed toy zebra down a frictionless chute. It starts at a height of 1.27 m above the bottom of the chute with an initial speed of 1.07 m/s. The toy animal emerges horizontally from the bottom of the chute and continues sliding along a horizontal surface with a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.223. How far from the bottom of the chute does the toy zebra come to rest? Assume g = 9.81 m/s2. Earrow_forward
- A hockey puck with mass 0.166 kg is pushed across the ice with a constant force of 0.89 N. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the puck and the ice is 0.22. After a distance of 2.6 m, what is the puck's speed in m/s?arrow_forwardKE = mv², Ug = mgh, Us=kx², E = KE + Ug + Us, E₁ = Ef, Wfric Ffried, Ffric = HkN, Et-Wfric = Ef Problem 1: In the Figure below a block slides along a path that is without friction until the block reaches the section of length L = 0.75 m, which begins at height h = 2 m on a ramp of angle 0 = 30°. In that section, the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.40. The block passes through point A with a speed of 8 m/sec. What is the speed of the block at point B (where the friction ends)? Answer: 3.5 m/sec B/ 0arrow_forwardA 20-kg sled is being pulled along the horizontal snow-covered ground by a horizontal force of 28 N. Starting from rest, the sled attains a speed of 2.6 m/s in 9.4 m. Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the runners of the sled and the snow.arrow_forward
- A piece of ice (m = 1 Kg) slides down the slope of a roof inclined at 50.0°. It starts from rest and slides 8.0 m along the roof, sliding off the edge at a height of 4.0 m above the level ground. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.14. V¡ = 0.0 m/s m = 500.0 g 8,0 m Hx = 0.14 30° 4.0 m (a) Draw a free-body diagram of the ice as it is sliding along the roof. (b) Calculate the acceleration of the object. (c)With what speed does it leave the roof?arrow_forwardThe 60-kg crate is projected along the floor with an initial speed of vo = 6.8 m/s at x = 0. The coefficient of kinetic friction is μk = 0.55. Calculate the time t required for the crate to come to rest and the corresponding distance x traveled. Answers: t = Hk X = i VO S marrow_forward60.A 60.0-kg skier with an initial speed of 12.0 m/s coasts up a 2.50-m high rise as shown. Find her final speed at the top, given that the coefficient of friction between her skis and the snow is 0.80. K₁ 35° V₁ = ? 2.5 marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON