
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A 12.0 kg weight hangs from a 7.50 m pole as illustrated in the diagram. The pole has a mass of 8.0 kg. Determine the tension in the cable, and the "Frictional" and "Normal" forces felt from the wall.
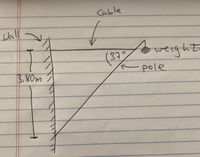
Transcribed Image Text:Cable
iJll
(37)
weight
B.80m's
pole
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 8 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The second photo has background info to help solve the practice problemarrow_forwardThe input piston and output plunger of a hydraulic car lift are at the same level, as shown in the drawing. The cross-sectional area of the input piston is 12 cm2, while that of the output plunger is 1200 cm2. The force F1 applied to the input piston has a magnitude of 160 N. What is the weight W of the car? Neglect the weight of the piston and plungerarrow_forward4. The bar has a mass of 10 kg and is subjected to a couple moment of M-50 N'm and a force of P-80 N, which is always applied perpendicular to the end of the bar. The stiffness of spring is k-30 N/m and its free length is 0.5 m. The spring remains in the vertical position due to the roller guide at B. Determine the total work done by all the force acting on the bar when it has rotated downward from q=0° to 90° 0.75 fint.arrow_forward
- Please asaparrow_forwardIn the structure shown below, determine the magnitude of the roller reaction force at support A in kN. Consider 0 = 35 degrees, and w = 3 kN. Ignore the weight of the structure. Draw the FBD before proceeding to set up the equations. A 3 m 0 2m -4 m W Barrow_forwardWill upvote for immediate solutionarrow_forward
- As shown, a truss is loaded by the forces P = 2.18 kN and Pa = 0.930 kN and has the dimension a = 2.90 m P1 H P2 a E B a/2 a/2 Determine FRc, the magnitude of the force in member BC, using the method of sections. Assume for your calculations that each member is in tension, and include in your response the sign of each force that you obtain by applying this assumption.arrow_forward(2) An artist designs an oval mobile that is supposed to hang horizontal as shown. If the weights at both A and B are each 8 kN, what is the tension at C and the counterweight force at D? You may neglect the weight of the oval. 2 m 1 m 2 marrow_forward**30. The drawing shows an A-shaped stepladder. Both sides of the ladder are equal in length. This ladder is standing on a frictionless horizontal surface, and only the crossbar (which has a negligible mass) of the "A" keeps the ladder from collapsing. The ladder is uniform and has a mass of 30.00 4.00 m Crossbar 1.00 m, 20.0 kg. Determine the tension in the crossbar of the ladder.arrow_forward
- The mass of the board suspended below is 70 kg. What is the tension in the rope, and what is the resulting Normal Force from the Pivot?arrow_forwardIf the masses of both the bodies, as shown in the below figure, are reduced to 50 percent, then tension in the string will be (A) Same (B) Half (C) Double (D) None of thesearrow_forwardA ski resort chair lift has towers spaced 44 m horizontaly appart. The upper tower is 15 m higher than the previous tower. If the chairs are 14 m horizontally appart and the first chair is 5 m past the lower tower what is the tension on both ends of the cable? The mass of each chair is 350 Kg and the height above the lower tower for each chair's attachment to the cable is 0.55624 m, 4 m, 9.33 m. Lower Tower Cable Tension = Upper Tower Cable Tension = KN. kN.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY