
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
When a motor is set on a pivoted mount seen below, its weight can be used to maintain tension in the drive belt. When the motor is not running the tensions T1 and T2 are equal. The total mass of the platform and the motor is 100.0 kg, and the diameter of the drive belt pulley is 16.0 cm. when the motor is off, find: (a) the tension in the belt, and (b) the force at the hinged platform support at point C. Assume that the center of mass of the motor plus platform is at the center of the motor.
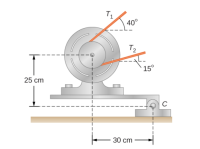
Transcribed Image Text:40°
T2
15°
25 cm
30 сm
1.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 8 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A metal rod of mass M = 6 kg and length L = 0.5 m, is attached at one end by a hinge to a vertical wall. It is initially supported at the other end so that it is in static equilibrium and lies horizontally. hinge support (a) (i) Determine the magnitude and direction of the force on the bar due to the support. (ii) Determine the magnitude and direction of the force on the bar due to the hinge. (b) Show that the moment of inertia of the bar about the end that is attached to the wall is ly = 0.5 kg m2 (c) The support is removed and the bar swings down about the end attached to the hinge. What is the acceleration of a point on the end of the rod just after the support is removed (at this instant the acceleration vector will point directly down)? Give your result in terms of g.arrow_forwardA 30 kg barrel is sitting on a handcart as shown below. Determine the normal forces at A and B. Please show all work and drawl FBDarrow_forward2) An object with a mass of m = 50 kg is suspended, as shown. What are the reactions (external and internal) exerted on member ABC? T 0.6 m A D 0.2 m -0.8 m- E -0.6 m 0.2 m marrow_forward
- Calculate the forces in members AB, BH, and BG. Members BF and CG are cables which can support tension only. Forces are positive if in tension, negative if in compression. A 5m B 5 m 54 54 Answers: AB = i BG= BH = i 8 KN H i G 16 kN c 5 m 54° 54% E D kN kN kNarrow_forwardA ski resort chair lift has towers spaced 44 m horizontaly appart. The upper tower is 15 m higher than the previous tower. If the chairs are 14 m horizontally appart and the first chair is 5 m past the lower tower what is the tension on both ends of the cable? The mass of each chair is 350 Kg and the height above the lower tower for each chair's attachment to the cable is 0.55624 m, 4 m, 9.33 m. Lower Tower Cable Tension = Upper Tower Cable Tension = KN. kN.arrow_forwardQuestion 3) The position of the head and neck and the forces acting on the head are shown in the figure. the center of gravity of the head with a mass of m-9 kg is located at point C. Neck extensor muscles November 21, 2016 by making a y=55° angle with the vertical from point B to the skull, the neck muscle force with a intensity of FmNovember85N is affected. The center of the atlantooccipital joint is located at point B takes. For this flexion position of the head, F, which makes an angle a with the bed from point A, is influenced by the joint response force. (g take the gravitational acceleration as 9.81 m/s2.) According to this; a) Calculate the angle a where the Fjeklem reaction force is built with the horizontal. b) Calculate the Fjeklem reaction force. (Write your result in unit N.) W FMarrow_forward
- 1. The rectangular plate is suspended from verti- cal cables and is in equilibrium. The mass, m, of the plate and the dimension d are given. The weight of the plate acts through the center of the rectangle. What are the tensions T4, T; and Tc in each of the three cables? 1.5d B 2.5d 10.75d d Harrow_forwardPlease answer this within 30 mins! I will upvote !arrow_forwardCalculate the forces in members AB, BH, and BG. Members BF and CG are cables which can support tension only. Forces are positive if in tension, negative if in compression. 6 kN 10 kN 5 m в 5 m c 5 m D 55 55 55° 55% H G Answers: AB i kN BH = i kN BG = i kN IIarrow_forward
- A block and sphere are connected by a cord that passes over a pulley as shown. Neglect friction and assume the cord is massless. Take m1 = 2.00 kg, m2 = 7.65 kg, and ? = 49.0°. A triangular structure is oriented such that its base rests upon a horizontal surface, its left side is perpendicular to its base, and its right side forms an incline of angle ?. A pulley is attached to the structure's apex. Two objects are connected by a cord that passes over the pulley. A circular object labeled m1 is attached to the to the left end of the cord and hangs freely. A rectangular object labeled m2 is attached to the end of the cord and rests upon the incline. (a) What are the magnitude of acceleration (in m/s2) of the block and sphere? _____m/s2 (b) What is the tension (in N) in the cord? (Enter the magnitude.) ____N (c) What is the speed (in m/s) of each object 2.25 s after being released from rest? ____m/s (d)What If? If the incline under m2 is rough, what is the minimum value…arrow_forwardSix masses m1, m2, m3, m4, mM and mL, shown in figure below are to be completely balanced. The masses are : m1= 20.11 kg, m2 = 2 kg, m3 = 3 kg, m4= 6.3 kg, mM = 10.23 kg. The radii are : r1 = 0.1m, r2 = 0.12 m, r3 = 0.14 m, r4 = 0.12 m, rM = 0.1 m, rL = 0.5 m. The angles shown in the figure are: θ1 = 12º, θ2 = 103º, θ3 = 135º, Φ = 32º. The distances between different planes , shown in the figure are as follow: l1 =0.8 m, l2 = 0.7 m, l3 = 2.44 m. we need to find lm, l4 , mL and the angle αarrow_forward2 m B 6 m- X 6 m 2 m 6 m -10 m- 4 m 12 m 2 m y GIVEN: PLATE MASS IS 150KG ASK: WHAT IS TENSION OF EACH CABLE AT EQUILIBRIUMarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY