
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The 20 kg block is sliding down an inclined plane at a 30 ° inclined friction and is stopped by a spring with a spring constant k = 2 x 10 ^ 4 N / m. The block shifted to a total distance of 4 m from the point where it was released to the point where it stopped with the resistance of the spring. How many meters is the bow compressed when the block stops? (g = 10 m / s ^ 2)
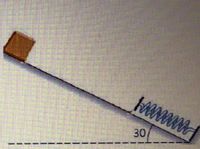
Transcribed Image Text:30
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 5:29 PM Sun Nov 5 Tt S An ideal spring is attached to the ceiling. While the spring is held at its relaxed length, a wooden block (M 850 g) is attached to the bottom of the spring, and a ball of clay (m 210g) is pressed onto the bottom of the block so that they stick together. The block+clay are gently lowered through a distance of d 2.7 cm and are then released, at which point they hang motionlessly from the bottom of the - spring. After a few minutes have passed, the clay unsticks it- self from the block and falls from rest to the ground. What is the resulting period T of the block's oscillation after the sep- aration occurs? For the limit check, investigate what happens to T if the block+clay only need to be lowered through an extremely short distance (d → 0) before they can be released motionlessly. = ✪ 4% =arrow_forwardA spring lies on a horizontal table, and the left end of the spring is attached to a wall. The other end is connected to a box. The box is pulled to the right, stretching the spring. Static friction exists between the box and the table, so when the spring is stretched only by a small amount and the box is released, the box does not move. The mass of the box is 0.90 kg, and the spring has a spring constant of 53 N/m. The coefficient of static friction between the box and the table on which it rests is μs = 0.77. How far can the spring be stretched from its unstrained position without the box moving when it is released?arrow_forwardThis relates the initial speed of the pendulum box to the height that it goes: V =squr 2 g h . The numbers: g = 9.81 m/s2 h = 3.6 cm V = squr 2 × 9.81 × 3.6 = 8.4 Correct the calculation or the answerarrow_forward
- A block of mass m = 3.5 kg is attached to a spring with spring constant k= 720 N/m. It is initially at rest on an inclined plane that is at an angle of θ = 23° with respect to the horizontal, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the plane is μk = 0.13. In the initial position, where the spring is compressed by distance of d = 0.19 m, the mass is at its lowest position and the spring is compressed the maximum amount. Take the initial gravitational energy of the block as zero. a) If the spring pushes the block up the incline, what distance, L in meters, will the block travel before coming to rest? The spring remains attached to both the block and the fixed wall throughout its motion.arrow_forwardIn a car's suspension system, each wheel is connected to a vertical spring; these springs absorb shocks when the car travels on bumpy roads. In one car, each spring has a spring constant of 4.6×104N/m.If this 1500 kg car is driven at 27 m/s through the bottom of a circular dip in the road that has a radius of 625 m, by how much do these springs compress compared to when the car is driven on a flat road?arrow_forwardA spring lies on a horizontal table, and the left end of the spring is attached to a wall. The other end is connected to a box. The box is pulled to the right, stretching the spring. Static friction exists between the box and the table, so when the spring is stretched only by a small amount and the box is released, the box does not move. The mass of the box is 0.80 kg, and the spring has a spring constant of 59 N/m. The coefficient of static friction between the box and the table on which it rests is μs = 0.74. How far can the spring be stretched from its unstrained position without the box moving when it is released?arrow_forward
- After driving a portion of the route, the taptap is fully loaded with a total of 26 people including the driver, with an average mass of 62 kgkg per person. In addition, there are three 15-kgkg goats, five 3-kgkg chickens, and a total of 25 kgkg of bananas on their way to the market. Assume that the springs have somehow not yet compressed to their maximum amount. How much are the springs compressed?arrow_forwardA factory worker drops a 10 kg steel block from rest. The block falls 30 cm onto a vertical spring standing on the floor. The spring constant of the spring is 400 N/m. Once the block has made contact with the spring, it continues to move downward, compressing the spring until it comes to rest. (The spring then decompresses, firing the block upward.) Determine the distance that the spring was compressed by the block. Assume two significant digits in given data.arrow_forwardA block of mass m = 4.5 kg is attached to a spring with spring constant k = 930 N/m. It is initially at rest on an inclined plane that is at an angle of θ = 25° with respect to the horizontal, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the plane is μk = 0.14. In the initial position, where the spring is compressed by a distance of d = 0.13 m, the mass is at its lowest position and the spring is compressed the maximum amount. Take the initial gravitational energy of the block as zero. Part (a) What is the block's initial mechanical energy, E0 in J? 7.859 Part (b) If the spring pushes the block up the incline, what distance, L in meters, will the block travel before coming to rest? The spring remains attached to both the block and the fixed wall throughout its motion.arrow_forward
- A block of mass m = 3.5 kg is attached to a spring with spring constant k = 730 N/m. It is initially at rest on an inclined plane that is at an angle of θ = 21° with respect to the horizontal, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the plane is μk = 0.11. In the initial position, where the spring is compressed by a distance of d = 0.12 m, the mass is at its lowest position and the spring is compressed the maximum amount. Take the initial gravitational energy of the block as zero. If the spring pushes the block up the incline, what distance, L, will the block travel before coming to rest? The spring remains attached to both the block and the fixed wall throughout its motionarrow_forwardA spring-loaded toy gun is aimed vertically and fired after a spherical projectile of mass m = 28.0 g is loaded by compressing the spring with force constant k = 830 N/m a distance of 9.20 cm. As the projectile travels a total distance of 56.0 cm along the barrel of the gun, it experiences a friction force of 2.00 N. What is the height reached by the projectile above its initial location with the spring compressed?arrow_forwardA 185.4 g mass-spring system is rapidly oscillating. The spring used in the system has a spring constant of 12.4 N/m. The system was initially displaced 1.50 m, and has a measured total energy (TE) of 14.95 J. What is the maximum velocity that the mass will reach during its oscillation?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON