
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
What is the magnitude of the reaction force at RAX and RAY in Newtons
What is the magnitude of the reaction force, RBX and RBY in Newtons.

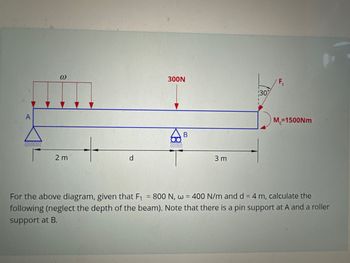
Transcribed Image Text:3
2m
d
300N
B
3 m
30%
F₁
M=1500Nm
For the above diagram, given that F₁ = 800 N, w = 400 N/m and d = 4 m, calculate the
following (neglect the depth of the beam). Note that there is a pin support at A and a roller
support at B.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Give an example of phase equilibrium and chemical equilibrium?arrow_forwardnel 21 3 coltelumie bas gailsboMaster-IDEM Consider the following diagram and find the homogeneous transformations e H, H and H₂ then show that H₂ = HH₂. Wenge 20PORSAPO U insbute ei bnal Awolad woda ei olilqms laantiinsqo won an Insmira otams 10tom of Naslov huqu sulay lenit ad stadeoleo mstava aid ol lagie teqni Z₂ Y2 (ber)VE X2 45° √2 1 Yo a R= [0.7803 erit d oil rinot boileju 00r-V Y₁ с 803 0.1268 2 Zo 101- xo (2005) (e (q 011 (4 b) Assume that the following matrix R is a rotational matrix. Determine a, b and c using the properties of rotation matrices. 14001-8 0.35361 0.6124 0.3536 0.70711 woled novig el lugiuo (1)ed bas tugai (3)p diw rasteva losino lovel bispil A (et 2arrow_forwardThe addition of C to Fe greatly increases the roomtemperature strength of the alloy, but an equal amount of C added to Ag has little effect. Why?arrow_forward
- Determine the composition and fraction with 50% Ni and 1300 ° Carrow_forwardFind the reactions: (geo,trig,and algebra)arrow_forwardAn alloy consisting of completely soluble cadmium (Cd) and zinc (Zn) in the liquid state, but neither of them dissolves in each other in the solid state. the table shown below shows the solidification temperatures for various alloys of cadmium and zinc. 1. Draw the equilibrium diagram according to the information given and data in the table and indicating all important temperature and phases. 2. Find the percentage of each phases and percentage of constituents of the alloy that contain 60 % Zn and at a temperature 300 °C. 3. Find the melting point for the following alloys 20 % Cd, 80% Cd 4. Draw the internal structure, noting the phases of the following alloys A) 30 % Cd at 290 °C b) 60 % Cd at room temperature. % of Zinc in alloy Start of solidification ("C) End of solidification ("C) 0 10 14 20 30 40 50 60 321 290 266 275 293 310 328 345 70 80 90 100 362 390 401 419 266 266 266 266 266 266 266 266 266 266 266 266arrow_forward
- Q4 (a) State the difference between PMM1 and PMM2. Give an example of a PMM1 and a PMM2.arrow_forward4. Consider a binary alloy of A atoms and B atoms that can exist in a solid phase or a liquid phase. This alloy can also exist in TWO DIFFERENT PHASES SIMULTANEOUSLY: solid and liquid. The system is composed of one mole of atoms, some of which are A atoms and some of which are B atoms. Take GA and GB as the molar Gibbs free energy of pure A and pure B respectively. XA and XB are the molar fractions of A and B atoms respectively. The atoms crystallize in identical crystal structures when they are solid. (a) The starting conditions are such that a partition sits between the A atoms and B atoms so they do NOT mix. (i) Write an expression for the molar Gibbs free energy for the combination of pure components. (ii) Draw schematically how the molar Gibbs free energy of the combination of pure components varies with alloy composition.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY