
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
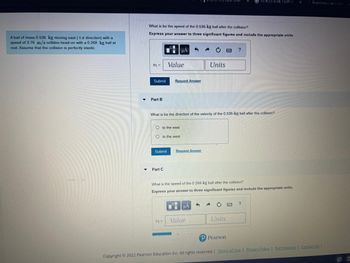
Transcribed Image Text:A ball of mass 0.536 kg moving east (+ direction) with a
speed of 3.76 m/s collides head-on with a 0.268 kg ball at
rest. Assume that the collision is perfectly elastic.
V1 =
What is be the speed of the 0.536-kg ball after the collision?
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
Submit
Part B
μA
Value
Oto the east
Oto the west
Part C
Request Answer
Submit Request Answer
V2 =
Certificates
What is be the direction of the velocity of the 0.536-kg ball after the collision?
Units
Value
What is the speed of the 0.268-kg ball after the collision?
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
?
Units
having a public health st
P Pearson
?
X
Registration Alms Com
Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education Inc. All rights reserved. | Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Permissions | Contact Us |
☐
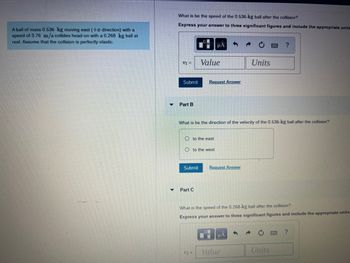
Transcribed Image Text:A ball of mass 0.536 kg moving east (+a direction) with a
speed of 3.76 m/s collides head-on with a 0.268 kg ball at
rest. Assume that the collision is perfectly elastic.
What is be the speed of the 0.536-kg ball after the collision?
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units
V1 =
Submit
Part B
Submit
Oto the east
Oto the west
Part C
μA
Value
Request Answer
What is be the direction of the velocity of the 0.536-kg ball after the collision?
V2 =
Request Answer
Units
What is the speed of the 0.268-kg ball after the collision?
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
μA
Value
?
Units
?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 0.060-kg tennis ball, moving with a speed of 4.4 m/s, has a head-on collision with a 9.5x10-2-kg ball initially moving in the same direction at a speed of 3.1 m/s. Part A Assuming a perfectly elastic collision, determine the speed of each ball after the collision. Enter your answers numerically separated by a comma. Express your answers using two significant figures. ? tennis ball' 'bal = m/s Submit Request Answer Part B Determine the direction of tennis ball after the collision. O The tennis ball moves in the direction of its initial motion. O The tennis ball moves in opposite direction. Submit Previous Answers v Correct Part C Determine the direction of 9.5x10-2-kg ball after the collision. The ball moves in the direction of its initial motion. The ball moves in opposite direction. DrevieueAnewerearrow_forwardAt time t₁ = 12 s, a car with mass 1200 kg is located at (116, 0, 24) m and has momentum (4000, 0, −3600) kg. m/s. The car's momentum is not changing. At time t₂ = 17 s, what is the position of the car? Your answer cannot be understood or graded. More Information marrow_forwardAn astronaut of mass 230 kg including his suit and jet pack wants to acquire a velocity of 2.2 m/s to move back toward his space shuttle. Part A Assuming the jet pack can eject gas with a velocity of 37 m/s, what mass of gas will need to be ejected? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. Submit THU HA Value Request Answer < Return to Assignment Units Provide Feedback!arrow_forward
- A 0.060-kgkg tennis ball, moving with a speed of 5.80 m/sm/s , has a head-on collision with a 0.090-kgkg ball initially moving in the same direction at a speed of 3.48 m/sm/s . Assume that the collision is perfectly elastic. Part A Determine the speed of the 0.060-kgkg ball after the collision. Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forwardA 46.4 kg football player moving at 5.05 m/s hits a 38.86 kg player moving the opposite direction at 3.63 m/s. After the hit, the 46.4 kg player moves opposite his original direction of motion at 1.72 m/s. How fast, and in what direction does the 38.86 kg player move after the hit?arrow_forwardExperiment 1. Before the experiment, the total momentum of the system is 0.4 kg m/s to the left. After the experiment, the total momentum of the system is 0.4 kg m/s to the right. A This describes an elastic collision (and it could NOT be inelastic). B This describes an inelastic collision (and it could NOT be elastic). C This is NEITHER an elastic collision nor an inelastic collision D This describes a collision that is EITHER elastic or inelastic, but more information is required to determine which.arrow_forward
- A ball of mass 0.584 kg moving east (+x direction) with a speed of 3.78 m/s collides head-on with a 0.292 kg ball at rest. Assume that the collision is perfectly elastic. Part A What is be the speed of the 0.584-kg ball after the collision? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. V1 = 1.26 Submit m S Previous Answersarrow_forwardA 0.075 slug softball is traveling at 60.00 feet per second to the left. A batter strikes the ball and sends it traveling at 90.00 feet per second to the right. The bat and softball are in contact for 0.05 seconds. At the start of the problem state which direction you choose to be positive. Draw and label a picture representation. a.)What is the initial momentum and direction of the softball? _______ b.)What is the final momemntum and direction of the softball? ______ c.)What is the impulse acting on the softball? ________ d.) What was the force of the bat striking the softball? __________arrow_forwardA 22-g bullet traveling 280 m/s penetrates a 1.8 kg block of wood and emerges going 120 m/s. Part A If the block is stationary on a frictionless surface when hit, how fast does it move after the bullet emerges? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. ? v3 = Value Unitsarrow_forward
- Which is the formula that describes the magnitude of impulse on an object? A. impulse = mass x acceleration B. impulse = mass x change in velocity C. impulse = mass * (velocity)2 x 0.5 D. impulse = mass x velocityarrow_forwardProblem 9.34 A0.060-kg tennis ball, moving with a speed of 5.8 m/s , has a head-on collision with a 9.5x10-2-kg ball initially moving in the same direction at a speed of 2.7 m/s. Part A Assuming a perfectly elastic collision, determine the speed of each ball after the collision. Enter your answers numerically separated by a comma. Express your answers using two significant figures. Hνα ΑΣφ ? m/s 'tennis ball Vhall= Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 2 attempts remaining Part B Determine the direction of tennis ball after the collision. The tennis ball moves in the direction of its initial motion. The tennis ball moves in opposite direction. Subm Previous Answers v Correct Part C МacВook Proarrow_forwardPlease asaparrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON