
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
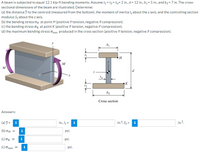
Transcribed Image Text:A beam is subjected to equal 12.1 kip-ft bending moments. Assume t = t2= tw= 2 in., d = 12 in., b1 = 5 in., and b2 = 7 in. The cross-
sectional dimensions of the beam are illustrated. Determine:
(a) the distance y to the centroid (measured from the bottom), the moment of inertia l, about the z axis, and the controlling section
modulus Sz about the z axis.
(b) the bending stress oy at point H (positive if tension, negative if compression).
(c) the bending stress ox at point K (positive if tension, negative if compression).
(d) the maximum bending stress omax produced in the cross section (positive if tension, negative if compression).
M
M
d
K
t2
b2
Cross scction
Answers:
(a) y = i
in., Iz = i
in.4, Sz = i
in.3.
(b) GH =
i
psi.
(c) OK =
i
psi.
(c) Gmax
i
psi.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Dont forget to draw the FREE BODY DIAGRAMS ALSO PLEASE! (:arrow_forwardQuestion 3 a. b. Calculate the second moment area of the section shown about an axis Y - Y through the centroid. 100 2.23. 120 mm 20 mm 20mm X ➜ [20mm Calculate the radius of curvature of the neutral axis when a bending moment of 25 KNm is acting on the section. E= 206 GPaarrow_forwardA beam is subjected to equal bending moments of Mz = 44 kip·ft. The cross-sectional dimensions are b1 = 6.5 in., d1 = 1.5 in., b2 = 0.90 in., d2 = 6.2 in., b3 = 2.6 in., and d3 = 1.8 in. Determine:(a) the centroid location (measured with respect to the bottom of the cross-section), the moment of inertia about the z axis, and the controlling section modulus about the z axis.(b) the bending stress at point H. Tensile stress is positive, while compressive stress is negative.(c) the bending stress at point K. Tensile stress is positive, while compressive stress is negative.(d) the maximum bending stress produced in the cross section. Tensile stress is positive, while compressive stress is negative.arrow_forward
- A beam is subjected to equal 21.7 kip-ft bending moments. Assume t₁ =t₂ = tw- 3 in., d = 15 in., b₁ = 6 in., and b₂ =8 in. The cross- sectional dimensions of the beam are illustrated. Determine: (a) the distance y to the centroid (measured from the bottom), the moment of inertial₂ about the z axis, and the controlling section modulus S₂ about the z axis. (b) the bending stress at point H (positive if tension, negative if compression). (c) the bending stress ok at point K(positive if tension, negative if compression). (d) the maximum bending stress max produced in the cross section (positive if tension, negative if compression). M Answers: (a) y = (b) 6μ = 6.978 (c) OK (c) omax = = i M in., I₂ = X i psi. psi. psi. 41 1₂ 2886.59 b₁ b₂ Cross section H K in.4, S₂ = i in.³.arrow_forward1. For the beam shown and given cross-section determine the maximum bending stress and the absolute maximum bending stress. 2. Determine the maximum shear stress in the beamarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY