Question
A 10kg box slides 4.0 m down the frictionless ramp shown in the figure, then collides with a spring whose spring constant is 200 N/m.(a) What is the maximum compression of the spring? (b) Now consider a new situation when the box is resting against the spring. No motion. The box is in equilibrium with the spring. What is the compression in the spring?
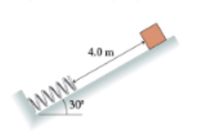
Transcribed Image Text:4.0 m
www-
30
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A block of mass 1.7 kg is attached to a horizontal spring that has a force constant 800 N/m as shown in the figure below. The spring is compressed 2.0 cm and is then released from rest. x x=0 (a) A constant friction force of 3.7 N retards the block's motion from the moment it is released. How much is the spring compressed when the speed of the block is a maximum. 0.463 cm (b) What is the maximum speed? Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. cm/sarrow_forwardAn ideal spring with k = 8 N/m is initially compressed 0.40 m. One end is attached to a wall and the other is attached to a 1.0 kg block. The block is released from rest and slides 0.20 m on the horizontal surface before coming to rest (the spring is still compressed by 0.20 m at this time). The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and surface is Fung Answer: 0.163 X X=0arrow_forwardThe 20 kg block is sliding down an inclined plane at a 30 ° inclined friction and is stopped by a spring with a spring constant k = 2 x 10 ^ 4 N / m. The block shifted to a total distance of 4 m from the point where it was released to the point where it stopped with the resistance of the spring. How many meters is the bow compressed when the block stops? (g = 10 m / s ^ 2)arrow_forward
- You attach a 1.90 kg block to a horizontal spring that is fixed at one end. You pull the block until the spring is stretched by 0.500 m and release it from rest. Assume the block slides on a horizontal surface with negligible friction. The block reaches a speed of zero again 0.500 s after release (for the first time after release). What is the maximum speed of the block (in m/s)?arrow_forwardAs shown in the figure, a 1.50-kg box is held at rest against a spring with a force constant k = 790 N/m that is compressed a distance d. When the box is released, it slides across a surface that is frictionless, except for a rough patch that has a coefficient of kinetic friction u, = 0.400 and is 6.00 cm in length. If the speed of the box is 1.50 m/s after sliding across the rough patch, determine the initial compression d of the spring. cm Equilibrium position v=0' rough patch wwwwwn 6.00 cmarrow_forwardA 3.00 kg box that is sliding on frictionless surface with a speed of 15 m/s approaches a horizontal spring. The spring has a spring constant of 1900 N/m. m 10000000 How far will the spring be compressed in stopping the box? Submit Answer Tries 0/10 How far will the spring be compressed when the box's speed is reduced to half of its initial speed? Note: This is not saying that the box starts with half of the original speed, the box still starts with 15 m/s, the question asks how far the spring will have been compressed when it has slowed the box to half of that speed. Submit Answer Tries 0/10arrow_forward
- A block sitting on a frictionless surface is attached to a spring of spring constant k. The other end of the spring is attached to the wall. The equilibrium length of the spring is x1. The spring is first compressed to a distance of x2, then released and extended to a length of x3. The elastic potential energy stored in the spring when it is extended to x3 can be calculated as: х, wwWO wwWO A block oscillating on the end of a spring Pick the correct answer PE = }ka? PE = }k(x3 – x2)² PE = 서(z3-z) PE = }k(x3 – x1)² PE = }k(x} – a})arrow_forwardA 25.0-kg block is released from rest at point A. The track is frictionless except for the portion between points B and C, which has a length of 10.00 m. The block travels down the track, hits a spring of force constant 2000 N/m, and compresses the spring 0.50 m from its equilibrium position before coming to rest momentarily. Determine the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the rough surface between points B and C.arrow_forwardA 3.0 kg box is sliding along a frictionless horizontal surface with a speed of 1.8 m/s when it encounters a spring. (a) Determine the force constant (in N/m) of the spring, if the box compresses the spring 4.7 cm before coming to rest. N/m (b) Determine the initial speed (in m/s) the box would need in order to compress the spring by 1.5 cm. m/s Additional Materials O Readingarrow_forward
- A 500-g block is released from rest and slides down a frictionless track that begins 1.86 m above the horizontal, as shown in the figure below. At the bottom of the track, where the surface is horizontal, the block strikes and sticks to a light spring with a spring constant of 16.0 N/m. Find the maximum distance the spring is compressed. 50 0g h karrow_forwardInitially sliding with a speed of 4.3 m/sm/s, a 2.0 kg block collides with a spring and compresses it 0.42 mm before coming to rest.What is the force constant of the spring?arrow_forwardOne end of a horizontal spring with k=80N/m is fixed on the wall. A 5kg block is moving at 2m/s when it touches on the free end of a spring. Find the maximum compression of spring Δ: a) if the floor is frictionless ... Δa=...b) if there is kinetic friction with magnitude 10N between block and the floor..... Δb=...c) the amount of thermal energy produced in case (a).. ΔEth-a=.... and (b)... ΔEth-b=.......arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios